What is the SI unit of inductance?
Ohm
Henry
Farad
Tesla
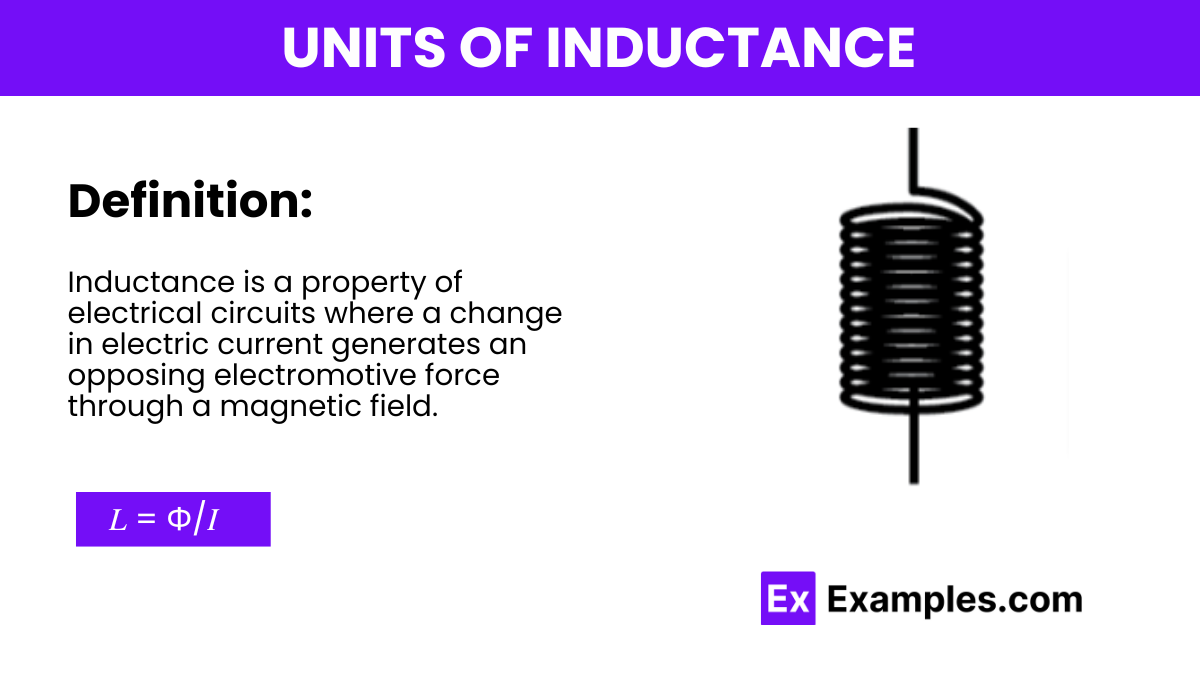
Here, 𝐿 is the inductance in henries (H), Φ is the magnetic flux in webers (Wb), and 𝐼 is the current in amperes (A). Thus, the Henry is defined such that an inductor has an inductance of one Henry when a change of one ampere per second in current through the coil produces an electromotive force of one volt across the coil.
The primary unit of inductance is the Henry (H), named after the American scientist Joseph Henry who discovered self-inductance. One Henry is defined as the inductance of a circuit in which a change in current at the rate of one ampere per second results in an electromotive force of one volt. This unit is integral to understanding how inductors behave in electrical circuits, particularly in how they store energy and oppose changes in current flow through the creation of a magnetic field.
In addition to the Henry, smaller units such as the millihenry (mH) and microhenry (µH) are commonly used, especially in electronics, where large inductances are rare. These subdivisions help in precise measurements and specifications for components like inductors and transformers used in various devices, from power supplies to radio transmitters. Each millihenry equals one-thousandth of a Henry, and each microhenry is one-millionth of a Henry, allowing for detailed descriptions of the inductive properties of smaller or more finely tuned circuits.
| Unit | Symbol | Equivalent to |
|---|---|---|
| Henry | H | 1 H = 1 volt second per ampere |
| Millihenry | mH | 1 mH = 0.001 H |
| Microhenry | µH | 1 µH = 0.000001 H |
| Nanohenry | nH | 1 nH = 0.000000001 H |
| Abhenry | abH | 1 abH = 10^(-9) H (used in the CGS system) |
Inductance, a key parameter in electrical circuits, particularly those involving coils and transformers, is measured in various units depending on the application’s scale and precision needs. Below is an overview of the primary units used to measure inductance along with their conversions, ensuring clarity for engineering, design, and educational purposes.
