Article Review
Article reviews are an essential part of academic article writing, providing an opportunity to evaluate and analyze published research. A well-written review can help readers understand the simple subject matter and determine the value of the article. In this article, we’ll cover what is an article review, provide step-by-step guidance on how to write one, and answer some common questions.
What is an Article Review?
An article review is a critical assessment of a scholarly article or research paper. It involves analyzing the content, methodology, and findings of the article and providing an evaluation of its strengths and weaknesses. The review typically includes a summary of the article’s main points, an evaluation of its contribution to the subject, and suggestions for improvement.
Examples of Article Review
1. Literary Analysis of “The Great Gatsby”
Title: “The American Dream in F. Scott Fitzgerald’s ‘The Great Gatsby'”
Summary: This article delves into the theme of the American Dream in “The Great Gatsby”. It explores how the characters of Jay Gatsby, Daisy Buchanan, and Tom Buchanan each represent different facets of this dream. The review highlights the contrast between Gatsby’s idealistic pursuit of wealth and love, and the moral decay of society depicted in the novel.
Evaluation: The article offers a thorough and insightful analysis, drawing on specific passages to support its claims. However, it occasionally lacks depth in exploring secondary characters.
Recommendation: Overall, this article is a valuable resource for understanding the complexities of the American Dream in Fitzgerald’s work. It is recommended for students and literary enthusiasts.
2. Scientific Study on Climate Change
Title: “Impact of Global Warming on Arctic Ice Melting Rates”
Summary: This article examines recent research on the accelerated melting of Arctic ice due to global warming. The study uses satellite data and climate models to project future ice loss and its implications for global sea levels.
Evaluation: The article presents data in a clear and accessible manner, making complex scientific concepts understandable for a general audience. The visual aids, such as graphs and maps, effectively complement the text.
Recommendation: This article is highly recommended for anyone interested in climate science and environmental studies. It provides a comprehensive overview of current research and its global significance.
3. Technology Review of the Latest iPhone
Title: “A Comprehensive Review of the iPhone 14 Pro”
Summary: The article provides an in-depth review of the iPhone 14 Pro, covering its design, performance, camera capabilities, and new features. It compares the latest model with previous versions and other smartphones on the market.
Evaluation: The review is detailed and well-organized, highlighting both strengths and weaknesses of the device. However, it could benefit from more user testimonials to provide a broader perspective.
Recommendation: This review is a must-read for potential buyers considering the iPhone 14 Pro. It offers valuable insights into the device’s capabilities and overall performance.
4. Health and Wellness Article on Yoga Benefits
Title: “The Health Benefits of Practicing Yoga Daily”
Summary: This article explores the various physical and mental health benefits of incorporating yoga into a daily routine. It discusses how yoga can improve flexibility, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being.
Evaluation: The article is informative and engaging, backed by scientific research and expert opinions. It includes practical tips for beginners and links to additional resources.
Recommendation: This article is highly recommended for individuals seeking to improve their health through yoga. It provides a comprehensive guide to the benefits and practice of yoga.
5. Historical Analysis of World War II
Title: “The Role of Codebreakers in World War II”
Summary: The article examines the critical role that codebreakers played in the Allied victory during World War II. It focuses on the efforts at Bletchley Park and the breaking of the Enigma code.
Evaluation: The article is well-researched and presents a compelling narrative of the contributions of codebreakers. It includes firsthand accounts and historical documents to support its analysis.
Recommendation: This article is recommended for history buffs and students. It offers a fascinating insight into a lesser-known aspect of World War II and highlights the importance of intelligence work in warfare.
Examples of Article Review for Students
Review of “The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive Performance”
Title: The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive Performance: A Detailed Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the article’s investigation into how lack of sleep affects cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
Summary: The article explores various studies showing that sleep deprivation significantly impairs cognitive performance, leading to reduced attention spans, poor memory retention, and slower reaction times.
Critique: The article is thorough in its examination of the negative effects of sleep deprivation. However, it could include more information on the long-term consequences and potential mitigation strategies. Some studies cited have small sample sizes, which could limit the findings’ reliability.
Conclusion: Overall, the article effectively highlights the critical impact of sleep on cognitive functions, though it would benefit from more comprehensive data and solutions to counteract sleep deprivation.
Review of “Renewable Energy Sources and Their Impact on the Environment”
Title: Renewable Energy Sources and Their Impact on the Environment: An In-Depth Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the article discussing the environmental impacts of various renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydroelectric power.
Summary: The article covers the benefits of renewable energy in reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. It also examines potential environmental concerns such as habitat disruption and resource consumption.
Critique: The article provides a balanced view of renewable energy’s benefits and challenges. However, it lacks detailed case studies and comparative analysis with non-renewable energy sources. The discussion on environmental impacts could be more nuanced.
Conclusion: The article is informative and highlights the importance of renewable energy, though it would be stronger with more specific examples and a deeper environmental impact analysis.
Review of “The Influence of Advertising on Consumer Behavior”
Title: The Influence of Advertising on Consumer Behavior: A Comprehensive Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the article’s exploration of how advertising affects consumer purchasing decisions and behavior.
