What is the primary function of a modulator in a communication system?
To amplify the signal
To convert a signal to a different frequency
To demodulate the signal
To filter the signal

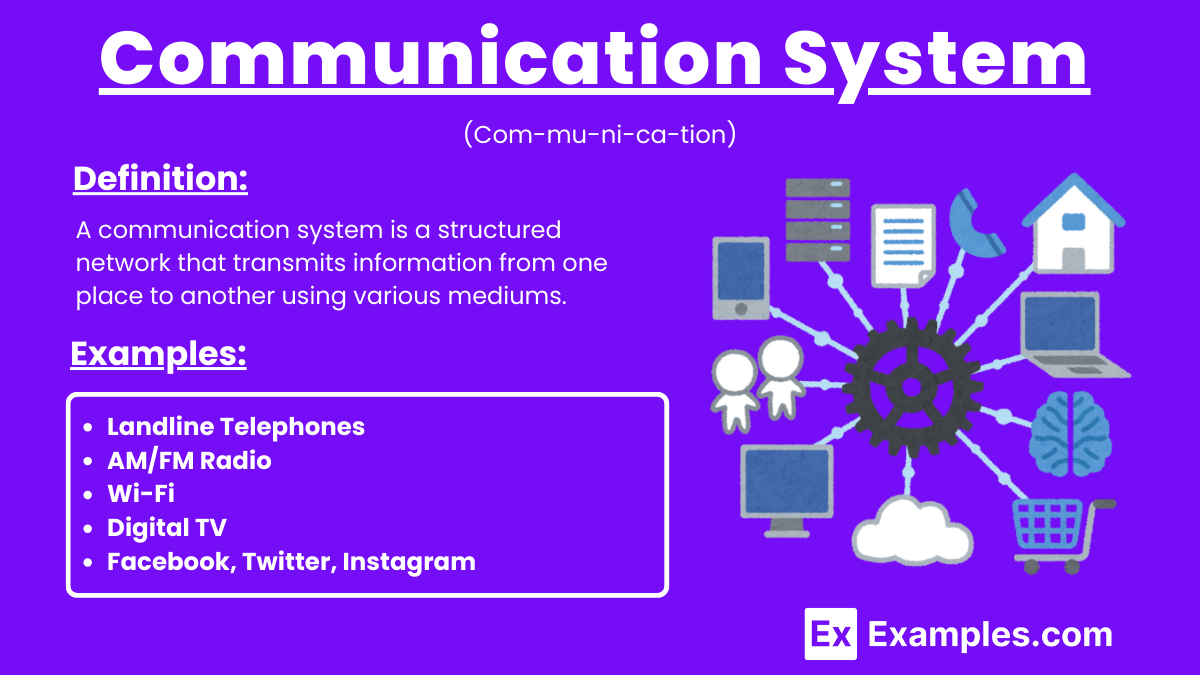
A communication system is a structured assembly of processes and components designed to transfer information from one location to another. It involves a transmitter, which encodes the message into a signal, a communication channel that carries the signal, and a receiver that decodes the signal back into the original message. These systems can operate through various mediums such as electrical, optical, or radio frequencies, and are essential for enabling data exchange in telecommunication networks, broadcasting, and internet communications. The efficiency and reliability of a communication system are crucial for effective information dissemination in modern society.
A communication system is a structured network that transmits information from one place to another using various mediums. It includes a transmitter, a communication channel, and a receiver to send, carry, and decode messages, facilitating data, voice, and video exchange across distances.
