What is the square of 3?
6
9
12
15
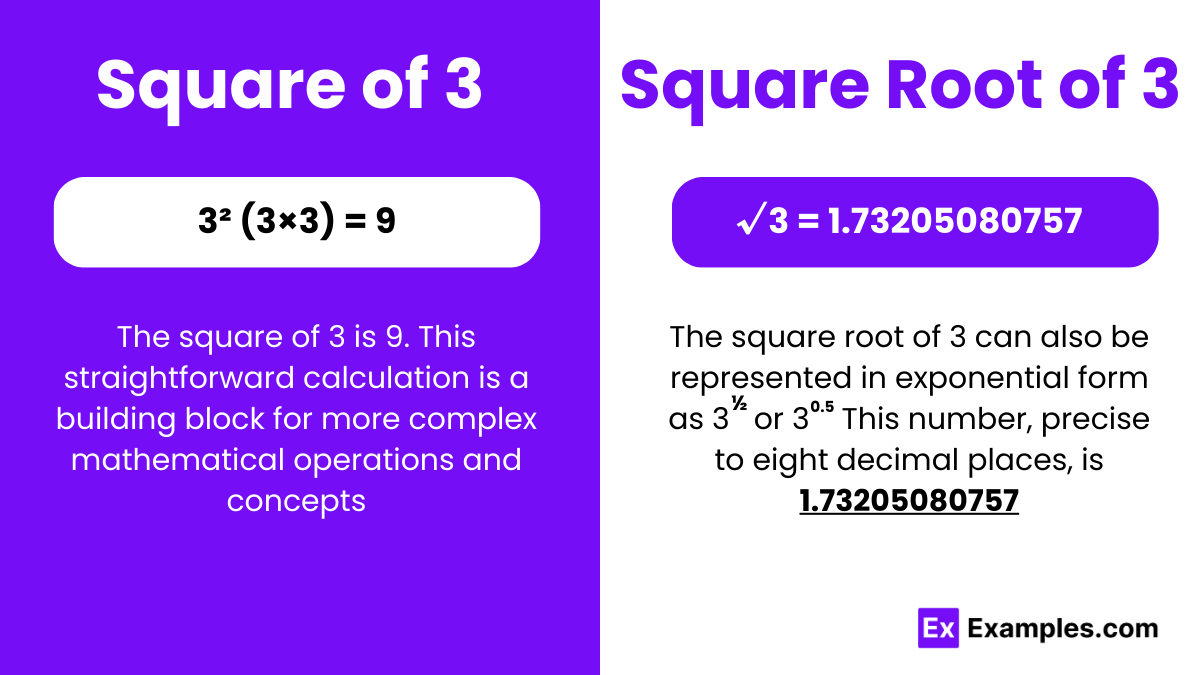
To calculate the square of 3, you simply multiply 3 by itself:
Therefore, the square of 3 is 9. This straightforward calculation is a building block for more complex mathematical operations and concepts, including algebraic equations, geometric formulas, and statistical models.
The square root of 3, denoted as √3, refers to the positive number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 3. It is an example of an irrational number, which means it cannot be exactly expressed as a simple fraction of two integers. The digits after the decimal point in its decimal representation continue infinitely without repeating. The approximate value of √3 is 1.73205080757.
This value is significant in various areas of mathematics and geometry, particularly in calculating the height of an equilateral triangle when the length of its side is known. In an equilateral triangle, the height can be found by multiplying the length of one side by √3/2. The square root of 3 also appears in trigonometry, especially in the sine and cosine of 30° and 60° angles, and in many areas of physics and engineering where triangular or hexagonal symmetries are relevant.
Exponential Form: 3^1/2 or 3^0.5
Radical Form: √3
This means it cannot be precisely represented as a fraction of two integers. Its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. The concept of irrationality indicates that the square root of 3 has an infinite number of digits after the decimal point without any repeating pattern, making it impossible to express exactly as a simple fraction. The proof of the irrationality of numbers like the square root of 3 is based on the principle that no rational number’s square can result in 3, a conclusion that can be reached through logical reasoning similar to the proof of the irrationality of the square root of 2.
