What is the primary goal of biotechnology in medicine?
To develop new cooking methods
To create new pharmaceuticals and therapies
To improve agricultural yield
To enhance soil fertility

When yeast is added to the bread dough and placed into an oven, the yeast will create oxygen pockets that will increase the size of the baked bread. This is an example of the practical usage of biotechnology in terms of food production.
Biotechnology is the act of using advanced applications of biological manipulation and sciences and incorporating them into modern-day technology. If you want to learn more about biotechnology, you may refer to the various articles on the links above; good reads include the History of Biotechnology, Biotechnology Explorer, and the History of Biotechnology.
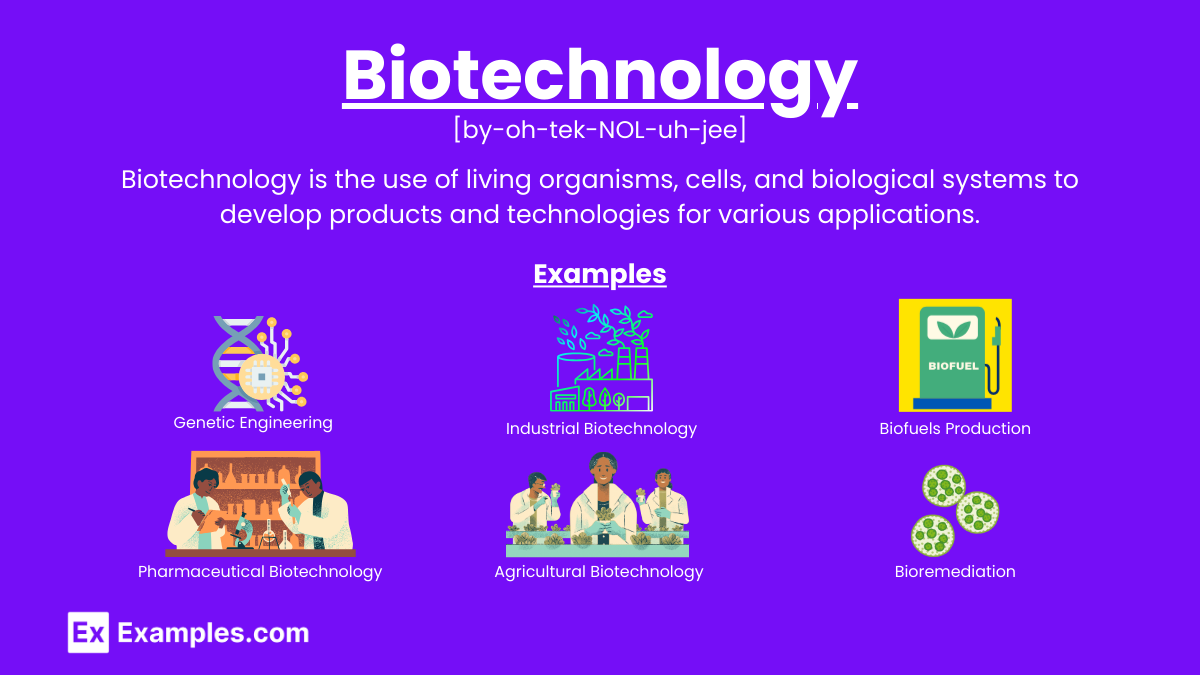
Biotechnology is a broad field that combines biology and technology to develop innovative solutions in various industries. Here are some key examples of biotechnology applications:
Genetic engineering involves modifying an organism’s DNA to achieve desired traits. This technology is used in:
Cloning produces identical copies of organisms or cells. There are two main types:
CRISPR-Cas9 is a revolutionary gene-editing technology that allows scientists to make precise changes to DNA. It is used in:
Bioremediation uses microorganisms to clean up environmental contaminants.
Examples include:
This branch focuses on developing drugs and vaccines using living organisms.
Key applications are:
Biofuels are produced from biological materials and offer a renewable energy source.
Examples include:
This field uses biological systems to produce industrial goods.
Examples include:
Agricultural biotechnology enhances crop and livestock production.
Key examples are:
Stem cell therapy involves using stem cells to regenerate damaged tissues and organs.
Applications include:
Synthetic biology designs and constructs new biological parts and systems.