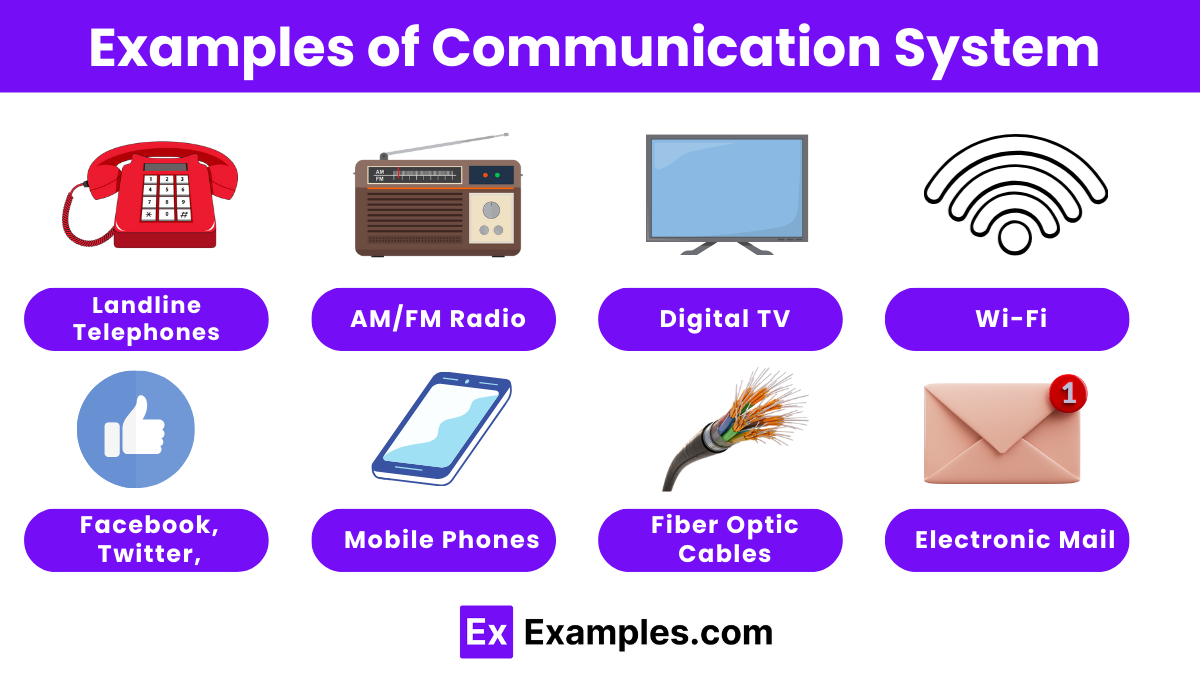
Communication systems are essential for transmitting information across different mediums and distances. Here are some common examples:
Communication systems can be broadly classified into several categories based on their mode of transmission, technology, and application. Below are the primary types of communication systems:
| Feature | Wireless Communication System | Wired Communication System |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Electromagnetic waves (radio, microwave, infrared) | Physical cables (twisted pair, coaxial, fiber optic) |
| Mobility | High mobility; users can move freely | Limited mobility; users restricted by cable length |
| Installation | Easier installation; no physical cables needed | More complex installation; requires cabling |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial cost due to infrastructure |
| Bandwidth | Varies; typically lower than wired | Typically higher; supports higher data rates |
| Interference | Susceptible to interference from obstacles/devices | Less susceptible to interference |
| Security | Higher risk of eavesdropping/unauthorized access | Generally more secure; physical access needed |
| Reliability | Can be affected by environmental factors | More reliable; consistent performance |
Communication systems are fundamental for transmitting information from one place to another. Here are the key principles
The basic components include the transmitter, transmission medium, and receiver. The transmitter encodes and sends the signal, the medium carries it, and the receiver decodes it.
The transmitter encodes the information into a signal suitable for transmission. It modulates the signal to match the transmission medium.
The receiver captures the transmitted signal and demodulates it to retrieve the original information. It often amplifies the signal for better clarity.
The transmission medium carries the signal from the transmitter to the receiver. It can be a physical medium like cables or a wireless medium like air.
Common transmission media include twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, optical fibers, and wireless channels like radio waves and microwaves.
Noise refers to any unwanted interference that distorts or disrupts the signal during transmission, affecting the quality and clarity of the received information.
Digital communication involves transmitting information using discrete signals, typically binary code, which represents data as sequences of 0s and 1s.
Digital communication offers better noise resistance, easier error detection and correction, higher security, and more efficient data compression and storage.
Simplex allows one-way communication, half-duplex allows two-way communication but not simultaneously, and full-duplex allows simultaneous two-way communication.
Multiplexing is a technique that combines multiple signals into one medium to improve efficiency. It allows simultaneous transmission of several signals over a single channel.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary function of a modulator in a communication system?
To amplify the signal
To convert a signal to a different frequency
To demodulate the signal
To filter the signal
Which of the following is a common modulation technique used in analog communication systems?
Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM)
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
In digital communication, what does the term 'bit rate' refer to?
The number of bits transmitted per second
The frequency of the carrier wave
The amplitude of the signal
The distance between transmitter and receiver
What is the role of an antenna in a communication system?
To encode the signal
To modulate the signal
To transmit and receive electromagnetic waves
To filter out noise
Which modulation technique is used to encode data into variations in the amplitude of a carrier signal?
Frequency Modulation (FM)
Amplitude Modulation (AM)
Phase Modulation (PM)
Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM)
What is the main advantage of Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) in communication systems?
It increases signal strength
It allows multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously
It reduces signal distortion
It simplifies the receiver design
Which of the following describes the term 'bandwidth' in a communication system?
The amount of data a system can handle per second
The range of frequencies a signal occupies
he distance a signal travels
The strength of the signal
In a communication system, what does 'noise' refer to?
The loss of signal strength
The interference that degrades the signal
The amplification of the signal
The encoding of the signal
What is the purpose of error detection in digital communication?
To increase the transmission speed
To ensure the signal is correctly modulated
To identify and correct errors in the transmitted data
To amplify the signal
Which system allows multiple signals to share the same channel by dividing the channel into time slots?
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

