A-B Whole Square
The algebraic identity (𝑎−𝑏)² represents the square of the difference between two numbers, 𝑎 and 𝑏. This formula expands to 𝑎²−2𝑎𝑏+𝑏², integrating concepts from integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. It finds utility in various mathematical fields including algebra, where it helps simplify expressions and solve equations. The identity also plays a role in statistical methods like the least squares method, which is used for data fitting. Understanding (𝑎−𝑏)² is fundamental in exploring more complex numerical and algebraic studies, including square and square roots.
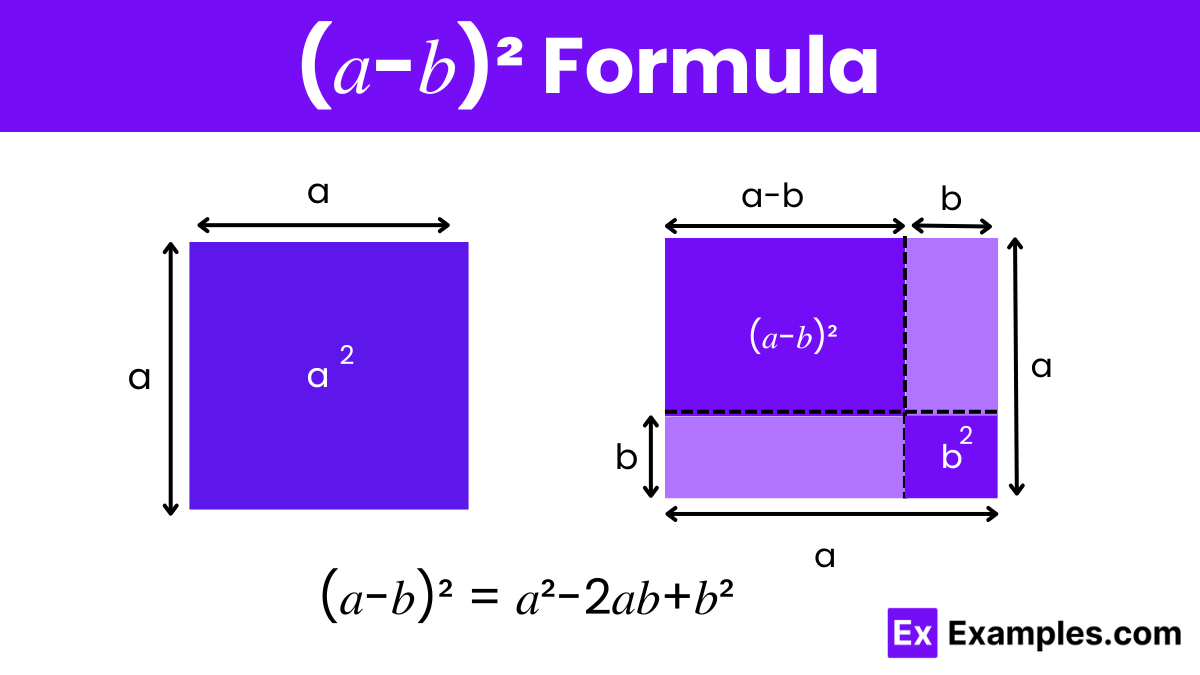
What is (a – b) Whole Square Formula?
The formula for (𝑎−𝑏)², commonly referred to as the square of a binomial difference, is an important algebraic identity. It is expressed as:
This formula represents the expanded form of squaring the difference between any two numbers, 𝑎 and 𝑏. Here’s a breakdown of the components:
- 𝑎²: the square of the first term.
- −2𝑎𝑏: twice the product of the two terms, with a negative sign indicating subtraction.
- 𝑏²: the square of the second term.
