Paradox
Literature is filled with complexities, contradictions, and ambiguity, but that’s what makes them interesting to the average reader. Imagine if narratives and other forms of writing were nothing but simple sentences with literal meanings. Where’s the fun in that? Literature exists to allow one’s mind to wander in a world of creativity.
1. Paradox Theory and Paradox of Success
2. Terms Paradox Example
3. Leaders as Paradox Navigators
4. Six Paradoxes of Leadership
5. Notes on The Grandfather Paradox
6. Strategy Paradox Template
7. Paradox of Time Travel
8. Data Paradox Example
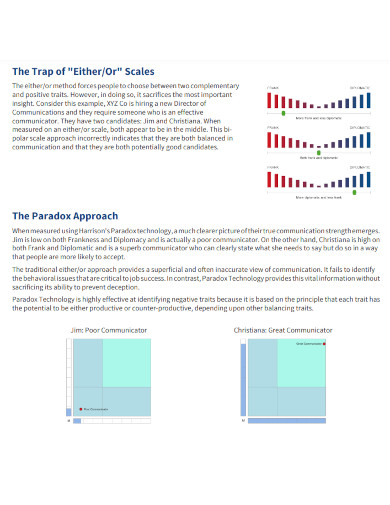
9. Paradox Technology Example
10. Efficiency Paradox Example
11. Microfoundations of Organizational Paradox
12. Paradox without Self-Reference
13. Understanding Simpson’s Paradox
14. Presenters Paradox Template
What is a Paradox?
A paradox is a type of figurative language that can seem silly or contradictory in form, yet it can still be true, or at least make sense in the context given. This is sometimes used to illustrate thoughts or statements that differ from traditional ideas.
How to Write Paradox
So, instead of taking a given statement literally, an individual must comprehend it from a different perspective. Using paradoxes in speeches and descriptive writings can also add wit and humor to one’s work, which serves as the perfect device to grab a reader or a listener’s attention. To write a good paradox, here are your steps.
Step 1: Choose a Topic
To start writing your paradox for either your sentences, your essays, or speeches, the first thing you must do is to decide on the topic or decide on a subject you want to write about. Basically, it can be anything simple to something complex. The important part is to choose what you want to talk about.
Step 2: Identify and Combine the Ideas
Once you have chosen a topic, the next thing you need is to identify and combine the ideas you chose. Identifying the opposing ideas. These ideas must contradict one another or should not be true. Once you have done that, it is time to combine your ideas. Merging two opposing ideas into a single sentence. Make sure to keep it clear and concise.
Step 3: Edit and Revise When Necessary
Edit and revise your paradox sentences. This includes grammatical errors, misspelled words, and sentence fragments. Revising helps in making sure that your paradox sentences are really paradox sentences and that they follow the format of a paradox sentence.
Step 4: Use with a Purpose
Only use paradox when you want to make a clear and concise point or when you would want to convey the truth. Well made paradox sentences are useful tools that you can use to challenge critical thinking with your readers, conversations, or even for your speeches.
FAQs
What is the difference between literary paradox and logical paradox?
There’s a key difference between a literary and logical paradox. For starters, if a meaning of a statement is contradictory in a manner that may not be resolved into something sensible, then it cannot be considered as logical. There’s always the likelihood of building misinterpretations when readers fail to catch the deeper messages conveyed by the author.
What is the difference between paradox and oxymoron?
Most people tend to confuse a paradox with an oxymoron, and it’s not hard to see why. Most oxymoron examples appear to be compressed version of a paradox, in which it is used to add a dramatic effect and to emphasize contrasting thoughts. Although they may seem greatly similar in form, there’s are slight differences that set them apart.
How can you use paradox in writing?
From poetry to literature, and from speeches, stanzas, elements of poetry, to song lyrics, paradox helps add color to any form of writing to keep readers and listeners engaged. This can either create humor or express confusion among an audience due to its absurdity. Paradoxes serve as an effective literary tool used to test the limits of one’s understanding. This can then lead to unexpected insights, which is why some of the most famous authors in history have used paradoxes in their works.
Like other types of figurative languages, such as onomatopoeic words and hyperbole expressions, paradoxes allow authors to explore the complications of literary writing to challenge the extent of human judgment. If anything, paradoxes are simple brain teasers. They are commonly used in literature and everyday life to leave us questioning our own thoughts.