Summary: The article examines various advertising techniques and their psychological effects on consumers, including the use of emotional appeal, repetition, and celebrity endorsements.
Critique: The article effectively discusses different advertising strategies and their impact on consumers. However, it could include more recent examples and data to reflect current trends. Additionally, it would benefit from a broader range of perspectives, including consumer psychology.
Conclusion: The article provides a solid overview of advertising’s influence on consumer behavior, but it needs more up-to-date examples and a wider scope of analysis.
Review of “The Role of Nutrition in Child Development”
Title: The Role of Nutrition in Child Development: An Analytical Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the article’s discussion on the critical role of nutrition in children’s physical and cognitive development.
Summary: The article highlights the importance of a balanced diet for children’s growth, emphasizing nutrients such as proteins, vitamins, and minerals. It also examines the consequences of malnutrition and dietary deficiencies.
Critique: The article is well-researched and presents a comprehensive view of the subject. However, it could benefit from more practical dietary recommendations and a discussion on the challenges faced by different socioeconomic groups.
Conclusion: The article effectively underscores the importance of nutrition in child development, though it would be improved by including practical advice and addressing socioeconomic disparities.
Review of “Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Opportunities and Challenges”
Title: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Opportunities and Challenges: A Detailed Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the article’s exploration of the potential benefits and obstacles of implementing artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare.
Summary: The article discusses various AI applications in healthcare, such as diagnostic tools, personalized medicine, and administrative support. It also addresses ethical concerns, data privacy issues, and the need for regulatory frameworks.
Critique: The article provides a balanced and insightful analysis of AI in healthcare. However, it could include more case studies and examples of successful AI implementations. The discussion on ethical concerns is somewhat limited and could be expanded.
Conclusion: The article offers a thorough overview of AI’s potential in healthcare, but it would benefit from more real-world examples and a deeper exploration of ethical issues.
Examples of Article Review for Research
Review of “The Impact of Remote Work on Employee Productivity”
Title: The Impact of Remote Work on Employee Productivity: A Research Review
Introduction: This review assesses the research article’s investigation into how remote work influences employee productivity, examining both positive and negative aspects.
Summary: The research article explores various factors affecting productivity in remote work settings, such as flexible schedules, work-life balance, and the use of digital communication tools. It presents data from surveys and case studies to support its findings.
Critique: The article provides a comprehensive analysis backed by empirical data. However, it could benefit from a more detailed exploration of the long-term impacts of remote work and potential industry-specific variations. Additionally, the research could include a larger, more diverse sample size.
Conclusion: The research article effectively highlights the key factors influencing productivity in remote work environments, though it would be strengthened by broader data and long-term impact analysis.
Review of “Climate Change and Agricultural Sustainability”
Title: Climate Change and Agricultural Sustainability: A Review of Current Research
Introduction: This review evaluates the research article’s examination of the relationship between climate change and agricultural sustainability, focusing on crop yields and farming practices.
Summary: The article discusses the effects of changing weather patterns, increased CO2 levels, and extreme weather events on agricultural productivity. It includes case studies and statistical models to illustrate potential future scenarios.
Critique: The research is thorough and well-supported by data. However, it could include more practical recommendations for farmers and policymakers. The article would also benefit from a more detailed discussion of regional differences and adaptation strategies.
Conclusion: The research article provides valuable insights into the challenges posed by climate change to agriculture, though it would be improved by offering actionable solutions and considering regional variations.
Review of “The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Modern Healthcare”
Title: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Modern Healthcare: A Comprehensive Research Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the research article’s exploration of AI’s applications in healthcare, including diagnostic tools, patient care, and administrative efficiency.
Summary: The article outlines various AI technologies used in healthcare, such as machine learning algorithms for diagnostics, robotic surgeries, and AI-driven patient management systems. It presents data from clinical trials and expert opinions to support its claims.
Critique: The research is well-rounded and provides a clear overview of AI’s potential in healthcare. However, it could address more of the ethical considerations and data privacy issues associated with AI implementation. Additionally, more real-world examples of AI applications would enhance the article’s relevance.
Conclusion: The research article effectively showcases AI’s transformative potential in healthcare, though it could be strengthened by a deeper exploration of ethical issues and more practical examples.
Review of “The Psychological Effects of Social Media Use on Adolescents”
Title: The Psychological Effects of Social Media Use on Adolescents: A Research-Based Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the research article’s examination of how social media affects adolescents’ mental health, focusing on anxiety, depression, and self-esteem.
Summary: The article presents data from longitudinal studies and surveys to show the correlation between social media use and various psychological issues. It discusses the impact of online interactions, cyberbullying, and the pressure to conform to social norms.
Critique: The research is detailed and presents significant findings. However, it could benefit from a more balanced view that includes positive aspects of social media, such as support networks and educational content. Additionally, the sample sizes in some studies are limited, which may affect the generalizability of the results.
Conclusion: The research article provides a comprehensive overview of the negative psychological effects of social media on adolescents, though it would be improved by a more balanced perspective and larger sample sizes.
