Active Voice and Passive Voice
Active voice and passive voice are grammatical constructions that affect the clarity and focus of a sentence. In an active sentence, the subject performs the action expressed by the verbs. For example, “The teacher explains the lesson” clearly shows that the teacher (subject) is performing the action of explaining (verb) the lesson (object). In contrast, a passive sentence occurs when the object of the action becomes the subject of the sentence, often resulting in less direct and less engaging statements. For example, “The lesson is explained by the teacher” places the focus on the lesson rather than the teacher. While passive voice is useful in some contexts, especially when the doer of the action is unknown or unimportant, active voice generally provides more clarity and energy to writing.
What is Active Voice and Passive Voice?
- Active voice is a grammatical construction where the subject of a sentence performs the action expressed by the verb.
- Passive voice is a grammatical construction where the subject of the sentence receives the action of the verb. In a passive sentence, the object of the action becomes the subject, as in “The lesson is explained by the teacher.”
Examples of Active voice and Passive voice
- Active: The cat chased the mouse.
Passive: The mouse was chased by the cat. - Active: She wrote a beautiful poem.
Passive: A beautiful poem was written by her. - Active: The chef prepared a delicious meal.
Passive: A delicious meal was prepared by the chef. - Active: The students completed the assignment.
Passive: The assignment was completed by the students. - Active: The gardener planted new flowers.
Passive: New flowers were planted by the gardener. - Active: He fixed the broken window.
Passive: The broken window was fixed by him. - Active: The team won the championship.
Passive: The championship was won by the team. - Active: The artist painted a stunning mural.
Passive: A stunning mural was painted by the artist. - Active: They renovated the old house.
Passive: The old house was renovated by them. - Active: The company launched a new product.
Passive: A new product was launched by the company. - Active: The doctor treated the patient.
Passive: The patient was treated by the doctor. - Active: The police officer caught the thief.
Passive: The thief was caught by the police officer. - Active: The children built a sandcastle.
Passive: A sandcastle was built by the children. - Active: The author published a new book.
Passive: A new book was published by the author. - Active: The teacher explained the lesson.
Passive: The lesson was explained by the teacher. - Active: The dog fetched the ball.
Passive: The ball was fetched by the dog. - Active: The singer performed a new song.
Passive: A new song was performed by the singer. - Active: The programmer developed a new app.
Passive: A new app was developed by the programmer. - Active: The judge announced the verdict.
Passive: The verdict was announced by the judge. - Active: The director filmed a new movie.
Passive: A new movie was filmed by the director. - Active: The engineer designed a new bridge.
Passive: A new bridge was designed by the engineer. - Active: The baker made fresh bread.
Passive: Fresh bread was made by the baker. - Active: The athlete broke the record.
Passive: The record was broken by the athlete. - Active: The scientist discovered a new element.
Passive: A new element was discovered by the scientist. - Active: The volunteers cleaned the beach.
Passive: The beach was cleaned by the volunteers. - Active: The librarian organized the books.
Passive: The books were organized by the librarian. - Active: The manager scheduled a meeting.
Passive: A meeting was scheduled by the manager. - Active: The pilot flew the airplane.
Passive: The airplane was flown by the pilot. - Active: The photographer took stunning pictures.
Passive: Stunning pictures were taken by the photographer. - Active: The mechanic repaired the car.
Passive: The car was repaired by the mechanic.
