Open Communication vs Direct Communication
Embark on a journey to understand the nuances of Open vs Direct Communication with this complete guide. Featuring real-life Communication Examples, this article delves into how these styles operate, their implications, and ways to effectively apply them. From personal relationships to workplace dynamics, learn the importance of choosing the right communication approach. Enhance your interaction skills with insights and strategies that cater to diverse situations and audiences.
Download Open Communication vs Direct Communication Advantages and Disadvantages PDF
What is Open Communication vs Direct Communication? – Meaning
Open Communication refers to a style where dialogue is transparent, inclusive, and encourages a free flow of information and ideas among all participants. It’s about creating an environment of trust and understanding. In contrast, Direct Communication is about conveying messages in a straightforward and unambiguous manner. It’s characterized by clarity, brevity, and often a focus on efficiency and getting the point across quickly. Understanding the difference between Open Communication and Direct Communication is essential for effective interaction, as each has its place and benefits depending on the context and desired outcome.
Difference between Open Communication vs Direct Communication
The difference between Open Communication and Direct Communication lies in approach and execution. Open Communication fosters an environment of transparency and inclusivity, crucial for nurturing Open Communication in Relationships and promoting Open Communication in the Workplace. It allows for a free exchange of ideas, leading to comprehensive understanding and Open Communication Benefits. Direct Communication, on the other hand, is about being clear and concise, often prioritizing brevity over elaboration, which can be critical in fast-paced settings but may lack the emotional depth vital for the Importance of Open Communication in Relationships.
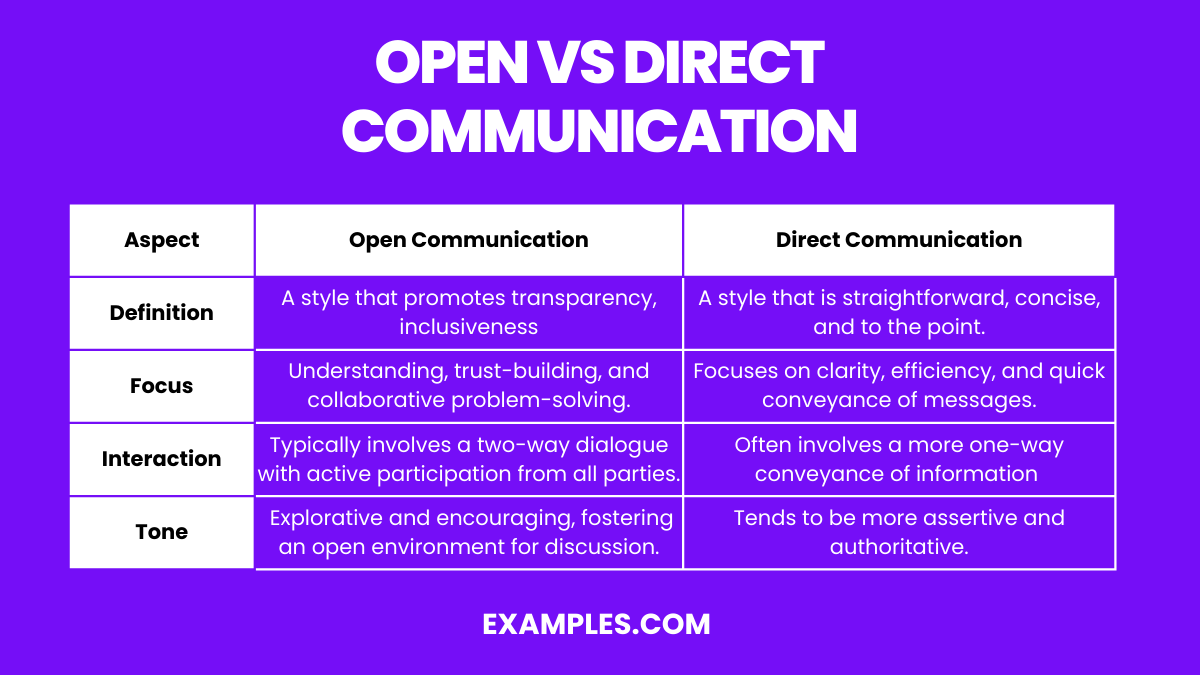
Here’s a comparative table explaining the differences between Open Communication and Direct Communication:
| Feature | Open Communication | Direct Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A style that promotes transparency, inclusiveness, and a free exchange of ideas. | A style that is straightforward, concise, and to the point. |
| Focus | Encourages understanding, trust-building, and collaborative problem-solving. | Focuses on clarity, efficiency, and quick conveyance of messages. |
| Interaction | Typically involves a two-way dialogue with active participation from all parties. | Often involves a more one-way conveyance of information or instructions. |
| Tone | Generally more explorative and encouraging, fostering an open environment for discussion. | Tends to be more assertive and authoritative, leaving little room for misinterpretation. |
| Suitability | Best for complex issues requiring collective input, relationship building, or when emotional sensitivity is important. | Effective for scenarios requiring quick decision-making, clear instructions, or when time is of the essence. |
10 Open Communication Examples
Embrace the transformative power of open communication with these ten unique examples. This guide underscores the Importance of Open Communication in fostering a collaborative and transparent environment. From healthcare to the workplace, each example illustrates the beneficial impact of open dialogue and provides insights into addressing communication barriers. Enhance your understanding and practice of open communication to improve relationships, decision-making, and overall satisfaction.
- Team Brainstorming Sessions: Open forums for sharing ideas lead to innovative solutions. Encourages Honest Communication and collaborative thinking.