Review of “The Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Programs”
Title: The Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Programs: A Research Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the research article’s evaluation of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) programs and their impact on mental health and well-being.
Summary: The article reviews various studies on MBSR, highlighting its benefits for reducing stress, anxiety, and depression. It includes meta-analyses and randomized controlled trials to provide a robust evidence base.
Critique: The research is comprehensive and well-supported by empirical data. However, it could explore more on the long-term benefits and potential limitations of MBSR programs. The article would also benefit from discussing the accessibility and applicability of these programs across different populations.
Conclusion: The research article effectively demonstrates the benefits of MBSR programs for mental health, though it could be enhanced by addressing long-term effects and broader applicability.
Journal Article Review Examples
Review of “The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance”
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance: A Comprehensive Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the journal article’s investigation into the relationship between social media usage and academic performance among students.
Summary: The article discusses various studies that explore how social media affects students’ academic outcomes. It highlights both positive effects, such as improved communication and resource sharing, and negative impacts like distraction and reduced study time.
Critique: The article is thorough, providing a balanced view supported by empirical data. However, it could benefit from more longitudinal studies to understand long-term effects. Additionally, the article does not address differences in impact based on the type of social media platform used.
Conclusion: The journal article effectively highlights the dual impact of social media on academic performance. To strengthen the research, including more long-term studies and platform-specific analyses would be beneficial.
Review of “Climate Change Adaptation in Urban Areas”
Title: Climate Change Adaptation in Urban Areas: An Analytical Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the journal article’s discussion on how urban areas are adapting to climate change, focusing on infrastructure and policy changes.
Summary: The article examines various adaptation strategies employed by cities worldwide, such as green infrastructure, zoning laws, and disaster preparedness programs. It presents case studies from different regions to illustrate successful adaptation efforts.
Critique: The article is well-researched and provides a comprehensive overview of adaptation strategies. However, it could include more data on the effectiveness of these strategies over time. Additionally, the article would benefit from a discussion on the socio-economic challenges that hinder adaptation in less developed areas.
Conclusion: The journal article provides valuable insights into urban climate change adaptation strategies. It would be strengthened by including long-term effectiveness data and addressing socio-economic barriers.
Review of “The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Personalized Medicine”
Title: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Personalized Medicine: A Detailed Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the journal article’s exploration of AI applications in personalized medicine, including diagnostics and treatment plans.
Summary: The article discusses how AI technologies, such as machine learning and data analytics, are revolutionizing personalized medicine. It highlights examples where AI has improved diagnostic accuracy and tailored treatment plans to individual patient needs.
Critique: The article is insightful and well-supported by clinical data. However, it could delve deeper into the ethical considerations and potential biases in AI algorithms. Additionally, more real-world examples of AI implementation in diverse healthcare settings would enhance the article’s applicability.
Conclusion: The journal article effectively demonstrates the transformative potential of AI in personalized medicine. To improve, it should include a more detailed discussion on ethics and practical applications across different healthcare systems.
Review of “The Psychological Impact of COVID-19 on Healthcare Workers”
Title: The Psychological Impact of COVID-19 on Healthcare Workers: A Research Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the journal article’s investigation into the mental health effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare workers.
Summary: The article presents data from surveys and interviews with healthcare professionals, highlighting increased levels of stress, anxiety, and burnout due to the pandemic. It discusses the factors contributing to these psychological impacts, such as workload, exposure risk, and lack of support.
Critique: The article provides a comprehensive analysis of the psychological challenges faced by healthcare workers during the pandemic. However, it could benefit from more longitudinal studies to understand long-term mental health outcomes. Additionally, the article would be improved by offering more detailed recommendations for institutional support and intervention strategies.
Conclusion: The journal article effectively sheds light on the mental health struggles of healthcare workers during COVID-19. To strengthen the research, including long-term studies and detailed support recommendations would be beneficial.
Review of “Sustainable Agriculture Practices and Food Security”
Title: Sustainable Agriculture Practices and Food Security: An In-Depth Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the journal article’s discussion on the role of sustainable agriculture practices in enhancing food security.
Summary: The article explores various sustainable agriculture techniques, such as crop rotation, organic farming, and agroforestry, and their impact on food security. It presents case studies demonstrating how these practices can increase crop yields and improve resilience to climate change.
Critique: The article is well-researched and provides a detailed analysis of sustainable agriculture practices. However, it could include more quantitative data on the economic viability of these practices for small-scale farmers. Additionally, the article would benefit from discussing the policy frameworks needed to support widespread adoption of sustainable agriculture.
Conclusion: The journal article effectively highlights the importance of sustainable agriculture for food security. It would be enhanced by including more economic data and policy recommendations to support these practices.
College Article Review Examples
Review of “The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Academic Performance”
Title: The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Academic Performance: A Detailed Review
Introduction: This review assesses the article’s exploration of how sleep deprivation impacts college students’ academic performance, focusing on cognitive functions and overall well-being.