Active voice and Passive voice Rules
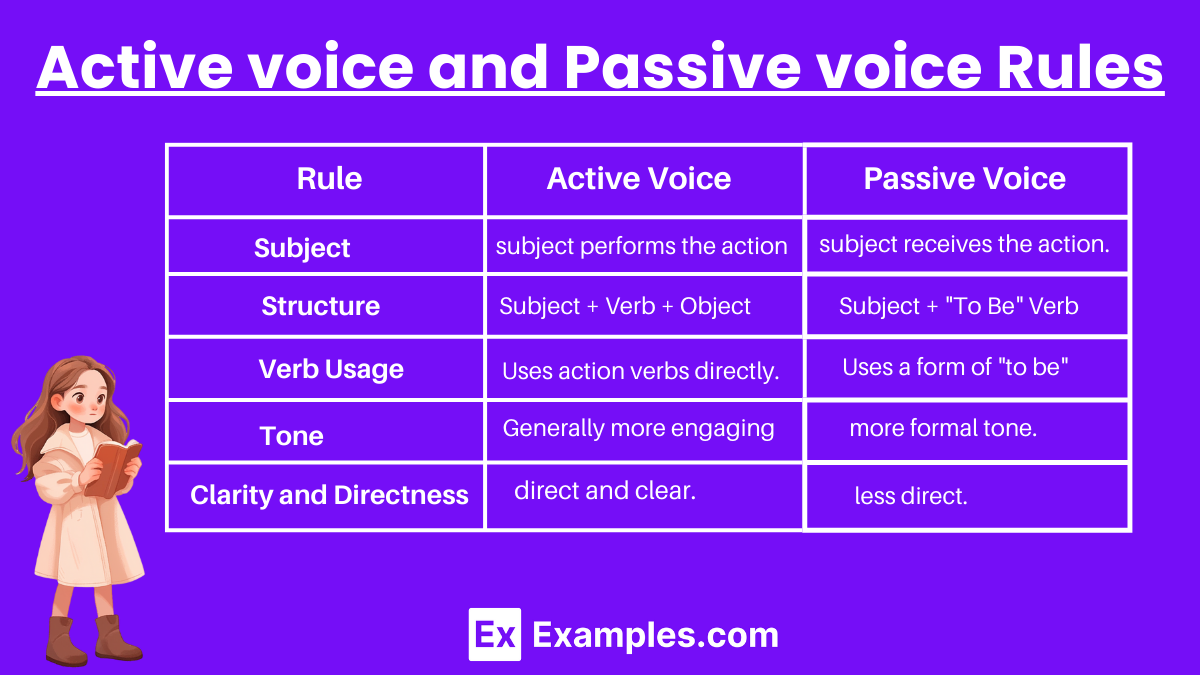
| Rule | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Subject Role | The subject performs the action. | The subject receives the action. |
| Verb Usage | Uses action verbs directly. | Uses a form of “to be” (is, am, are, was, were, be, being, been) + past participle. |
| Focus | Emphasizes the subject performing the action. | Emphasizes the action or the recipient of the action. |
| Structure | Subject + Verb + Object | Subject + “To Be” Verb + Past Participle + (Optional: by + Agent) |
| Agent (Doer) Mentioned | Always includes the doer of the action. | The doer of the action (agent) is optional and often omitted if unknown or unimportant. |
| Clarity and Directness | Sentences are direct and clear. | Sentences can be less direct. |
| Tone | Generally more engaging and less formal. | Can create a more formal tone. |
| Typical Use | Used in most writing for stronger and clearer sentences. | Used when the doer of the action is unknown, unimportant, or to emphasize the action. |
Converting Active to Passive Voice
- Active: The teacher explains the lesson.
Passive: The lesson is explained by the teacher. - Active: The chef cooked a delicious meal.
Passive: A delicious meal was cooked by the chef. - Active: The students completed the assignment.
Passive: The assignment was completed by the students. - Active: The manager approved the request.
Passive: The request was approved by the manager. - Active: The artist painted a beautiful portrait.
Passive: A beautiful portrait was painted by the artist. - Active: The committee will review the proposal.
Passive: The proposal will be reviewed by the committee. - Active: The company launched a new product.
Passive: A new product was launched by the company. - Active: The author wrote an engaging novel.
Passive: An engaging novel was written by the author. - Active: The mechanic repaired the car.
Passive: The car was repaired by the mechanic. - Active: The scientist discovered a new element.
Passive: A new element was discovered by the scientist.
Converting Passive to Active Voice
- Passive: The book was read by the students.
Active: The students read the book. - Passive: The cake was baked by Sarah.
Active: Sarah baked the cake. - Passive: The homework was completed by the children.
