What is the square of 5?
20
25
30
35

In mathematics, the concept of squaring numbers from 1 to 20 provides a fundamental basis for understanding various mathematical principles. Squares, the product of an integer multiplied by itself, showcase the relationship between algebra operations and geometric interpretations. This operation also highlights the distinction between rational numbers, which can be expressed as fractions, and irrational numbers, which cannot. Exploring these least square method helps in grasping algebraic concepts like the least squares and square root method, used in statistics for linear regression. This examination aids in solidifying one’s comprehension of integers, rationality, and numerical properties essential for advanced mathematical studies.
Square of 1 to 20 PDF Download
The square of a number refers to the product of the number multiplied by itself. For instance, the squares of the numbers 1 and 2 are 1 (1×1) and 4 (2×2) respectively, showcasing how each number expands in magnitude when squared.
Highest Value: 20² = 400
Lowest Value: 1² = 1
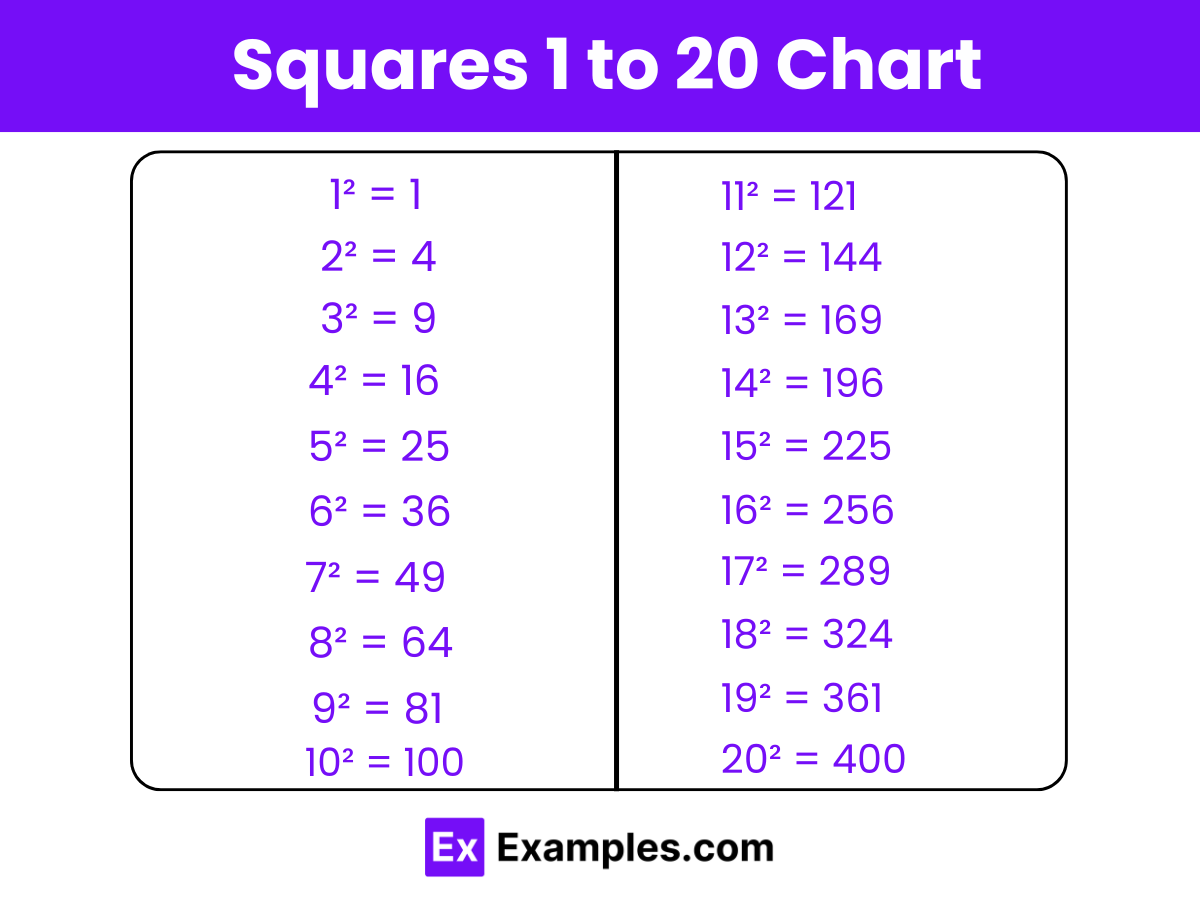
| Squares 1-10 | Squares 11-20 |
|---|---|
| 1² = 1 | 11² = 121 |
| 2² = 4 | 12² = 144 |
| 3² = 9 | 13² = 169 |
| 4² = 16 | 14² = 196 |
| 5² = 25 | 15² = 225 |
| 6² = 36 | 16² = 256 |
| 7² = 49 | 17² = 289 |
| 8² = 64 | 18² = 324 |
| 9² = 81 | 19² = 361 |
| 10² = 100 | 20² = 400 |
The table above lists the squares of integers from 1 to 20, showcasing how each number, when multiplied by itself, results in its square. This illustrates a basic algebraic concept where sequential integers demonstrate an exponential increase in their squared values, highlighting foundational principles of arithmetic progression and growth.
| Even Squares 2-10 | Even Squares 12-20 |
|---|---|
| 2² = 4 | 12² = 144 |
| 4² = 16 | 14² = 196 |
| 6² = 36 | 16² = 256 |
| 8² = 64 | 18² = 324 |
| 10² = 100 | 20² = 400 |
The table above neatly categorizes the squares of even numbers from 2 to 20 into two columns, illustrating the rapid growth in values as numbers increase. This visual representation helps underscore the exponential nature of squaring, particularly noticeable in even sequences, where each subsequent square is significantly larger than its predecessor.