Summary: The article examines studies showing that insufficient sleep negatively affects memory, concentration, and problem-solving skills, leading to lower grades and academic achievement. It also discusses the role of stress and lifestyle factors contributing to sleep deprivation.
Critique: The article provides a thorough analysis supported by empirical data. However, it could benefit from a broader range of studies, including different demographic groups. Additionally, practical solutions for improving sleep habits among students are not adequately addressed.
Conclusion: The article effectively highlights the critical relationship between sleep and academic performance but would be strengthened by more diverse studies and practical recommendations for students.
Review of “The Impact of Technology on Modern Education”
Title: The Impact of Technology on Modern Education: A Comprehensive Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the article’s discussion on the integration of technology in higher education and its effects on teaching and learning processes.
Summary: The article explores various technological tools used in education, such as online learning platforms, interactive simulations, and digital resources. It discusses the benefits, including increased accessibility and personalized learning, as well as challenges like digital divide and technological distractions.
Critique: The article is well-researched and balanced, highlighting both positive and negative aspects of technology in education. However, it could include more recent data and specific examples of successful technology implementations in colleges. Additionally, the article should address potential long-term impacts on traditional teaching methods.
Conclusion: The article provides valuable insights into the role of technology in education, though it would be enhanced by including more up-to-date examples and long-term impact analysis.
Review of “Mental Health Awareness Among College Students”
Title: Mental Health Awareness Among College Students: An Analytical Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the article’s exploration of mental health awareness programs in colleges and their effectiveness in addressing student mental health issues.
Summary: The article examines various initiatives aimed at improving mental health awareness, such as workshops, counseling services, and peer support groups. It highlights the importance of early intervention and the role of campus resources in supporting student well-being.
Critique: The article provides a comprehensive overview of mental health awareness programs and their benefits. However, it could benefit from more quantitative data on program effectiveness and student outcomes. Additionally, the article should discuss the barriers to accessing mental health services, such as stigma and resource limitations.
Conclusion: The article effectively underscores the significance of mental health awareness in colleges, but it would be improved by including more data on program effectiveness and addressing access barriers.
Review of “The Role of Extracurricular Activities in Student Development”
Title: The Role of Extracurricular Activities in Student Development: A Detailed Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the article’s discussion on how participation in extracurricular activities impacts college students’ personal and academic development.
Summary: The article explores various benefits of extracurricular activities, such as improved social skills, leadership development, and enhanced academic performance. It includes case studies and survey data to support its findings.
Critique: The article is well-rounded and provides clear evidence of the positive impacts of extracurricular activities. However, it could include more diverse examples from different types of colleges and regions. Additionally, the article should address potential negative aspects, such as time management challenges and academic pressure.
Conclusion: The article effectively highlights the importance of extracurricular activities in student development, though it would benefit from a more diverse range of examples and a balanced discussion of potential drawbacks.
Review of “The Influence of Social Media on College Students’ Mental Health”
Title: The Influence of Social Media on College Students’ Mental Health: A Research Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the article’s investigation into how social media usage affects the mental health of college students, focusing on both positive and negative impacts.
Summary: The article discusses various studies showing that social media can lead to increased anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation among students. It also highlights positive aspects, such as enhanced communication, social support, and access to mental health resources.
Critique: The article provides a balanced view, supported by empirical data and real-world examples. However, it could benefit from more recent studies and a deeper exploration of how different social media platforms uniquely impact mental health. Additionally, the article should include practical advice for students on managing social media use.
Conclusion: The article effectively addresses the complex relationship between social media and mental health among college students, but it would be strengthened by including more recent research and practical recommendations.
Scientific Article Review Examples
Review of “The Effects of Microplastics on Marine Life”
Title: The Effects of Microplastics on Marine Life: A Comprehensive Review
Introduction: This review assesses the scientific article’s investigation into the impact of microplastics on marine organisms, focusing on ingestion, toxicity, and ecological consequences.
Summary: The article presents various studies showing that microplastics are ingested by a wide range of marine species, leading to physical harm and chemical toxicity. It discusses how microplastics affect growth, reproduction, and survival rates of marine life.
Critique: The article is well-researched, providing detailed evidence of the harmful effects of microplastics. However, it could benefit from a broader geographic scope, including more diverse marine environments. Additionally, the article lacks a discussion on potential mitigation strategies to reduce microplastic pollution.
Conclusion: The article effectively highlights the detrimental impact of microplastics on marine life, but it would be strengthened by including a wider range of environments and discussing mitigation measures.
Review of “The Role of CRISPR-Cas9 in Gene Editing”
Title: The Role of CRISPR-Cas9 in Gene Editing: A Detailed Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the scientific article’s exploration of the CRISPR-Cas9 technology and its applications in gene editing, focusing on its potential and ethical considerations.
Summary: The article discusses the mechanism of CRISPR-Cas9 and its use in various fields such as medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology. It highlights successful case studies, including the treatment of genetic disorders and the development of disease-resistant crops.
Critique: The article is insightful and provides a comprehensive overview of CRISPR-Cas9. However, it could delve deeper into the ethical issues and potential unintended consequences of gene editing. Additionally, the article would benefit from more recent examples of CRISPR applications.
