Verb Forms
Verb Forms: This article explains the various forms of verbs in English grammar, including base, past, past participle, and present participle forms. It highlights regular and irregular verb patterns, providing examples to illustrate their uses.
What is a Verb Form?
A verb form refers to the various shapes or states a verb can take within a sentence to convey different tenses, moods, voices, or aspects. These forms include the base form (infinitive without “to”), past tense, past participle, and present participle. The form a verb takes depends on its function in a sentence, such as expressing actions, events, or states of being in different temporal frameworks. In English, verbs can also change form to show agreement with their subjects in person and number, which is particularly important for correct syntax and meaning.
What are the Verb Forms?
Verb forms are essential components of English grammar, representing different tenses and aspects of a verb. In English, there are primarily four basic forms of verbs: the base form, the past form, the past participle, and the present participle. The base form (or the infinitive form without “to,” such as “run” or “eat”) serves as the dictionary entry of a verb and is used for the simple present tense except in third person singular. The past form (such as “ran” or “ate”) is used to denote actions that occurred in the past. Both regular verbs, which follow a predictable pattern (like “walk” to “walked”), and irregular verbs, which do not follow these patterns (such as “go” to “went”), exhibit these forms.
The past participle form is used in perfect tenses and passive voice constructions. For regular verbs, this form is typically identical to the past form, like “walked,” whereas, for irregular verbs, it might differ, such as “eaten” from “eat.” The present participle form always ends in -ing (like “running” or “eating”) and is used for forming the progressive tenses. Understanding these verb forms is crucial for mastering verb conjugation and tense usage in English, aiding in both written and spoken communication.
Different forms of Verb
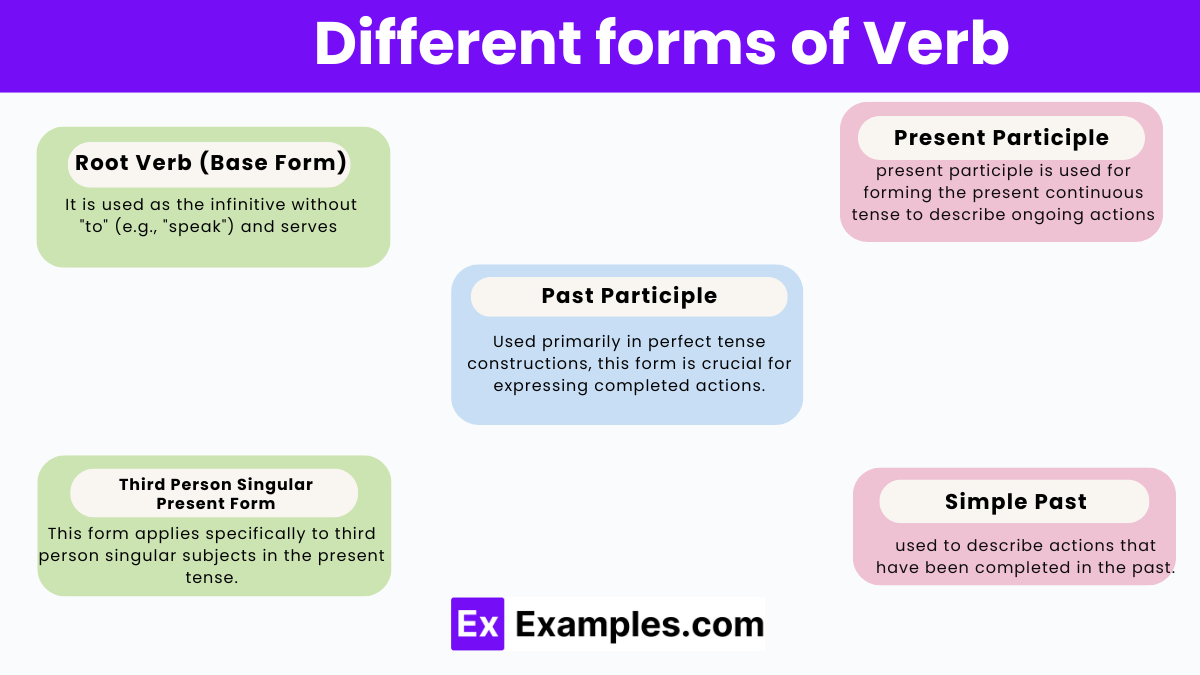
A verb form refers to the way a verb is modified to fit into a sentence, indicating various aspects such as tense, mood, and voice. These modifications help describe when and how actions take place, providing clarity and detail in communication. In English, there are five primary verb forms that are essential for constructing accurate and expressive sentences:
Root Verb (Base Form)
This is the original form of a verb, not conjugated for any tense or person. It is used as the infinitive without “to” (e.g., “speak”) and serves multiple grammatical purposes, including the formation of the simple present tense for most subjects, imperatives, and infinitives.
Example: “I like to read books during my free time.”
Third Person Singular Present Form of Verb
This form applies specifically to third person singular subjects in the present tense, usually ending in “s” or “es” (e.g., “he runs,” “she watches”). This modification distinguishes the subject’s singular nature in present tense constructions.
Example: “She listens to classical music while she works.”
Present Participle
Always ending in “-ing,” the present participle is used for forming the present continuous tense to describe ongoing actions (e.g., “running,” “eating”). It also serves as a gerund when used as a noun (e.g., “Swimming is fun”) and can function adjectivally to describe nouns (e.g., “running water”).
Example: “We are swimming in the lake this weekend.”
Simple Past
This form is used to describe actions that have been completed in the past. Regular verbs achieve this form by adding “-ed” to the base form (e.g., “talked”), whereas irregular verbs vary significantly (e.g., “went” from “go”).
Example: “He cooked a delicious meal last night.”
Past Participle
Used primarily in perfect tense constructions, this form is crucial for expressing completed actions relevant to the present, past, or future. Regular verbs often share the same form for simple past and past participle (e.g., “talked”), while irregular verbs may have unique forms (e.g., “written” from “write”). Past participles are also vital in forming passive voice sentences.
Example: “The book has been read by the entire class.”
Examples of Verb Forms
- I always enjoy to walk through the park in the mornings.
- She cooks dinner for her family every Sunday.
- They are playing soccer at the stadium tonight.
- We visited the museum during our last vacation.
- The windows have been cleaned and now they sparkle.
- He reads the newspaper every morning without fail.
- It rains here almost every afternoon.
- The cat is sleeping on the windowsill right now.
- Mark finished his homework an hour ago.
- The letters were written by the students last week.
- She loves to dance and sing at parties.
- The teacher explains the lesson clearly to the students.
- They are watching a movie in the living room.
- I met her while I was vacationing in Italy.
- The cake has been eaten by the time we arrived.
- He drives his kids to school every day.
- It snows heavily in the mountains during winter.
- The dog is barking loudly at the strangers.
- Susan painted her room blue yesterday.
- The documents have been signed by all parties involved.
FAQ’s
What is a gerund?
A gerund is a verb form that functions as a noun, ending in ‘-ing’. It is used to describe actions, states, or processes as subjects, objects, or complements.
How do I know which form of the verb to use?
The choice of verb form depends on the tense, aspect, mood, voice, and agreement with the subject in the sentence. Understanding the context and rules of English grammar can help determine the appropriate form.
Can irregular verbs follow the same patterns as regular verbs?
No, irregular verbs have unique forms for the past tense and past participle, and they do not follow regular patterns like adding ‘-ed’. Learning irregular verb forms individually is essential for using them correctly in sentences.