Masculine Gender
Masculine gender, a linguistic classification, denotes nouns and pronouns associated with male beings or entities. It embodies traits traditionally attributed to masculinity, such as strength, assertiveness, and vigor. In many languages, masculine gender governs the grammatical agreement of accompanying words, affecting articles, adjectives, and pronouns. This classification extends beyond biological distinctions, encompassing societal perceptions of masculinity. Across cultures, linguistic expressions of masculine gender vary, reflecting diverse interpretations of male characteristics and roles. Understanding masculine gender is crucial in linguistic analysis and communication, shaping perceptions and expressions of gender identity within linguistic frameworks.
What is a Masculine Gender?
Masculine Gender refers to the classification of nouns and pronouns associated with males, embodying traits like strength and assertiveness. It influences grammatical agreements in languages and extends beyond biological distinctions to societal perceptions of masculinity. Understanding it is crucial in linguistic analysis and communication, shaping gender identity expressions within linguistic frameworks.
Importance of Masculine Gender
- Language Structure: Masculine gender helps organize language by categorizing words related to males. This structure aids in communication clarity and efficiency.
- Cultural Representation: It reflects societal perceptions of masculinity, influencing how individuals and groups are represented in language. This representation can impact social dynamics and perceptions.
- Gender Identity Expression: Masculine gender provides a framework for individuals to express their gender identity linguistically. It allows people to articulate their masculinity and navigate social interactions.
- Grammatical Agreement: In many languages, masculine gender affects grammatical agreements with other words in a sentence. Understanding this agreement is crucial for accurate communication and language proficiency.
- Social Dynamics: Linguistic expressions of masculine gender can vary across cultures, reflecting diverse interpretations of male characteristics and roles. Recognizing these variations promotes cultural understanding and inclusivity.
Masculine Gender Roles
Masculine gender roles refer to the societal expectations, behaviors, and characteristics traditionally associated with males. These roles can vary across cultures and time periods but often include the following aspects:
- Provider and Protector: Historically, men have been expected to fulfill the role of provider for their families, often being the primary breadwinners. They are also often seen as protectors, responsible for ensuring the safety and well-being of their loved ones.
- Leadership and Authority: Men are often expected to take on leadership roles in various domains, including the workplace, politics, and community organizations. They are typically seen as authoritative figures who make decisions and exert influence.
- Emotional Restraint: Traditional masculine gender roles often discourage men from expressing vulnerability or emotionality openly. Instead, they may be expected to maintain emotional restraint and stoicism, avoiding displays of weakness.
- Physical Strength and Toughness: Men are frequently associated with physical strength and toughness, expected to be capable of performing physically demanding tasks and enduring hardship without complaint.
- Independence and Self-Sufficiency: Traditional masculine gender roles emphasize independence and self-sufficiency, with men encouraged to be self-reliant and capable of taking care of themselves and their families.
- Career Success and Ambition: Men are often encouraged to pursue career success and ambitious goals, with a focus on achieving financial stability and professional advancement.
- Heterosexuality and Sexual Dominance: Traditional masculinity often places emphasis on heterosexuality and sexual dominance, with men expected to assert their sexuality and pursue heterosexual relationships.
Characteristics of Masculine Gender
Characteristics associated with masculine gender encompass a wide range of traits and behaviors traditionally attributed to males. Here are some common characteristics:
- Strength and Physicality: Masculine gender often includes traits like physical strength, endurance, and athleticism. Men may be expected to excel in physical activities and sports.
- Assertiveness and Confidence: Men are often encouraged to be assertive, confident, and decisive in their actions and decision-making. They may display leadership qualities and take charge in various situations.
- Independence and Self-Reliance: Masculine gender roles often emphasize independence and self-sufficiency, with men expected to be capable of taking care of themselves and solving problems on their own.
- Emotional Restraint: Traditional masculine norms discourage the open expression of vulnerability or emotionality. Men may be expected to maintain emotional restraint and stoicism, avoiding displays of weakness.