Conclusion: The article effectively demonstrates the potential of CRISPR-Cas9 in gene editing, though it could be enhanced by addressing ethical considerations and providing more up-to-date examples.
Review of “Climate Change and Its Impact on Global Food Security”
Title: Climate Change and Its Impact on Global Food Security: An Analytical Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the scientific article’s examination of how climate change affects global food security, focusing on crop yields, food supply, and nutrition.
Summary: The article explores various factors influenced by climate change, including temperature changes, altered precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events. It discusses how these factors affect agricultural productivity and food availability.
Critique: The article is thorough and supported by extensive data. However, it could include more case studies from different regions to provide a global perspective. Additionally, the article would benefit from discussing adaptation strategies and policy recommendations to mitigate the impact of climate change on food security.
Conclusion: The article provides valuable insights into the effects of climate change on food security, but it would be improved by including more regional case studies and discussing mitigation strategies.
Review of “The Advancements in Renewable Energy Technologies”
Title: The Advancements in Renewable Energy Technologies: A Research Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the scientific article’s discussion on the latest advancements in renewable energy technologies, including solar, wind, and bioenergy.
Summary: The article highlights recent innovations in renewable energy, such as improved solar panel efficiency, advanced wind turbine designs, and sustainable bioenergy production methods. It presents data on the cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits of these technologies.
Critique: The article is well-researched and presents a clear overview of advancements in renewable energy. However, it could benefit from a more detailed analysis of the challenges and limitations associated with each technology. Additionally, the article should include projections on the future adoption of these technologies.
Conclusion: The article effectively showcases the progress in renewable energy technologies, though it would be enhanced by addressing challenges and providing future adoption projections.
Review of “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Healthcare”
Title: The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Healthcare: A Comprehensive Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the scientific article’s exploration of AI’s impact on healthcare, focusing on diagnostic tools, patient care, and administrative efficiency.
Summary: The article discusses various AI applications in healthcare, such as machine learning algorithms for disease diagnosis, robotic surgeries, and AI-driven patient management systems. It highlights the potential benefits and challenges of AI integration in healthcare.
Critique: The article is insightful and supported by clinical data. However, it could delve deeper into the ethical considerations and data privacy issues associated with AI in healthcare. Additionally, more real-world examples and case studies would enhance the article’s relevance.
Conclusion: The article effectively demonstrates AI’s transformative potential in healthcare, but it would be strengthened by addressing ethical concerns and including more practical examples.
Examples of Article Review for Psychology
Review of “The Influence of Parenting Styles on Child Development”
Title: The Influence of Parenting Styles on Child Development: A Comprehensive Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the article’s investigation into how different parenting styles affect children’s psychological and emotional development.
Summary: The article explores various parenting styles—authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, and neglectful—and their impacts on children’s behavior, self-esteem, academic performance, and social skills. It presents data from longitudinal studies and surveys.
Critique: The article is thorough and well-supported by empirical data. However, it could benefit from more recent studies and a broader demographic scope. Additionally, practical recommendations for parents based on the findings are not adequately addressed.
Conclusion: The article effectively highlights the significant role of parenting styles in child development. It would be strengthened by including more up-to-date research and practical advice for parents.
Review of “The Effects of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health”
Title: The Effects of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health: A Detailed Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the article’s exploration of the psychological effects of social media use on adolescents, focusing on issues like anxiety, depression, and self-esteem.
Summary: The article discusses various studies that show a correlation between social media use and increased rates of mental health issues among adolescents. It examines factors such as cyberbullying, social comparison, and screen time.
Critique: The article provides a balanced view supported by empirical data. However, it could include more recent studies and a deeper exploration of positive aspects of social media, such as support networks and educational content. Additionally, practical strategies for managing social media use are not sufficiently addressed.
Conclusion: The article effectively discusses the negative impacts of social media on adolescent mental health but would benefit from more recent research and practical recommendations.
Review of “Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Treating Depression”
Title: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Treating Depression: An Analytical Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the article’s discussion on the effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) in treating depression, focusing on clinical outcomes and patient experiences.
Summary: The article reviews various studies demonstrating CBT’s effectiveness in reducing depressive symptoms and preventing relapse. It discusses CBT’s core components, including cognitive restructuring and behavioral activation.
Critique: The article is well-researched and provides a comprehensive overview of CBT’s effectiveness. However, it could benefit from more detailed comparisons with other therapeutic approaches and a discussion on the accessibility and scalability of CBT. Additionally, the article should address potential limitations and criticisms of CBT.
Conclusion: The article effectively showcases CBT’s effectiveness in treating depression, though it would be enhanced by including comparisons with other therapies and addressing accessibility issues.
Review of “The Role of Mindfulness Meditation in Stress Reduction”
Title: The Role of Mindfulness Meditation in Stress Reduction: A Research Review
Introduction: This review analyzes the article’s examination of mindfulness meditation as a technique for reducing stress and improving mental health.