Examples include:
Genetically modified (GM) foods are created using biotechnology to enhance nutritional content, improve resistance to pests, and increase yield. Common examples include:
Biodegradable plastics are produced using microorganisms that break down the plastic into natural substances like water, carbon dioxide, and compost. These plastics are used in:
Biotechnology has revolutionized medical diagnostics, making it easier and faster to detect diseases. Examples include:
Many modern medicines are developed through biotechnology, including:
Biofuels are produced from biological materials and offer a renewable energy source, such as:
Many personal care products incorporate biotechnology to enhance their effectiveness. Examples include:
This area uses biotechnology to improve crop production and quality, such as:
Biotechnology helps manage and remediate environmental issues, including:
Fermentation is a biotechnological process used to produce foods and beverages, such as:
Textile production has benefited from biotechnology, resulting in:
GM crops are engineered to have specific traits that improve their performance and resilience. Common examples include:
Biopesticides are derived from natural materials such as animals, plants, bacteria, and certain minerals. They help in managing agricultural pests without the environmental impact of conventional pesticides. Examples include:
Biofertilizers consist of living microorganisms that enhance soil fertility and promote plant growth by increasing the availability of essential nutrients. Examples include:
Tissue culture involves growing plants from small tissues or cells in a nutrient-rich medium under sterile conditions. This technique is used for:
MAS uses molecular markers to select plants that have desirable traits, speeding up the breeding process. Examples include:
CRISPR-Cas9 is a precise gene-editing tool used to modify plant genomes for improved traits. Applications in agriculture include:
Biofortification involves breeding crops to increase their nutritional value. This can be achieved through conventional breeding or genetic engineering. Examples include:
Microbial inoculants, or soil inoculants, introduce beneficial microorganisms to the soil to enhance plant growth. Examples include:
Biodegradable mulches are made from renewable resources and decompose naturally, reducing plastic waste in agriculture. Examples include:
Biotechnology is also used in animal husbandry to improve livestock health and productivity. Examples include:
Gene therapy involves altering the genes inside a patient’s cells to treat or prevent disease. Examples include:
Monoclonal antibodies are lab-made proteins that can bind to specific targets in the body. They are used in:
mRNA vaccines use a small piece of the genetic code from a virus to stimulate an immune response. Examples include:
Stem cell therapy uses stem cells to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. Applications include:
CRISPR-Cas9 is a gene-editing technology that allows precise modifications to DNA. Medical applications include:
Pharmacogenomics studies how genes affect a person’s response to drugs, leading to personalized medicine. Examples include:
Biopharmaceuticals are drugs produced using biotechnology. Examples include:
Regenerative medicine aims to restore or establish normal function by repairing or replacing damaged tissues. Techniques include:
Biotechnology has advanced diagnostic tools, making disease detection faster and more accurate. Examples include:
Biotechnology plays a crucial role in the development of vaccines. Examples include:
Bioremediation uses microorganisms to break down or neutralize pollutants from the environment. Examples include:
Phytoremediation involves using plants to absorb, accumulate, and detoxify contaminants from soil and water. Examples include:
Biofiltration uses living material to capture and biologically degrade pollutants from air and water. Examples include:
Composting converts organic waste into nutrient-rich compost through the action of microorganisms. Examples include:
Anaerobic digestion is the process by which microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen to produce biogas and digestate. Examples include:
Biodegradable plastics are derived from renewable resources and decompose naturally through the action of microorganisms. Examples include:
Constructed wetlands are engineered systems that mimic natural wetlands to treat wastewater. Examples include:
Microbial fuel cells use bacteria to convert organic matter directly into electricity. Examples include:
Biosensors are analytical devices that combine a biological component with a physicochemical detector to monitor environmental conditions. Examples include:
Bioaugmentation involves introducing specific strains of microorganisms into contaminated environments to enhance the degradation of pollutants. Examples include:
Genetically modified (GM) foods are engineered to have specific traits that improve their quality and yield. Examples include:
Biopharmaceuticals are medical drugs produced using biotechnology. Examples include:
Vaccines developed through biotechnological processes include:
Biofuels are produced from biological materials and offer a renewable energy source. Examples include:
Biodegradable plastics are derived from renewable resources and break down naturally. Examples include:
Enzymes produced through biotechnology are used in various industries to enhance processes. Examples include:
Microorganisms engineered for specific purposes in various industries include:
Tissue engineering uses biotechnological methods to develop artificial organs and tissues. Examples include:
Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed. Examples include:
Biotechnology enhances agricultural productivity and sustainability. Examples include:
Industrial enzymes are used to catalyze chemical reactions in various manufacturing processes. Examples include:
Biofuels are produced from renewable biological sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Examples include:
Bioplastics are derived from renewable biomass sources and are biodegradable. Examples include:
Fermentation is used to produce a wide range of industrial products. Examples include:
Bioremediation uses microorganisms to degrade environmental pollutants. Examples include:
Biotechnology is used to produce pharmaceuticals through microbial and cell culture processes. Examples include:
Biocatalysis uses natural catalysts, such as protein enzymes, to conduct chemical transformations. Examples include:
Biomining uses microorganisms to extract metals from ores and waste materials. Examples include:
Microorganisms are used to produce food ingredients and additives. Examples include:
Biotechnology contributes to the production of renewable energy sources. Examples include:
CRISPR-Cas9 is a revolutionary gene-editing technology that allows for precise modifications to DNA. Examples include:
mRNA vaccines use messenger RNA to instruct cells to produce a protein that triggers an immune response. Examples include:
Synthetic biology involves designing and constructing new biological parts, devices, and systems. Examples include:
CAR-T cell therapy is an immunotherapy that modifies a patient’s T cells to better recognize and attack cancer cells. Examples include:
3D bioprinting uses layer-by-layer printing techniques to create tissue and organ structures. Examples include:
Bioplastics are made from renewable biological sources and are often biodegradable. Examples include:
NGS technologies allow rapid sequencing of entire genomes. Examples include:
Regenerative medicine focuses on repairing or replacing damaged tissues and organs. Examples include:
Microbiome research studies the communities of microorganisms living in and on our bodies. Examples include:
Modern biotechnology in agriculture involves genetic engineering, molecular markers, and other technologies. Examples include:
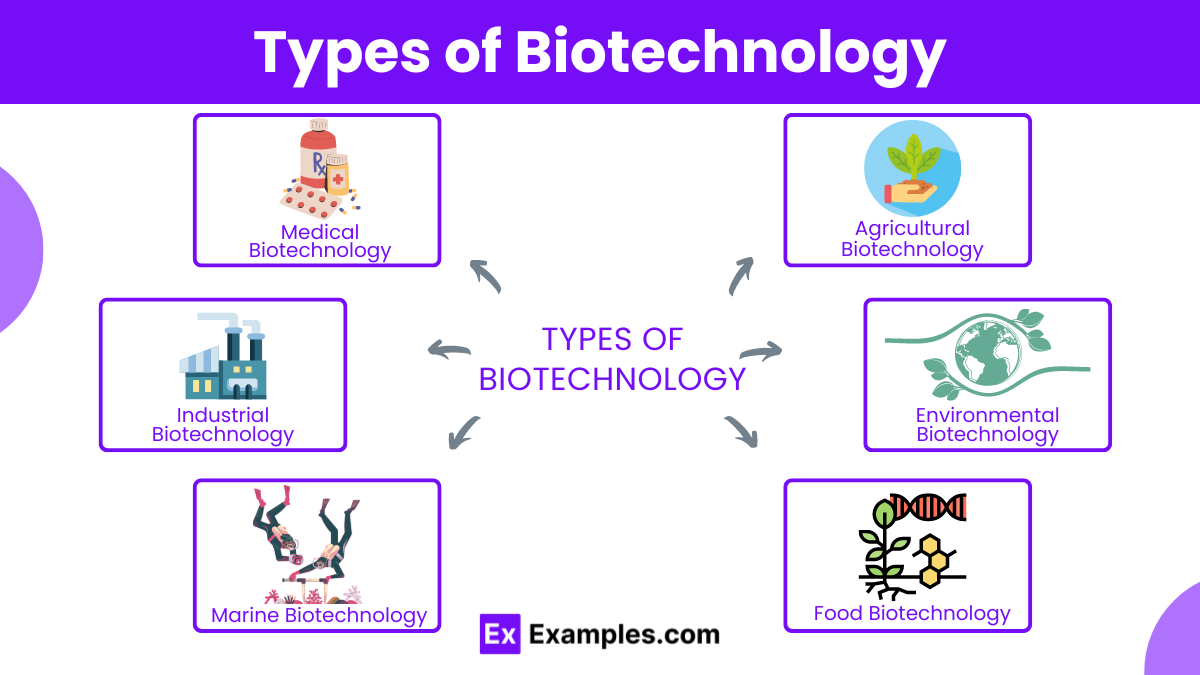
Biotechnology encompasses a variety of techniques and processes aimed at modifying living organisms to develop products or processes for specific purposes. Below are the main types of biotechnology, each with its unique applications and significance:
Medical biotechnology focuses on improving human health through the development of pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, and treatments. It encompasses:
Agricultural biotechnology aims to enhance the quality and yield of crops and livestock. Key areas include:
Industrial biotechnology, also known as white biotechnology, applies biotechnological methods for industrial purposes, such as:
Environmental biotechnology focuses on solving environmental problems through biological processes. This includes:
Marine biotechnology explores the potential of marine organisms for various applications:
Food biotechnology aims to improve the quality, safety, and production efficiency of food products:
Biotechnology plays a crucial role in various aspects of modern life, impacting healthcare, agriculture, environmental conservation, and industry. Here are some key points highlighting the importance of biotechnology:
Biotechnology has a wide range of applications across various fields, enhancing our ability to address challenges and improve the quality of life. Here are some key applications:
Biotechnology revolutionizes healthcare by developing advanced treatments, personalized medicine, and innovative therapies like gene therapy and stem cell therapy, improving patient outcomes and disease management.
GMOs are organisms whose genetic material has been altered using biotechnology to enhance traits like pest resistance, nutritional value, and yield in crops and livestock.
Biotechnology promotes sustainability through bioremediation, waste management, and the development of biofuels and bioplastics, reducing pollution and reliance on fossil fuels.
Gene therapy involves inserting, altering, or removing genes within an individual’s cells to treat or prevent diseases, offering potential cures for genetic disorders and certain cancers.
Biotechnology enhances agriculture by developing GMOs, biofertilizers, and biopesticides, improving crop yield, resistance to pests and diseases, and soil fertility.
Biopharmaceuticals are medical drugs produced using biotechnology, including proteins, antibodies, and vaccines, designed to treat diseases more effectively than traditional medicines.
Fermentation uses microorganisms to convert organic substances into products like alcohol, antibiotics, and vitamins, playing a crucial role in food production and pharmaceuticals.
Ethical concerns include genetic modification, cloning, gene therapy, and privacy issues related to genetic information, requiring careful consideration and regulation to address societal impacts.
Biotechnology enhances food production through GMOs, improving crop yields, nutritional content, and resistance to pests, and through fermentation, creating diverse and nutritious food products.
CRISPR is a powerful gene-editing tool that allows precise, targeted changes to DNA, revolutionizing genetic research, disease treatment, and agricultural development.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary goal of biotechnology in medicine?
To develop new cooking methods
To create new pharmaceuticals and therapies
To improve agricultural yield
To enhance soil fertility
Which of the following techniques is used to amplify DNA sequences?
Electrophoresis
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
Gel filtration
Centrifugation
What is the role of genetic engineering in agriculture?
To create genetically modified crops with desirable traits
To improve the taste of food
To reduce soil erosion
To increase the nutritional content of food without altering genetics
Which biotechnology process involves inserting a gene from one organism into another?
Cloning
Gene therapy
Recombinant DNA technology
Cell fusion
In biotechnology, what is the purpose of a plasmid?
To store genetic information in plant cells
To act as a vector for gene transfer in bacterial cells
To degrade harmful chemicals in the environment
To regulate gene expression in eukaryotic cells
What is the primary function of CRISPR-Cas9 technology?
To produce large quantities of proteins
To sequence entire genomes
To edit specific DNA sequences in living organisms
To clone cells
Which type of biotechnology is used to produce insulin?
Environmental biotechnology
Industrial biotechnology
Medical biotechnology
Agricultural biotechnology
How does gene therapy aim to treat genetic disorders?
By replacing faulty genes with healthy ones
By using drugs to manage symptoms
By surgically removing affected tissues
By altering environmental factors
Which of the following is a common application of biotechnology in environmental management?
Developing new food flavors
Enhancing soil nutrient levels
Improving crop yields
Creating biodegradable plastics
What is the purpose of using a biosensor in biotechnology?
To measure biological and chemical reactions
To genetically modify organisms
To purify proteins
To culture cells
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

