Adverse vs Averse
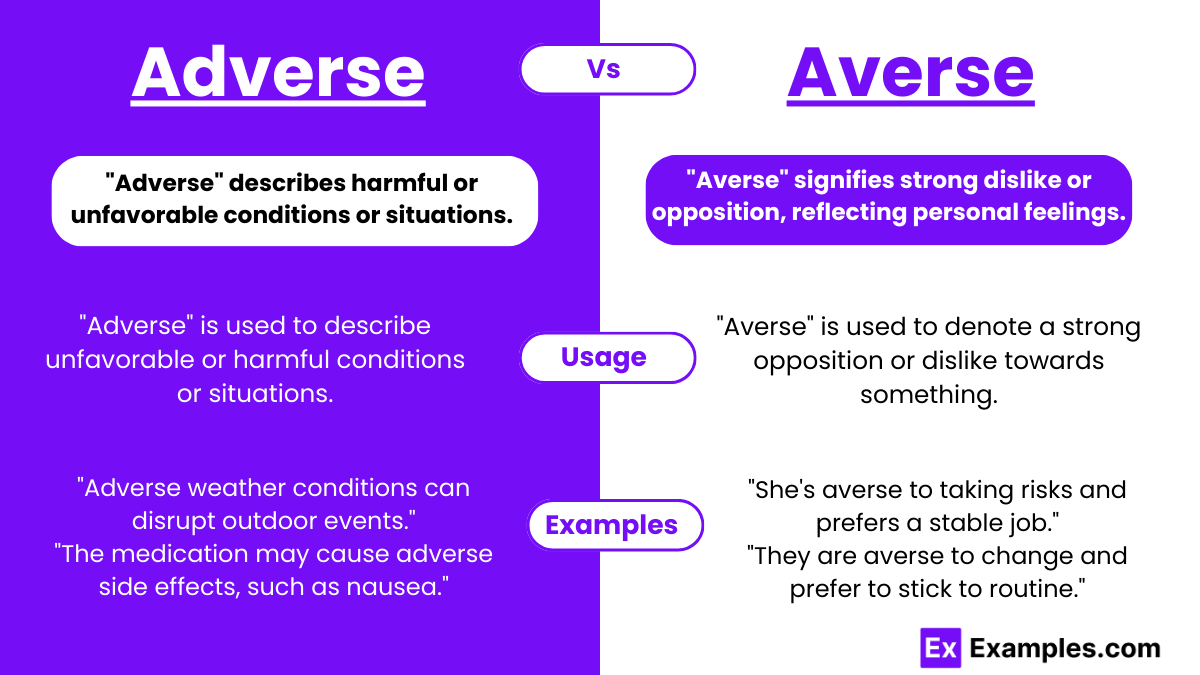
Exploring the nuanced distinction between “adverse” and “averse” sheds light on their correct application, pivotal for articulate expression. “Adverse” typically characterizes detrimental or unfavorable conditions or effects, often linked with external circumstances or events like medication side effects or ecological impacts. It paints a picture of challenges or obstacles emanating from outside forces, influencing outcomes in a negative manner. This term finds its roots in situations that bear hostility or impose hindrance, predominantly in contexts concerning non-human elements.
On the flip side, “Averse” delves into the realm of personal sentiment, highlighting a strong disinclination or opposition towards something. It’s intimately tied to individual preferences or tendencies, especially in avoiding specific actions or scenarios. This adjective is commonly tethered to human attitudes or behaviors, reflecting a deliberate stance of avoidance or resistance. The etymology of both terms traces back to Latin, illustrating a fascinating linguistic evolution from physical orientation to metaphorical opposition, thereby enriching their application in modern discourse.
Adverse and Averse – Meanings
Adverse: Adverse refers to conditions or situations that are unfavorable or harmful and can create obstacles or difficulties. This term is often used to describe negative effects or outcomes that are external to oneself, such as adverse weather conditions, adverse reactions to medications, or adverse trends in the economy. Adverse implies a sense of opposition from external factors, impacting scenarios or entities in a way that is detrimental. It is commonly applied in contexts where the focus is on the negative impact or challenge posed by the external environment or circumstances.
Averse: Averse describes a strong disinclination or opposition towards something, typically reflecting a personal feeling or attitude. This term is used to convey someone’s reluctance or refusal to engage with particular actions, situations, or behaviors due to dislike or discomfort. Averse is about personal preference or sentiment, often related to individual choices or behaviors. It is frequently used in conjunction with “to,” as in being “averse to risk,” indicating a deliberate avoidance of certain activities or conditions based on personal feelings or inclinations.
Summary
Adverse and averse both signify a form of opposition but differ in their application. Adverse is typically used to describe detrimental or negative aspects of non-human elements, like “adverse weather conditions” or “adverse reactions to treatment.” It encapsulates external challenges or harmful effects. Conversely, averse is more personal, indicating a strong reluctance or opposition from individuals towards specific actions or scenarios, such as being “averse to risk” or exhibiting a “dislike for taking chances.” It underscores a subjective distaste or avoidance based on personal feelings or preferences.