Summary: The article discusses various studies that show how mindfulness meditation can reduce stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms. It explains the underlying mechanisms, such as increased self-awareness and emotional regulation.
Critique: The article is insightful and supported by empirical data. However, it could include more longitudinal studies to understand the long-term effects of mindfulness meditation. Additionally, the article should address potential barriers to practicing mindfulness, such as time constraints and individual differences in response to meditation.
Conclusion: The article effectively highlights the benefits of mindfulness meditation for stress reduction but would be improved by including long-term studies and discussing barriers to practice.
Review of “The Impact of Sleep on Cognitive Function”
Title: The Impact of Sleep on Cognitive Function: A Comprehensive Review
Introduction: This review evaluates the article’s investigation into the relationship between sleep and cognitive function, focusing on memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
Summary: The article presents various studies demonstrating that adequate sleep is crucial for optimal cognitive performance. It discusses how sleep deprivation negatively affects cognitive functions and the underlying biological mechanisms involved.
Critique: The article is thorough and well-supported by empirical data. However, it could benefit from a more detailed exploration of the differences in sleep needs across different age groups and a discussion on strategies to improve sleep quality. Additionally, practical recommendations for individuals suffering from sleep disorders are not adequately addressed.
Conclusion: The article effectively highlights the critical role of sleep in cognitive function but would be strengthened by including more age-specific research and practical advice for improving sleep quality.
Types of Article Reviews
Article reviews are critical assessments of scholarly articles, often used to evaluate the quality, relevance, and significance of the research. Understanding the different types of article reviews helps in identifying the purpose and approach suitable for various academic and professional needs. Here are the main types of article reviews:
1. Narrative Review
A narrative review provides a comprehensive summary of literature on a specific topic. It focuses on discussing the findings of the research studies and offers a narrative explanation of the trends and themes.
Characteristics:
- Summarizes and synthesizes a body of literature.
- Identifies gaps in current research.
- Provides a background for understanding the topic.
- Less structured compared to systematic reviews.
Example: Reviewing literature on the impact of social media on mental health.
2. Systematic Review
A systematic review is a methodical and comprehensive literature review that aims to answer a specific research question. It uses systematic methods to collect secondary data, critically appraise research studies, and synthesize findings.
Characteristics:
- Uses explicit, systematic methods.
- Pre-defined criteria for selecting studies.
- Often includes meta-analysis.
- Highly structured and replicable.
Example: Evaluating the effectiveness of different interventions for reducing hypertension.
3. Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical technique that combines the results of multiple studies to identify overall trends and determine the effectiveness of interventions.
Characteristics:
- Integrates quantitative data from multiple studies.
- Provides a higher statistical power.
- Often included in systematic reviews.
- Focuses on effect sizes and statistical significance.
Example: Combining data from various studies on the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy for anxiety.
4. Critical Review
A critical review evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of a scholarly article. It involves analyzing the methodology, arguments, evidence, and contributions of the article.
Characteristics:
- In-depth critique of a single article.
- Focuses on the validity and reliability of the research.
- Discusses the implications and limitations.
- Offers suggestions for improvement.
Example: Critiquing the research design and conclusions of a study on climate change impacts on agriculture.
5. Literature Review
A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, providing a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works.
Characteristics:
- Broad overview of existing research.
- Identifies patterns and trends.
- Highlights gaps in current knowledge.
- Provides a foundation for new research.
Example: Reviewing literature on renewable energy sources and their environmental impacts.
6. Scoping Review
A scoping review maps the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It aims to provide an overview of the range of research activity.
Characteristics:
- Identifies the scope of literature on a topic.
- Useful for emerging areas of research.
- Highlights areas for future research.
- Less detailed than systematic reviews.
Example: Exploring the range of studies on artificial intelligence applications in healthcare.
7. Integrative Review
An integrative review synthesizes theoretical and empirical literature to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a specific phenomenon or healthcare problem.
Characteristics:
- Combines qualitative and quantitative research.
- Generates new frameworks and perspectives.
- Addresses mature topics with substantial research.
- Useful for policy and practice implications.
Example: Integrating research on patient-centered care models in nursing.
8. Conceptual Review
A conceptual review focuses on theories and concepts in a particular field. It examines how these concepts are defined, measured, and applied in the literature.
Characteristics:
- Emphasizes theoretical frameworks.
- Analyzes the development of concepts over time.
- Identifies theoretical gaps.
- Proposes new conceptual models.