Estimation Method:
To find the value of √3 in an easy and understandable way, try the following simple estimation method:
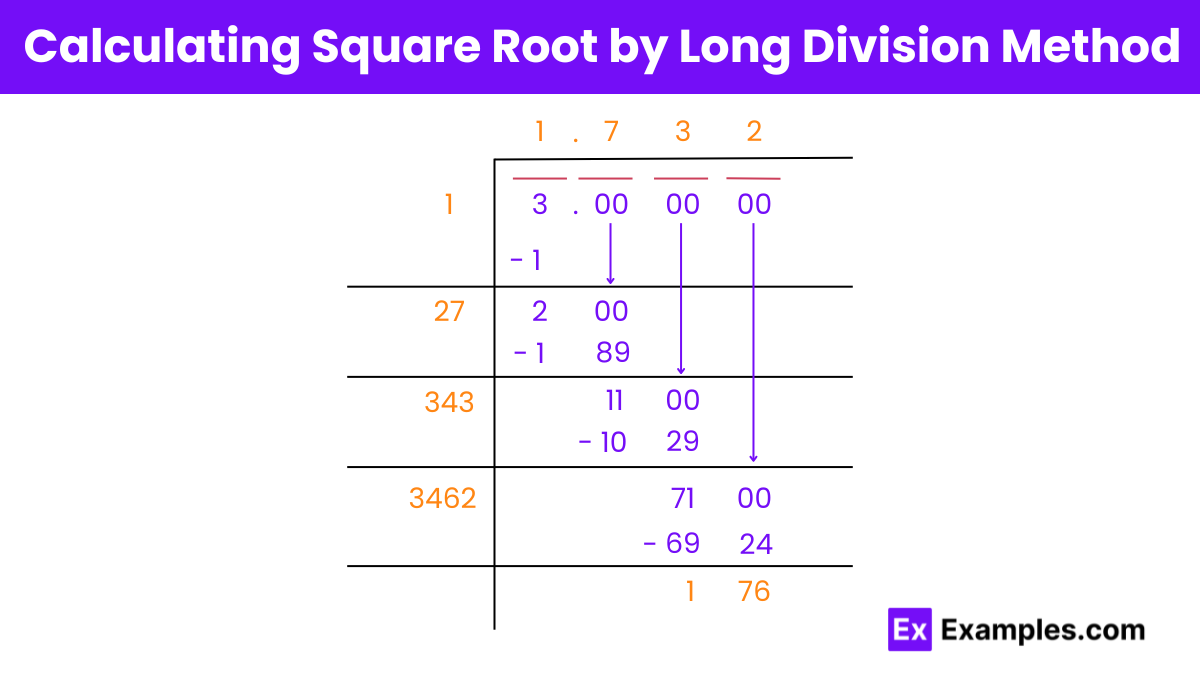
To find the square root of 3 using the long division method, follow these steps:
Setup: Write 3 as 3.000000, grouping zeroes in pairs after the decimal.
Initial Number: Choose a number whose square is less than 3. Here, it’s 1.
First Division: Divide 3 by 1, getting a quotient of 1 and a remainder of 2.
Expand Dividend: Bring down a pair of zeroes next to the remainder, making it 200.
Double the Divisor: Add the divisor (1) to itself to start the new divisor (2) and look for a digit (X) such that 2X times X is less than 200. X equals 7 here.
Update Quotient and Divisor: Place 7 in the quotient, making the new divisor for the next step 27 + 7 = 34.
Repeat for Precision: Continue the process, adjusting the divisor and bringing down zeroes to calculate further decimals.
The square root of 3 is an irrational number, approximately 1.732, which cannot be expressed as an exact fraction of two integers. A perfect square has an integer as its square root.
Yes, √3 is a real number. It represents the positive number that, when squared, equals 3. However, it is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be exactly expressed as a fraction.
Yes, 3 is an integer. Integers include all whole numbers, both positive and negative, as well as zero. Since 3 is a whole number without a fractional or decimal component, it qualifies as an integer.
The square root of 3 is between 1 and 2. More precisely, it’s between the square roots of 1 (√1=1) and 4 (√4=2), approximately 1.732.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the square of 3?
6
9
12
15
Which of the following is closest to the square root of 3?
1.7
1.8
1.9
2.0
If x² = 3, what is x?
1.5
1.7
1.8
1.9
Simplify √3 to its decimal form.
1.71
1.72
1.73
1.74
What is (3)²?
6
8
9
12
Find the approximate value of √3 to two decimal places.
1.71
1.72
1.73
1.74
Which number is not a square of an integer but closest to 3?
1
2
4
5
What is 3 raised to the power of 0.5?
1.7
1.73
1.75
1.8
Calculate 3 × 3.
6
7
8
9
What is √9 divided by √3?
1
2
3
4
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