Also Check here:
Proof of A minus B Whole Square Formula
To prove the algebraic identity (𝑎-𝑏)² = 𝑎²-2𝑎𝑏+𝑏², we can use the method of expanding the expression through basic algebraic principles. Here’s the step-by-step proof:
Step 1: Write the expression
Start with the expression (𝑎−𝑏)². This signifies the square of the binomial 𝑎−𝑏.
Step 2: Expand the square
Remember that squaring a binomial involves multiplying the binomial by itself:
(𝑎−𝑏)² = (𝑎−𝑏)(𝑎−𝑏)
Step 3: Apply the distributive property (also known as the FOIL method for binomials)
- First terms: Multiply the first term in each binomial: 𝑎⋅𝑎 = 𝑎2
- Outer terms: Multiply the outer terms of the binomials: 𝑎⋅(−𝑏) = −𝑎𝑏
- Inner terms: Multiply the inner terms of the binomials: (−𝑏)⋅𝑎 = −𝑏𝑎
- Last terms: Multiply the last terms in each binomial:(−𝑏)⋅(−𝑏) = 𝑏²
Step 4: Combine like terms
Now, combine all the terms from the expansion:
𝑎²−𝑎𝑏−𝑎𝑏+𝑏²
Combine the middle terms:
−𝑎𝑏−𝑎𝑏 = −2𝑎𝑏
Step 5: Write the final expression
So, the expression simplifies to:
𝑎²−2𝑎𝑏+𝑏²
This completes the proof that (𝑎-𝑏)² = 𝑎²-2𝑎𝑏+𝑏². This identity is very useful in algebra for simplifying expressions and solving equations, and it holds true for all real numbers, including integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers.
Examples of A-B Whole Square
The formula for (a−b)² is a fundamental algebraic identity used to expand and simplify expressions. The identity is:
(a−b)² = ab²−2ab+b²
This formula shows that the square of the difference between two terms, a and b, is the square of the first term, minus twice the product of the two terms, plus the square of the second term. Here are some examples to illustrate how to apply this formula in various scenarios:
Example 1: Basic Numbers
Problem: Calculate (5−3)².
Solution: Using the formula:
(5−3)² = 5²−2⋅5⋅3+3² = 25−30+9 = 4
So, (5−3)² = 4.
Example 2: Algebraic Terms
Problem: Simplify (𝑥−4)2(x−4)2.
Solution: Apply the formula:
(𝑥−4)² = 𝑥²−2⋅𝑥⋅4+4² = 𝑥2−8𝑥+16
Thus, (𝑥−4)² simplifies to 𝑥²−8𝑥+16.
Example 3: Variables with Coefficients
Problem: Expand (3𝑎−2𝑏)².
Solution: Using the identity:
(3𝑎−2𝑏)² = (3𝑎)²−2⋅3𝑎⋅2𝑏+(2𝑏)² = 9𝑎²−12𝑎𝑏+4𝑏²
So, (3𝑎−2𝑏)² expands to 9𝑎²−12𝑎𝑏+4𝑏².
FAQs
What are some practical applications of the (𝑎−𝑏)² formula in real-life scenarios?
In real-life, the (𝑎−𝑏)² formula can be used in project planning to calculate variances, in finance to compute financial forecasts and risk assessments, and in engineering to design and analyze the stability of structures. It also plays a role in optimizing processes and solving problems that involve squared differences.
Why is the (𝑎−𝑏)² formula important in mathematics?
The (𝑎−𝑏)² formula is crucial for simplifying and solving algebraic equations, aiding in data analysis (e.g., in statistical methods like the least squares method), and understanding geometric relationships. It’s a foundational tool in algebra that extends to various applications in higher mathematics and applied sciences.
What is the formula for (𝑎−𝑏)² and what does each term represent?
The formula for (𝑎−𝑏)² is 𝑎²−2𝑎𝑏+𝑏². Here, 𝑎² represents the square of the first term, −2𝑎𝑏 is twice the product of the two terms and indicates subtraction, and 𝑏² is the square of the second term. This identity helps simplify and solve quadratic expressions in algebra.