Example: Reviewing the evolution of the concept of resilience in psycholog
More Article Review Examples & Samples in PDF
1. Formal Article Review

lo.unisa.edu.au
2. Article Review Guideline

ethernet.edu.et
3. Format for Review Article

ijirmf.com
4. Scientific Article Review

twp.duke.edu
5. Research Experience Article Review

sjsu.edu
6. Review of Research Articles

ucalgary.ca
Components of Article Review
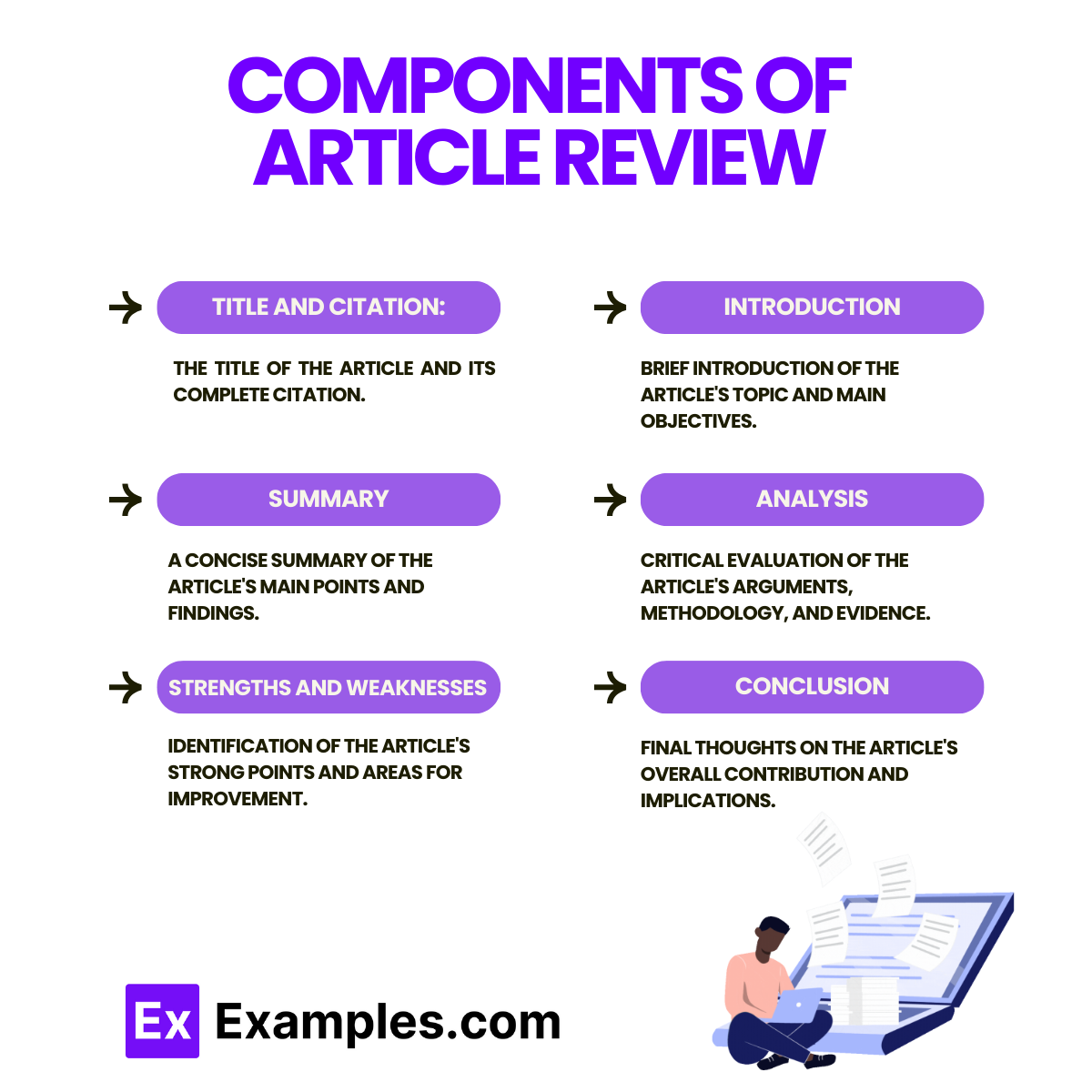
An article review involves evaluating and summarizing a scholarly article, presenting critical insights, and reflecting on its implications. Understanding the essential components helps in crafting a thorough and insightful review. Here are the key components:
1. Title
Characteristics:
- Clearly indicates the focus of the review.
- Should include the article’s title and author(s).
Example: “Review of ‘The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health’ by John Smith”
2. Introduction
Characteristics:
- Provides context for the review.
- Introduces the article’s main topic and objectives.
- States the purpose of the review.
Example:
The article “The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health” by John Smith explores the relationship between social media usage and mental health outcomes. This review aims to critically evaluate the article’s findings and discuss its implications for future research.
3. Summary of the Article
Characteristics:
- Concisely summarizes the article’s main points.
- Includes the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
Example:
The article investigates both positive and negative effects of social media on mental health. Using a mixed-methods approach, the study finds that while social media can enhance social support and community building, it also contributes to anxiety, depression, and cyberbullying.
4. Critical Analysis
Characteristics:
- Evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of the article.
- Discusses the validity and reliability of the research.
- Analyzes the methodologies used and the evidence provided.
- Considers the implications of the findings.
Example:
The article provides a balanced view of social media’s impact, effectively synthesizing current research. However, it lacks in-depth analysis of the methodologies used, which could affect the validity of the findings. Future research should include longitudinal studies to better understand causal relationships.
5. Conclusion
Characteristics:
- Summarizes the key points of the review.
- Restates the significance of the article.