- Competitiveness: Masculine gender may involve a competitive nature, with men striving to excel and outperform others in various domains, including academics, careers, and sports.
- Risk-Taking and Adventurousness: Men may be encouraged to take risks and seek out adventure, displaying a willingness to explore new experiences and challenges.
- Protector and Provider: Traditional masculine roles often include the expectation for men to protect and provide for their families and loved ones. They may feel a sense of responsibility for the safety and well-being of others.
- Intellectual Curiosity and Problem-Solving: Masculine gender can involve traits like intellectual curiosity, analytical thinking, and problem-solving skills. Men may be encouraged to pursue education and engage in intellectual pursuits.
- Sense of Honor and Duty: Men may feel a strong sense of honor and duty, with a commitment to fulfilling their responsibilities and obligations to others.
- Heterosexuality and Sexual Dominance: Traditional masculine norms often emphasize heterosexuality and sexual dominance, with men expected to assert their sexuality and take the lead in romantic and sexual relationships.
Nouns and Pronouns of Masculine Gender
Masculine Nouns:
- Father – “His father is a doctor.”
- Son – “The son helped his mother with the groceries.”
- Uncle – “My uncle lives in the city.”
- Brother – “His brother plays soccer on weekends.”
- King – “The king ruled the kingdom with wisdom.”
- Actor – “The actor received an award for his performance.”
- Lion – “The lion is the king of the jungle.”
- Bull – “The bull grazed in the field.”
- Stallion – “The stallion galloped across the meadow.”
- Hero – “He was hailed as a hero for his bravery.”
Masculine Pronouns:
- He – “He is going to the store.”
- Him – “I gave the book to him.”
- His – “This is his car.”
- Himself – “He fixed the car himself.”
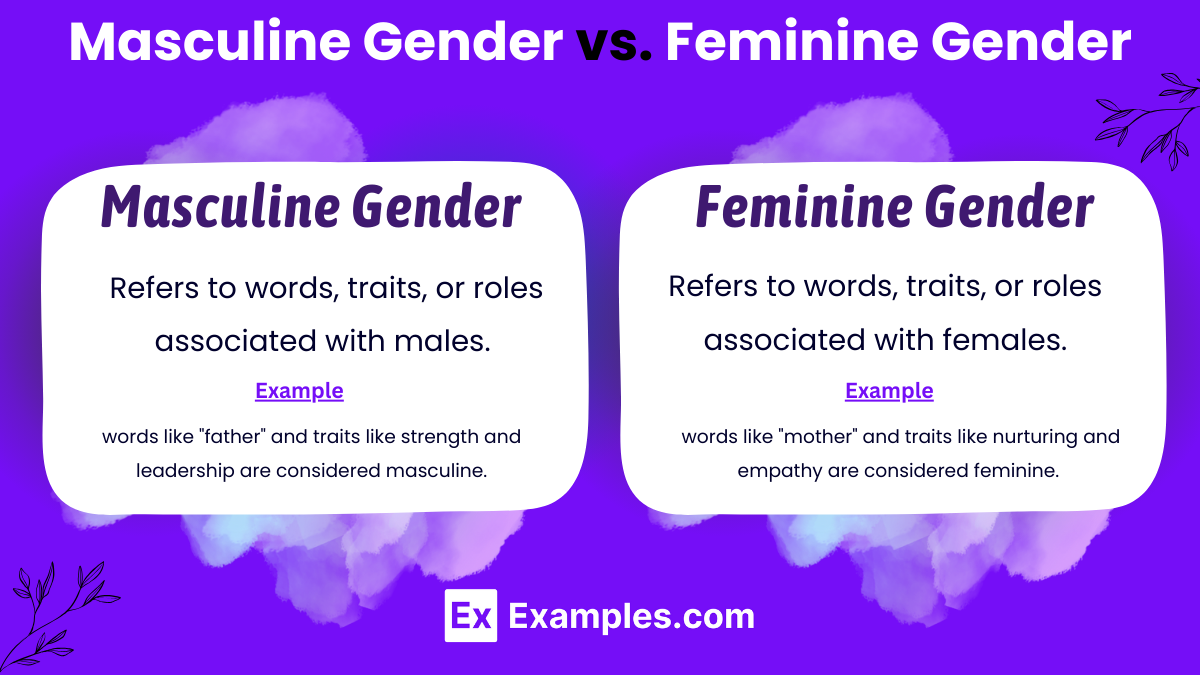
Masculine Gender vs. Feminine Gender
| Aspect | Masculine Gender | Feminine Gender |
|---|---|---|
| Associated Traits | Strength, assertiveness, independence | Nurturing, empathy, sensitivity |
| Historical Roles | Provider, protector, leader | Caregiver, nurturer, homemaker |
| Societal Expectations | Leadership, competitiveness, self-reliance | Compassion, cooperation, relationship-building |
| Career Emphasis | Professional success, ambition | Work-life balance, caregiving |
| Emotional Expression | Stoicism, problem-solving, independence | Emotional openness, empathy, expression |
| Language Usage | Pronouns: he, him, his, himself | Pronouns: she, her, hers, herself |
| Social Dynamics | Dominance, competition, hierarchy | Collaboration, community, inclusivity |
| Cultural Representations | Heroes, warriors, leaders | Nurturers, caregivers, educators |
Examples Words of Masculine Gender
- Father: A male parent in a family, often responsible for providing guidance and support.