- Patient Rounds in Hospitals: Doctors and nurses discussing patient care openly improve outcomes. Demonstrates Open Communication in Healthcare.
- Weekly Staff Meetings: Regular meetings in the workplace where everyone updates and discusses progress. Highlights Why is Open Communication Important in Workplace.
- Relationship Check-ins: Partners regularly discussing feelings and plans, strengthening bonds. A practice showing the Importance of Open Communication in Relationships.
- Suggestion Boxes at Work: Employees submitting ideas and feedback anonymously. Shows How to Create Culture of Open Communication at Workplace.
- Public Forums for Community Issues: Residents and officials discussing community problems and solutions together. Illustrates How to Promote Open Communication.
- Leadership Town Halls: Leaders addressing the entire organization, taking questions and feedback. Reflects Open Communication in Leadership.
- Crisis Communication Teams: Groups formed to communicate effectively during emergencies. Emphasizes quick, transparent information dissemination.
- Social Media Customer Service: Brands interacting with customers directly and openly online. Shows responsiveness and customer care.
- Creative Workshops: Spaces where individuals are free to express and critique ideas in a supportive environment. Encourages creativity and Open Mind Communication.
10 Direct Communication Examples
Uncover the efficacy and clarity that direct communication brings with these ten examples. This guide highlights the straightforward, no-nonsense approach of direct dialogue in various settings. From leadership to personal relationships, each scenario demonstrates the impact of clear and concise communication, providing insights into how it is used and ways to balance it with openness for better understanding and outcomes.
- Managers Assigning Tasks: Managers clearly outlining tasks and expectations to employees. Enhances efficiency and Open Communication with Manager.
- Doctors Explaining Procedures: Doctors providing clear, unambiguous information to patients. Critical for informed consent and Open Communication with Patients.
- Parent-Child Rules Discussion: Parents setting clear boundaries and consequences with their children. Balances authority and Open Communication with Child.
- Teachers’ Instructions in Classroom: Teachers giving clear, direct instructions for assignments to students. Ensures understanding and Open Communication with Students.
- Project Debriefs: Leaders giving specific feedback on what went well and what didn’t post-project. Promotes learning and Open Communication in Leadership.
- Family Decision Making: Family members stating their opinions clearly when making decisions together. Combines decisiveness and Open Communication in Family.
- Client Briefings: Providing clients with concise, relevant information about products or services. Ensures clarity and Open Communication with Stakeholders.
- Team Conflict Resolution: Addressing conflicts directly and promptly among colleagues. Fosters resolution and Open Communication with Colleagues.
- Emergency Announcements: Immediate and clear instructions during emergencies. Vital for safety and understanding Open Communication vs Closed Communication.
- Guidelines to Parents from Schools: Schools providing straightforward rules and guidelines to parents. Enhances cooperation and Open Communication with Parents.
Comparison between Verbal vs Written Communication
Verbal Communication:
- Immediate Interaction: Verbal communication allows for real-time interaction, enabling instant feedback and clarification.
- Non-Verbal Cues: Tone, body language, and facial expressions convey additional context and emotions in verbal conversations.
- Spontaneity: Verbal communication is often more spontaneous and less structured, which can be beneficial for informal discussions.
- Engagement: It tends to be more engaging due to the presence of vocal cues and the ability to ask questions and receive immediate responses.
- Less Formal: Verbal communication is generally less formal and can promote a sense of familiarity.
Written Communication:
- Permanent Record: Written communication provides a permanent record that can be referenced later, making it valuable for documentation and legal purposes.
- Clarity: Written communication allows for careful composition, leading to clarity and precision in conveying complex information.
- Remote Communication: It facilitates communication across distances and time zones, making it suitable for asynchronous communication.
- Thoughtful Response: Written communication allows individuals to craft thoughtful responses, making it suitable for conveying sensitive or complex messages.
- Reduced Misunderstanding: Written communication can reduce misunderstandings because messages are often well-considered and can be reviewed.
Relationship between Verbal vs Written Communication
The relationship between verbal and written communication is intricate and complementary, each serving distinct roles in conveying information and emotions:
- Interplay of Expression: Verbal communication excels in conveying tone, emotion, and immediacy, making it ideal for personal interactions and situations requiring nuance. Written communication, on the other hand, offers clarity, permanence, and the opportunity for careful structuring of thoughts, making it suitable for formal and official information exchange.
- Support and Reinforcement: In many contexts, written communication often supports or documents verbal communication. For instance, a verbal agreement may be followed by a written contract, combining the immediate, relational aspect of verbal communication with the clarity and permanence of written text.
- Contextual Flexibility: The choice between verbal and written communication often depends on the context. Verbal communication is preferred in immediate, interactive scenarios, while written communication is chosen for detailed, recordable, and extensive information sharing.
- Adaptation to Audience and Purpose: Effective communicators skillfully choose between verbal and written methods based on their audience and purpose. A sensitive message might be delivered verbally to convey empathy, while a complex instructional guide is often written for clarity and reference.
- Complementary Use in the Digital Age: In today’s digital world, the lines between verbal and written communication are increasingly blurred. Digital platforms merge these forms, like in video chats (verbal) and emails or instant messaging (written), demonstrating their interdependent relationship in effective communication strategies.
In conclusion, the choice between open communication vs. direct communication plays a pivotal role in shaping relationships and outcomes. As evidenced by examples, open communication fosters trust, collaboration, and innovation, while direct communication emphasizes clarity and efficiency. Recognizing signs of ineffective Communication is Essential. To improve, adapt Communication Styles and foster a culture that values both approaches, ultimately achieving more productive and harmonious interactions.