Business Communication vs Corporate Communication
Delving into the distinctions between Business Communication and Corporate Communication, this guide provides a detailed exploration, enriched with relevant communication examples. While Business Communication covers a wide spectrum of interactions within a business environment, Corporate Communication zeroes in on how a corporation engages with both internal and external audiences. This guide offers key insights into their individual roles, applications, and impact on organizational success, helping professionals understand and effectively implement these distinct communication strategies in their respective fields.
Download Business Communication PDF
Download Corporate Communication PDF
Difference Between Business Communication and Corporate Communication
The distinction between Business Communication and Corporate Communication is a nuanced yet crucial aspect in the professional world. Business Communication broadly encompasses all types of communication within a business, including operational and interpersonal exchanges. In contrast, Corporate Communication is more specifically focused on how a corporation engages and presents itself to its internal and external stakeholders, often concerning public relations, branding, and investor relations. Understanding these differences is essential for professionals to effectively tailor their communication strategies to meet the diverse needs of their audience and organizational goals.
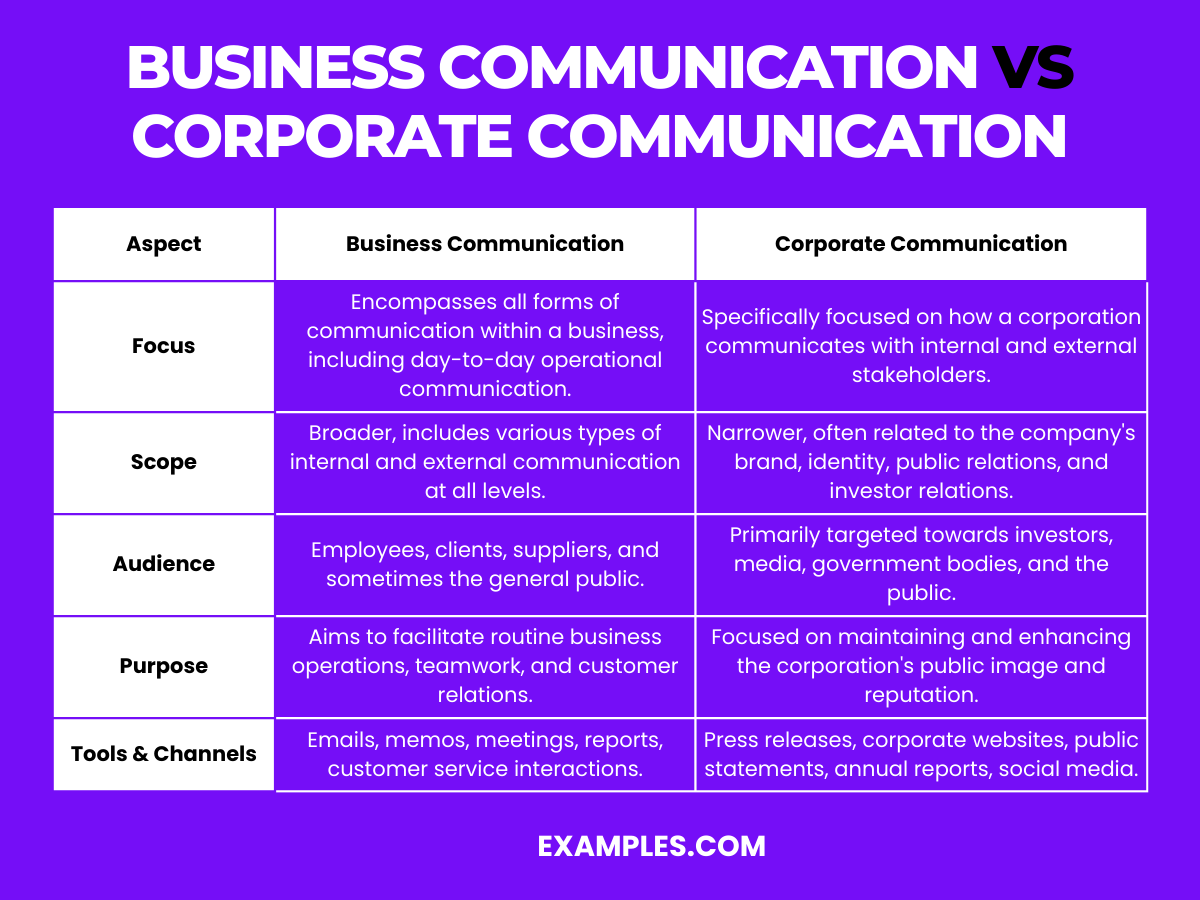
| Aspect | Business Communication | Corporate Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Encompasses all forms of communication within a business, including day-to-day operational communication. | Specifically focused on how a corporation communicates with internal and external stakeholders. |
| Scope | Broader, includes various types of internal and external communication at all levels. | Narrower, often related to the company’s brand, identity, public relations, and investor relations. |
| Audience | Employees, clients, suppliers, and sometimes the general public. | Primarily targeted towards investors, media, government bodies, and the public. |
| Purpose | Aims to facilitate routine business operations, teamwork, and customer relations. | Focused on maintaining and enhancing the corporation’s public image and reputation. |
| Tools & Channels | Emails, memos, meetings, reports, customer service interactions. | Press releases, corporate websites, public statements, annual reports, social media. |
This table outlines the key differences between Business Communication and Corporate Communication, highlighting their distinct focus, scope, audience, purpose, and the tools and channels used in each. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective communication strategy implementation in a business context.
10 Business Communication Examples
Business Communication is integral in navigating the corporate world, involving various methods and tools for effective information exchange. It’s essential for coordinating activities, fostering teamwork, and maintaining client relations. Here are 10 distinct examples of Business Communication, each with its specific purpose:
- Email Communication: Widely used for internal and external corporate correspondence.
- Business Meetings: For team discussions and decision-making.
- Reports: Detailed written documents for information sharing.
- Presentations: Visual and oral communication for ideas and data sharing.
- Business Letters: Formal written communication with external parties.
- Memos: Internal notes for quick information sharing.
- Newsletters: Regular company updates to employees or customers.
- Press Releases: Public announcements for media and stakeholders.
- Corporate Websites: Official online presence for information dissemination.
- Social Media: For brand promotion and customer engagement.
Each of these examples plays a crucial role in facilitating clear and effective communication within and outside a business.
10 Corporate Communication Examples
Corporate Communication is a strategic tool for managing a company’s external and internal communication. It’s vital for shaping corporate identity, maintaining public relations, and ensuring effective investor relations. Here are 10 examples of Corporate Communication:
- Annual Reports: Comprehensive reports documenting yearly performance.
- Press Releases: Official statements for media on company news.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Reports: Detailing company’s social and environmental efforts.
- Investor Presentations: Communicating financial health and prospects to investors.
- Crisis Communication: Managing communication during adverse events.
- Corporate Branding Materials: Visual and textual representations of the brand.
- Employee Communication: Internal newsletters or intranet for employee engagement.
- Public Relations Campaigns: Promotional activities to enhance public perception.
- Corporate Websites: Official online presence for stakeholders.
- Corporate Events: Events for networking and brand promotion.
Each of these examples serves a specific purpose, from maintaining transparency with stakeholders to shaping the company’s public image.
Comparison Between Business Communication and Corporate Communication
In the intricate fabric of organizational dynamics, the terms “Business Communication” and “Corporate Communication” often intertwine, yet hold distinct meanings and applications. This comprehensive guide provides a deep dive into understanding these two forms of communication, critical in the corporate world. With a focus on clarifying the nuances and highlighting differences, we explore the key points to delineate Business Communication from Corporate Communication, optimizing our analysis for the “Business Communication vs Corporate Communication” theme.
- Definition: Business Communication refers to the exchange of information and ideas within a business environment, while Corporate Communication is a strategic tool for managing perceptions and interactions with both internal and external stakeholders.
- Scope: Business Communication covers a broad range of interactions including employee management, customer relations, and marketing, whereas Corporate Communication has a more narrowed focus, dealing primarily with brand management, public relations, and corporate image.