- Son: A male child or offspring of parents.
- Uncle: The brother of one’s parent, typically male.
- Brother: A male sibling who shares one or both parents with another.
- King: A male monarch who rules a kingdom or territory.
- Actor: A male performer who portrays characters in plays, movies, or television shows.
- Lion: A large, carnivorous cat species, known for its mane and as the “king of the jungle.”
- Bull: A male bovine animal, often recognized for its strength and size.
- Stallion: A male horse that has not been gelded, typically used for breeding purposes.
- Hero: A male figure admired or idealized for courage, outstanding achievements, or noble qualities.
- Groom: A man who is about to be married or has recently been married.
- Nephew: The son of one’s sibling, usually male.
- Actor: A male performer who acts in plays, movies, or television shows.
- Husband: A male partner in a marriage or committed relationship.
- Bachelor: An unmarried man, often used to refer to a man who is socially active but not committed to marriage.
- Duke: A noble title given to a male member of royalty or nobility.
- Emperor: A male ruler of an empire or sovereign state.
- Warrior: A male fighter or soldier engaged in warfare or conflict.
- Gentleman: A polite and courteous man, often characterized by good manners and behavior.
- Patriarch: The male head of a family or tribe, often regarded as the oldest and most respected member.
Examples of Masculine Gender in sentence
- The father took his son to the park to play catch.
- The uncle taught his nephew how to ride a bike.
- The firefighter rushed into the burning building to save lives.
- He greeted his brother with a warm hug after not seeing him for years.
- The king announced his decision to expand the kingdom’s borders.
- The actor received a standing ovation for his captivating performance.
- The lion roared loudly, asserting dominance in the pride.
- The bull charged at the matador during the bullfight.
- The groom smiled nervously as he awaited his bride’s arrival.
- The emperor‘s decree was followed without question by his subjects.
What is a Masculine Word?
A masculine word is a term or noun that typically denotes or represents males, embodying qualities associated with masculinity such as strength, dominance, and assertiveness within language and societal contexts.
What are the types of Masculinity?
Types of masculinity include traditional, emphasizing toughness and dominance; modern, valuing emotional expression and egalitarianism; and alternative, challenging traditional norms with diverse expressions of gender and identity.
What is Masculinity with example?
Masculinity refers to the qualities, behaviors, and attributes traditionally associated with men and masculinity. This can include traits like strength, courage, assertiveness, and independence. For example, a man who demonstrates bravery in the face of danger exhibits traits of masculinity.