Active: The children completed the homework. - Passive: The letter was written by John.
Active: John wrote the letter. - Passive: The song was sung by the choir.
Active: The choir sang the song. - Passive: The game was won by our team.
Active: Our team won the game. - Passive: The movie was directed by Steven Spielberg.
Active: Steven Spielberg directed the movie. - Passive: The house was painted by my uncle.
Active: My uncle painted the house. - Passive: The novel was published by the author.
Active: The author published the novel. - Passive: The speech was given by the president.
Active: The president gave the speech.
Differences between Active Voice and Passive Voice
| Aspect | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The subject performs the action. | The action is performed on the subject. |
| Sentence Structure | Subject + Verb + Object | Object + Form of “to be” + Past Participle + “by” + Subject |
| Focus | Emphasizes the subject doing the action. | Emphasizes the action or the object receiving the action. |
| Clarity | Generally clearer and more direct. | Can be less clear, more wordy, and indirect. |
| Example Sentence | The cat (subject) chased (verb) the mouse (object). | The mouse (object) was chased (verb) by the cat (subject). |
| Use in Writing | Preferred for most writing due to its directness. | Used to emphasize the action or object, or when the subject is unknown or unimportant. |
| Verb Forms | Uses a single verb form (e.g., chased). | Uses a form of “to be” + past participle (e.g., was chased). |
| Tone | Usually more dynamic and engaging. | Often more formal and impersonal. |
| Common in | Everyday conversation, fiction, and journalism. | Scientific writing, formal reports, and situations where the doer is unknown. |
| Action Orientation | Action-oriented, showing who does what. | Result-oriented, showing what happens to whom. |
Uses of Active Voice and the Passive Voice
Uses of Active Voice and Passive Voice
- Emphasizing Action or Result:
- Use passive voice to emphasize the action or its result rather than who performed it.
- Example: “The experiment was completed successfully.”
- Unknown or Unimportant Subject:
- When the doer of the action is unknown, unimportant, or obvious.
- Example: “The window was broken.”
- Formal Writing:
- Often used in scientific, technical, or formal writing.
- Example: “The data were analyzed.”
- Object Focus:
- When the focus is on the object receiving the action.
- Example: “The book was read by thousands.”
- Emphasizing Action or Result:
- Use passive voice to emphasize the action or its result rather than who performed it.
- Example: “The experiment was completed successfully.”
- Unknown or Unimportant Subject:
- When the doer of the action is unknown, unimportant, or obvious.
- Example: “The window was broken.”
- Formal Writing:
- Often used in scientific, technical, or formal writing.
- Example: “The data were analyzed.”
- Object Focus:
- When the focus is on the object receiving the action.
- Example: “The book was read by thousands.”
FAQs
When should I use active voice?
Use active voice for clarity and directness, especially in instructions, narratives, and when the subject’s action is important.
When should I use passive voice?
Use passive voice to emphasize the action or the receiver of the action, or when the subject is unknown or unimportant.
How do I identify passive voice?
Look for a form of the verb “to be” (am, is, are, was, were) followed by a past participle, e.g., “was written.”
Can passive voice be correct?
Yes, passive voice is grammatically correct and useful in certain contexts, such as scientific writing or when the actor is unknown.
Is passive voice always longer?
Passive sentences are often longer because they require additional words, such as forms of “to be” and the past participle.
Why do writers prefer active voice?
Active voice is usually clearer and more engaging, making writing more straightforward and dynamic.
How do I change passive to active voice?
Identify the agent performing the action and make it the subject of the sentence, e.g., “The cake was eaten by the child” becomes “The child ate the cake.”
Can passive voice be effective in writing?
Yes, it can be effective for varying sentence structure, focusing on the action, or when the subject is less important.
What are some common passive voice mistakes?
Common mistakes include overusing passive voice, making sentences unclear, or using it unnecessarily when active voice would be stronger.
How does passive voice affect readability?
Passive voice can make sentences more complex and harder to read, often leading to less engaging writing.