- Provides final thoughts and suggestions for future research.
Example:
In conclusion, Smith’s article offers valuable insights into the complex relationship between social media and mental health. While the study is comprehensive, addressing methodological limitations in future research would enhance our understanding of this important issue.
6. Personal Reflection
Characteristics:
- Discusses the reviewer’s personal perspective on the article.
- Explains how the article’s findings relate to the reviewer’s own experiences or studies.
- Offers insights on how the article influenced their understanding of the topic.
Example:
As a student, I find the article’s discussion on the negative impacts of social media particularly relevant. It underscores the importance of mindful social media use to maintain mental well-being. This review has deepened my understanding of the subject and will inform my future research.
7. References
Characteristics:
- Lists all the sources cited in the review.
- Follows a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
Example: Smith, J. (2023). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health. Journal of Psychological Studies, 45(2), 123-145.
How to write an Article Review?
Writing an article review involves summarizing and critically evaluating a scholarly article. This process helps in understanding the article’s contributions and limitations, and it enhances critical thinking skills. Follow these steps to write an effective article review:
1. Read and Understand the Article
- Read the Article Thoroughly: Start with a quick overview to understand the main idea, then read in detail.
- Identify Key Points: Note the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
- Understand the Context: Research the background information and the article’s significance in its field.
2. Plan Your Review
- Outline the Structure: Plan the sections of your review: Introduction, Summary, Critical Analysis, Conclusion, Personal Reflection, and References.
- Determine the Focus: Decide what aspects of the article you will highlight and critique.
3. Write the Introduction
- Provide Context: Introduce the topic of the article and its relevance.
- State the Purpose: Explain the purpose of your review.
- Mention the Article: Include the title of the article and the author’s name.
Example:
The article “The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health” by John Smith explores the relationship between social media usage and mental health outcomes. This review aims to critically evaluate Smith’s findings and discuss their implications for future research.
4. Summarize the Article
- Concise Summary: Summarize the main points of the article without inserting personal opinions.
- Include Key Elements: Mention the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
Example:
Smith’s article investigates both positive and negative effects of social media on mental health. Using a mixed-methods approach, the study finds that social media can enhance social support and community building but also contributes to anxiety, depression, and cyberbullying.
5. Critical Analysis
- Evaluate Strengths and Weaknesses: Discuss the strengths of the article, such as comprehensive literature review or innovative methodology. Point out weaknesses, such as limited sample size or potential biases.
- Analyze Methodology and Evidence: Critically assess the research methods and the evidence provided.
- Discuss Implications: Consider the significance of the findings and how they contribute to the field.
Example:
The article provides a balanced view of social media’s impact, effectively synthesizing current research. However, it lacks an in-depth analysis of the methodologies used, which could affect the validity of the findings. Future research should include longitudinal studies to better understand causal relationships.
6. Write the Conclusion
- Summarize Key Points: Briefly restate the main points of your review.
- Restate the Article’s Significance: Emphasize the importance of the article’s contributions.
- Provide Final Thoughts: Offer any concluding thoughts and suggestions for future research.
Example:
In conclusion, Smith’s article offers valuable insights into the complex relationship between social media and mental health. While the study is comprehensive, addressing methodological limitations in future research would enhance our understanding of this important issue.
7. Personal Reflection
- Discuss Personal Insights: Share how the article relates to your own experiences or studies.
- Explain Impact on Understanding: Describe how the article influenced your understanding of the topic.
Example:
As a student, I find the article’s discussion on the negative impacts of social media particularly relevant. It underscores the importance of mindful social media use to maintain mental well-being. This review has deepened my understanding of the subject and will inform my future research.
8. Include References
- Cite the Article: Include a full citation of the article you reviewed.
- Follow Citation Style: Use the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
Example:
Smith, J. (2023). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health. Journal of Psychological Studies, 45(2), 123-145.
How do I start an article review?
Begin with a brief introduction that provides context, states the purpose of your review, and mentions the article’s title and author.
What should be included in the summary?
Summarize the main points of the article, including the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions without inserting personal opinions.
How do I write a critical analysis?
Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the article, analyze the methodology and evidence, and discuss the significance and implications of the findings.
How long should an article review be?
The length varies, but typically an article review is 2-4 pages, balancing summary, critical analysis, and personal reflection.
How do I conclude an article review?
Summarize the key points of your review, restate the article’s significance, and provide final thoughts and suggestions for future research.
What is the difference between a summary and a critique?
A summary restates the article’s main points objectively, while a critique evaluates the article’s strengths, weaknesses, and overall contribution.
How do I incorporate personal reflection?
Discuss how the article relates to your own experiences or studies and describe how it influenced your understanding of the topic.
Should I include direct quotes from the article?
Use direct quotes sparingly, only when they enhance your analysis. Always explain their relevance to your critique.
How do I properly cite the article in my review?
Follow the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) to include a full citation of the article at the end of your review.
Can I express my opinion in an article review?
Yes, but primarily in the critical analysis and personal reflection sections. Ensure your opinions are supported by evidence from the article.