- Objective: The main objective of Business Communication is to facilitate efficient and effective operational processes, while Corporate Communication aims to build and maintain a positive reputation.
- Audience: Business Communication often targets internal audiences such as employees and managers, whereas Corporate Communication is concerned with external stakeholders like investors, media, and the public.
- Channels Used: Business Communication uses channels like emails, reports, and meetings, while Corporate Communication relies on press releases, social media, and corporate events.
- Frequency and Formality: Business Communication tends to be more frequent and less formal, whereas Corporate Communication often involves carefully planned and formalized content.
- Feedback Mechanisms: In Business Communication, feedback is immediate and direct, aiding quick decision-making. In contrast, Corporate Communication feedback is often indirect, gathered through media perception and public opinion.
- Crisis Management: Corporate Communication plays a crucial role in crisis management, shaping the narrative to mitigate damage, while Business Communication focuses on internal coordination and response during crises.
- Content Type: Business Communication content is often informational or instructional, while Corporate Communication content is strategic and brand-focused.
- Measurability: The impact of Business Communication can be measured more directly through productivity metrics, whereas the effectiveness of Corporate Communication is gauged through brand perception and public relations outcomes.
- Strategy Involvement: Corporate Communication is deeply intertwined with an organization’s overall strategy, while Business Communication focuses more on the execution of day-to-day operations.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Corporate Communication must navigate a complex landscape of legal and ethical considerations, especially in public disclosures, unlike Business Communication which is more internally focused.
- Internal Collaboration: Business Communication often involves collaborative efforts across various departments, while Corporate Communication requires a unified front to external audiences.
- Language and Tone: The language in Business Communication is typically straightforward and jargon-free, whereas Corporate Communication often employs persuasive and polished language.
- Training and Skills Required: Professionals in Corporate Communication usually need specialized training in public relations and media handling, while Business Communication skills are more general and diversified.
Relationship Between Business Communication and Corporate Communication
Understanding the relationship between Business Communication and Corporate Communication is essential in the corporate landscape. These two forms of communication, though distinct, are interconnected and play a synergistic role in organizational success. This guide explores how Business Communication and Corporate Communication coexist and complement each other, offering insights optimized for the theme “Business Communication vs Corporate Communication.”
- Interdependent Functions: Business Communication and Corporate Communication are interdependent. Effective Business Communication within a company can positively influence the external perception handled by Corporate Communication.
- Shared Goals: Both forms aim to enhance organizational effectiveness but through different avenues. Business Communication focuses on internal efficiency and clarity, while Corporate Communication aims to build a strong external image and brand reputation.
- Flow of Information: Information flows from Business Communication initiatives can inform Corporate Communication strategies. Internal communication trends can shape how a corporation communicates its values and objectives to the outside world.
- Feedback Loop: The feedback from Corporate Communication efforts, such as public perception and media responses, can influence internal Business Communication policies and strategies.
- Brand Consistency: Both Business and Corporate Communication must maintain brand consistency. Internal communications set the tone for employee understanding of the brand, which is echoed in Corporate Communication to the public.
- Crisis Management: In times of crisis, the role of Business Communication in internal coordination becomes crucial for the effectiveness of Corporate Communication in managing external perceptions and media relations.
- Strategic Alignment: Strategic alignment between these two communication forms ensures that internal practices (Business Communication) align with external messaging (Corporate Communication).
- Cultural Influence: The organizational culture shaped by internal Business Communication impacts how external stakeholders perceive the company, which is a realm managed by Corporate Communication.
- Training and Development: Training programs and development initiatives, part of Business Communication, prepare employees to align with the messaging and values projected by Corporate Communication.
- Change Management: During organizational changes, the role of Business Communication in effectively informing and guiding employees complements Corporate Communication’s role in maintaining a stable external image.
In conclusion, distinguishing between Business Communication and Corporate Communication is crucial for organizational effectiveness. Through examples, we’ve seen their unique impacts and signs. Understanding these differences enables businesses to implement targeted strategies for internal efficiency and external reputation management, thereby enhancing overall corporate success. Recognizing and addressing the nuances of each can lead to more cohesive and effective communication strategies.