Difference Between Adverse and Averse
Unraveling “Adverse vs. Averse” reveals their distinct roles in expressing opposition, critical for precise communication.
| Aspect | Adverse | Averse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refers to harmful or unfavorable conditions. | Indicates a strong dislike or reluctance. |
| Typical Application | Used for situations, effects, or conditions. | Used for personal feelings or inclinations. |
| Connotation | Negative impact from external factors. | Personal opposition or discomfort. |
| Usage in Sentences | “Adverse weather conditions.” | “Averse to taking risks.” |
| Nature | Objective; relates to external circumstances. | Subjective; relates to personal feelings. |
| Common Collocations | Adverse effects, adverse conditions. | Risk averse, averse to. |
| Etymology | From Latin “adversus” meaning hostile or opposing. | From Latin “aversus” meaning turned away. |
| Related Words | Adversity, adversary. | Aversion, aversive. |
| Field of Use | Medicine, environment, finance. | Personal preferences, psychology. |
| Opposition Type | Against one’s interests or well-being. | Against one’s tastes or preferences. |
Examples of Adverse and Averse
Understanding the distinction between “adverse” and “averse” enhances clarity in communication. Here are examples to illustrate their unique applications:
Adverse Examples:
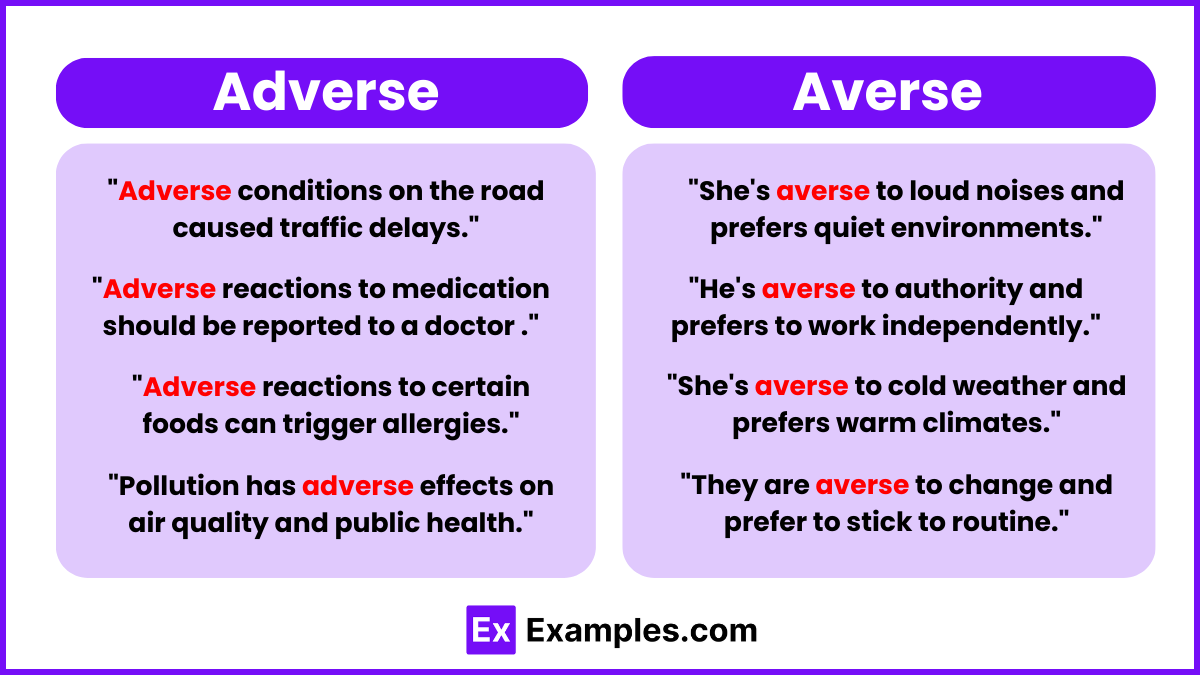
- Adverse weather conditions disrupted the flight schedules.
- The patient experienced adverse reactions to the new medication.
- The new policy had an adverse effect on the economy.
- Adverse market trends impacted the company’s profits.
- The hikers faced adverse terrain, slowing their progress.
Averse Examples:
- She is averse to smoking, avoiding it at all costs.
- The investor was averse to high-risk opportunities.
- He’s averse to change, preferring to stick to his routine.
- They were averse to the idea of moving to a colder climate.
- The cat is averse to water, always staying dry.
When to Use Adverse and Averse
Choosing between “adverse” and “averse” hinges on context and subject. Here’s when to use each:
-
Usage of “Adverse”
- Describing negative effects or outcomes.
- Referring to unfavorable conditions or situations.
- Discussing obstacles or challenges from external sources.
-
Usage of “Averse”
- Expressing personal dislike or reluctance.
- Indicating opposition or disinclination towards something.
- Describing someone’s attitude or feelings against a specific action or situation.
FAQs
Is It Adverse or Averse Conflict?
In describing opposition or disagreement, use “averse.” “Averse conflict” implies a strong disinclination or avoidance of conflict, reflecting a personal attitude towards disputes.
What Does It Mean if Someone Is Not Adverse to Something?
If someone is “not adverse” to something, it’s a misuse of “adverse.” Correctly, “not averse” means the person does not have a strong dislike or opposition to it.
Is Adverse Positive or Negative?
“Adverse” is inherently negative, indicating harmful or unfavorable conditions, effects, or outcomes. It reflects detrimental circumstances or impacts.
Am I Not Adverse or Averse?
You would be “not averse,” not “not adverse,” when expressing a lack of opposition or dislike towards something, highlighting personal feelings or inclinations.
Is Risk Averse or Adverse?
The correct term is “risk averse,” describing a person’s inclination to avoid risky situations or investments due to a preference for safety or certainty.