What is the multiplier of 6 when calculating 6 × 8?
6
8
14
48


A multiplier is a number used in mathematics to multiply another number. It’s a fundamental concept in arithmetic and is essential for understanding various mathematical operations, especially in algebra and higher-level math.
A multiplier is a quantity by which a given number (the multiplicand) is multiplied to obtain a product.
The multiplier formula is used to determine the number of times one number (the multiplicand) is taken to reach a specific product. The formula is expressed as:
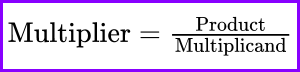
This calculation is fundamental in various mathematical and real-world applications.
Finding the multiplier involves determining the number by which a given number (multiplicand) must be multiplied to obtain a desired product. This process is essential in solving various mathematical problems, including algebraic equations and real-life applications. Below are the steps to find the multiplier along with examples for better understanding.
Suppose you have a product of 36 and a multiplicand of 6, and you need to find the multiplier.
Multiplier=36/6=6
Thus, the multiplier is 6.
Arithmetic multipliers are used in basic arithmetic operations to scale numbers. For instance, in the multiplication 5×4=20, 4 is the multiplier that scales 5 to 20.
In algebra, multipliers are coefficients that scale variables. For example, in the equation 3x=15, 3 is the multiplier that scales the variable x to 15.
Geometric multipliers involve scaling dimensions in geometry. For example, if each side of a square is multiplied by 2, the area of the square is multiplied by 2²=4.
In vector mathematics, scalar multipliers scale the magnitude of vectors. For example, multiplying vector v by scalar k results in a new vector kv with a magnitude scaled by k.
Though not strictly a mathematical concept, economic multipliers measure the effect of a change in economic activity. For example, a fiscal multiplier indicates how much economic output increases with addition of government spending.
Commutative Property: Multiplication is commutative, meaning the order of the multiplicand and multiplier can be switched without changing the product. For instance, 4×7=7×4=28.
Associative Property: The way in which numbers are grouped in multiplication does not change the product. For example, (2×3)×4=2×(3×4).
Identity Property: Multiplying any number by 1 leaves the number unchanged. Here, 1 is called the multiplicative identity.
In economics, a multiplier effect is the idea that an initial spending can lead to a larger increase in overall economic activity. For example, an increase in government spending can boost consumer income, which in turn increases consumer spending and further stimulates the economy.
In physics, multipliers are used to express how physical quantities scale with each other. For example, in optics, the magnification of a lens is the multiplier that describes how much larger or smaller an image is compared to the object.
In algebra, the concept of a multiplier extends to algebraic expressions and equations. For example:
x⋅y
Here, x can be seen as the multiplier of y.
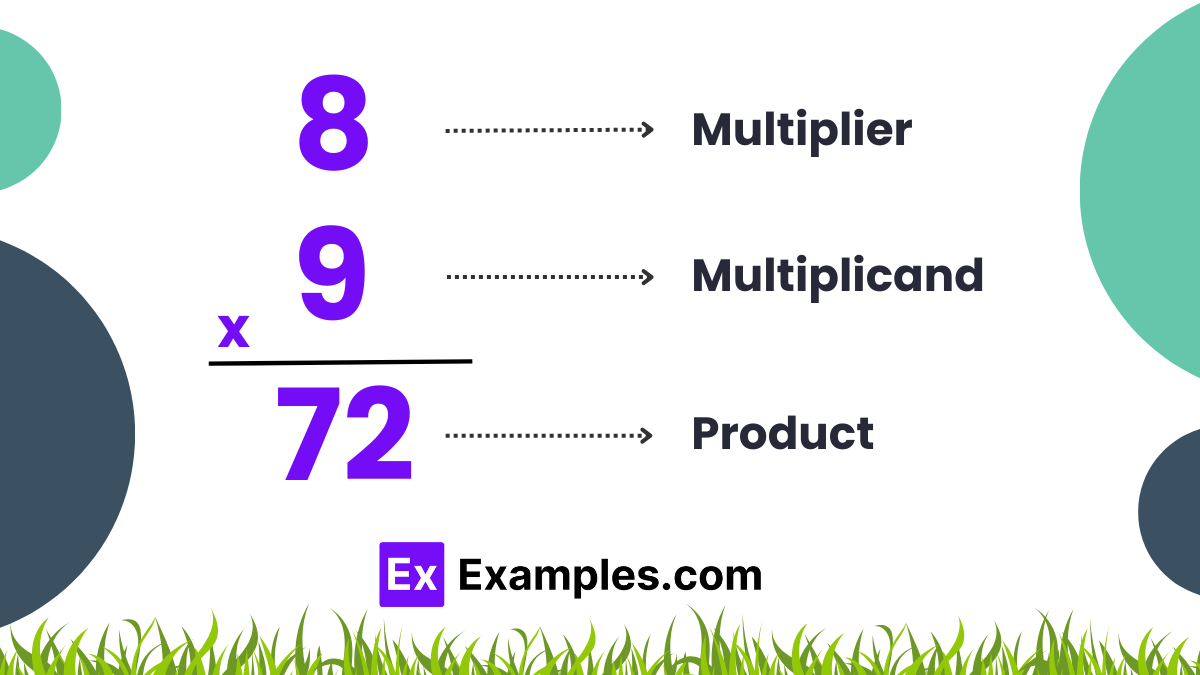
In multiplication, the multiplicand is the number being multiplied, and the multiplier is the number by which the multiplicand is multiplied. For example, 5×3, 5 in is the multiplicand, and 3 is the multiplier.
To find the multiplier of a number, divide the product by the multiplicand. The formula is: Multiplier= Product/Multiplicand
This yields the number of times the multiplicand is counted.
A multiplier is a number by which another number (the multiplicand) is multiplied to get a product. It indicates how many times the multiplicand is considered in the multiplication process.
The three types of multipliers are:
Fiscal multipliers in economics
Financial multipliers in investments
Numerical multipliers in basic arithmetic and algebra
A multiplier is also referred to as a scaling factor or coefficient in various contexts, indicating its role in scaling up or down the value of the multiplicand.
You can use multiplier in a sentence like this: “In the equation 6×4=24, the number 4 is the multiplier, indicating how many times the number 6 is taken.”
No, the number to be multiplied is called the multiplicand. The multiplier is the number that specifies how many times the multiplicand is considered.
A multiplier is a number that determines how many times another number (the multiplicand) is counted in multiplication. For example, in 3×4=12, 4 is the multiplier.
In mathematical notation, the multiplicand usually comes first, followed by the multiplier. For example, in 5×3, 5 is the multiplicand, and 3 is the multiplier.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the multiplier of 6 when calculating 6 × 8?
6
8
14
48
If the multiplier is 5 and the multiplicand is 7, what is the product?
30
35
40
45
A number is multiplied by 12 to give a result of 96. What is the original number?
6
8
10
12
If a number is multiplied by 9 and the result is 81, what is the number?
7
8
9
10
A number multiplied by 15 equals 150. What is the number?
10
12
15
20
If a number multiplied by 7 gives a result of 91, what is the number?
12
13
14
15
A number is multiplied by 8 to give a result of 72. What is the number?
8
9
10
11
What is the product of 14 and 6?
78
84
90
96
If a number multiplied by 3 equals 21, what is the number?
6
7
8
9
A number is multiplied by 5 and the product is 45. What is the number?
8
9
10
11
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

