What is the approximate square root of 50?
6.5
7.0
7.5
8.0

Estimating square roots is a vital skill in mathematics, particularly useful in algebra and statistics, where precise calculations are essential but exact values are not always necessary. This technique involves approximating the square and square roots of both perfect and non-perfect squares, which can be either rational or irrational numbers. It relies on understanding the properties of integers and their placement between perfect squares to find a close estimate. This method also intersects with the least squares method in statistics, where estimations are crucial for fitting models to data. Mastering this skill enhances numerical reasoning and aids in solving complex problems across various mathematical disciplines.
Here’s a basic guide on how to estimate square roots using a simple numerical approach:
Identify the Nearest Perfect Squares: Locate the two perfect squares between which your number falls. For instance, if you are estimating the square root of 20, recognize that 16 (4²) and 25 (5²) are the nearest perfect squares.
Determine the Proximity: Assess how close the number is to the lower or the higher perfect square. This will help you decide how to adjust your estimate. For 20, since it is closer to 16 than to 25, you start with 4 as a base.
Linear Interpolation (if applicable): Use a simple interpolation between the two closest square roots. For example: The square root of 16 is 4, and the square root of 25 is 5 is 4 units away from 16 and 5 units away from 25 Estimate the fraction of the distance from 4 to 5 that corresponds to how close 20 is to 16 relative to the interval from 16 to 25. Formulaically, you could express it as:
Estimated Square Root = 4+4/9×(5−4) = 4.44
Adjust Based on Context: Depending on the level of precision required and the context of your work, round your result to an appropriate number of decimal places.
Finding the square root of a number is a fundamental operation in mathematics, important for various applications in algebra, geometry, physics, engineering, and beyond. There are several methods to calculate square roots, ranging from simple estimation to more precise algorithmic approaches. Here’s an overview of some common methods:
This is one of the simplest ways to find square roots, particularly effective for small numbers or when only an approximate value is needed.
Before calculators, square root tables were commonly used to find square roots.
This method is useful for perfect squares and involves expressing the number as a product of prime factors.
The long division method is a more precise approach that is particularly useful for larger numbers or when a high degree of accuracy is needed.
The simplest modern method for most people.
This is an iterative numerical method used for finding successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function.
Formula: If 𝑥 is an approximation to √𝑎, then a better approximation can be found with the formula:
xnew = 1/2(x+a/x)
Problem: Find the square root of 20.
Result: The square root of 20 is approximately 4.5.
Problem: Find the square root of 72.
Result: The square root of 72 is 6√2.
Estimating the square root of a number involves finding a value that, when squared, is close to the original number. This method is particularly useful when an exact square root is not necessary or when dealing with numbers that do not have simple square roots (such as non-perfect squares). Estimation is crucial in situations where calculations must be performed quickly or without the aid of a calculator.
Estimating square roots is a fundamental skill in mathematics that applies to a range of fields, from algebra to engineering and sciences. It allows individuals to make quick assessments and decisions based on approximate values, which is essential for problem-solving in real-world situations where precision is less critical.
Estimating square roots is not just academic; it’s used in various professional and practical contexts, such as:
Estimating a square root provides a close approximation and is typically quicker and easier, especially without calculative tools. Calculating the exact square root, particularly for non-perfect squares, often requires more complex numerical methods or a calculator and results in a more precise value.
Yes, learning to estimate square roots is a valuable educational tool as it enhances numerical intuition and helps students understand the properties of numbers, especially the concept of squares and square roots. It also fosters a deeper appreciation of the relationship between geometry (square areas) and algebra.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the approximate square root of 50?
6.5
7.0
7.5
8.0
Estimate the square root of 30.
5.0
5.5
6.0
6.5
What is the approximate square root of 120?
10
10.5
11
11.5
Estimate the square root of 200.
14
14.5
15
15.5
What is the approximate square root of 75?
8
8.5
9
9.5
Estimate the square root of 70.
8
8.1
8.4
8.6
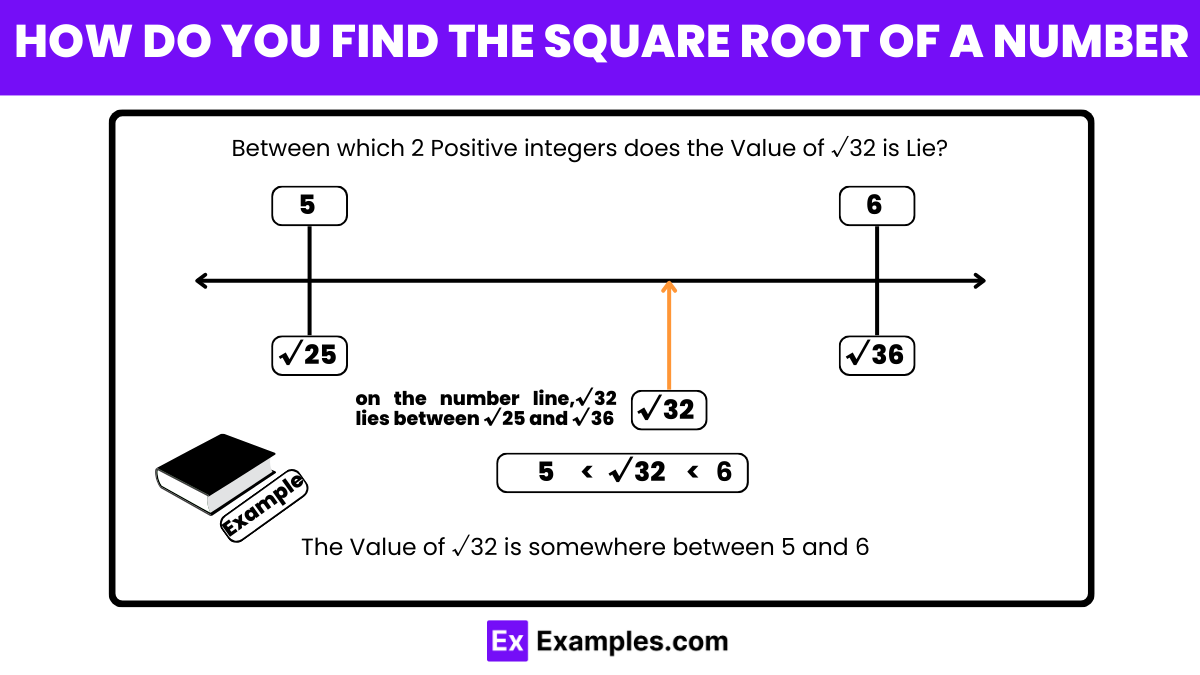
What is the approximate square root of 32?
5
5.5
6
6.5
What is the approximate square root of 0.81?
0.8
0.9
10
11
Estimate the square root of 0.04.
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
What is the approximate square root of 7.5?
2.6
2.7
2.8
2.9
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