| Odd Squares 1-9 | Odd Squares 11-19 |
|---|---|
| 1² = 1 | 11² = 121 |
| 3² = 9 | 13² = 169 |
| 5² = 25 | 15² = 225 |
| 7² = 49 | 17² = 289 |
| 9² = 81 | 19² = 361 |
The table above divides the squares of odd numbers from 1 to 19 into two columns, illustrating a clear exponential progression in their values. This format highlights the quadratic growth pattern, where each subsequent square significantly surpasses its predecessor in magnitude, emphasizing the effect of squaring larger odd numbers.
Knowing the squares of numbers is useful for mathematical calculations in algebra, geometry (calculating areas), statistics (variance calculations), and even in everyday applications like finance (interest computations).
The difference between the squares of consecutive numbers increases progressively by odd numbers. For instance, the difference between 2² and 1² is 3, between 3² and 2² is 5, and so on.
The value of square of 1 to 20 is the list of numbers obtained by multiplying an integer by itself. When we multiply a number by itself we will always get a positive number. For example, the square of 13 is 132 = 169.
Perfect squares play a crucial role in various mathematical concepts, such as geometry, algebra, and number theory. They are fundamental in understanding patterns, relationships, and properties of numbers.
The squares of numbers correspond to the areas of squares with side lengths equal to the respective numbers. For example, the square of 5 (25) represents the area of a square with side length 5 units.
The squares from 1 to 20 that are between 1 and 50 are 1², 2², 3², 4², 5², and 6². These are 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, and 36.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the square of 5?
20
25
30
35
What is 8²?
56
60
64
68
What is the result of 7²?
47
48
49
50
Find the square of 12.
120
130
140
144
Calculate the square of 10 using repeated addition.
90
95
100
105
Calculate 4² using breaking it down.
12
14
16
18
What is 6² ?
34
35
36
37
Find the square of 3 using repeated addition.
7
8
9
10
Calculate the square of 13.
168
169
170
171
Find the square of 18.
322
324
326
328
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