The fundamental SI unit of inductance, the Henry is defined as the inductance of a circuit in which a change in current of one ampere per second results in an induced voltage of one volt. It’s the standard unit used in most scientific and engineering applications.
A subunit of the Henry, one millihenry is equal to one-thousandth of a Henry (1 mH = 0.001 H). This unit is commonly used in electronic circuits where smaller inductance values are typical.
Further scaling down, the microhenry is one-millionth of a Henry (1 µH = 0.000001 H). It’s widely used in radio frequency (RF) applications and small inductors within electronic devices.
At the smaller end of the spectrum, one nanohenry equals one-billionth of a Henry (1 nH = 0.000000001 H). This unit is crucial in high-frequency electronic applications, including mobile phones and GPS systems.
Used primarily within the CGS system, one abhenry is equivalent to 10^(-9) Henrys. Although less common today, it’s occasionally referenced in specific scientific research and historical contexts.
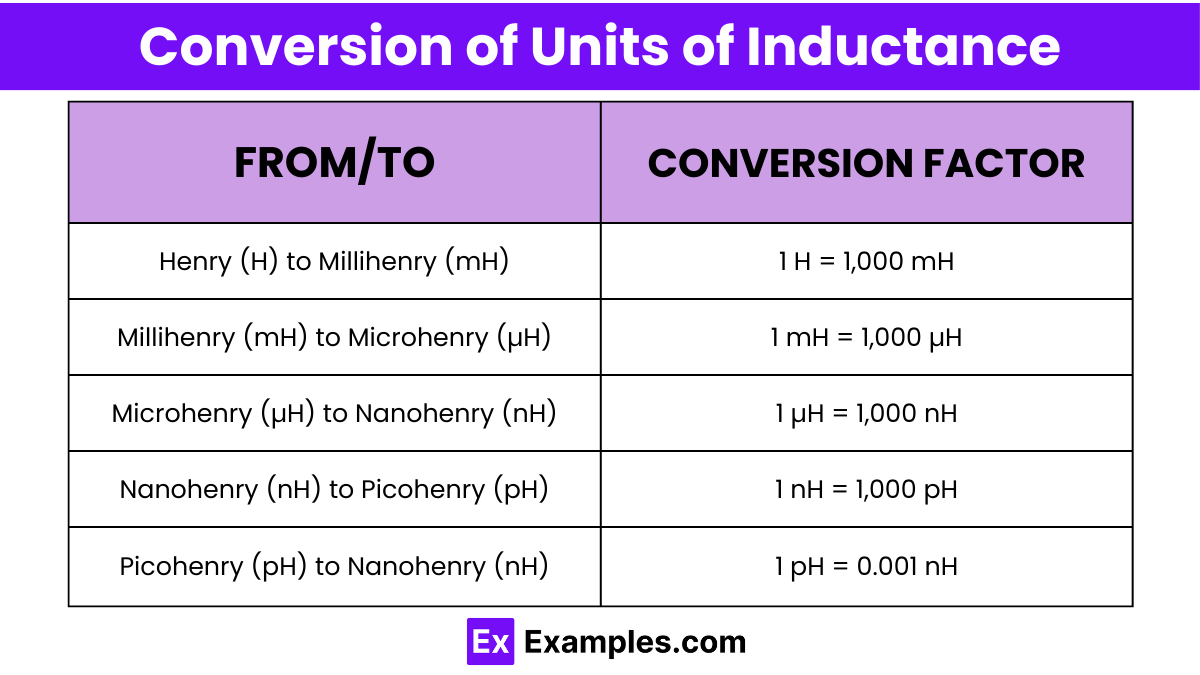
| From Unit | To Unit | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Henry (H) | Millihenry (mH) | 1 H = 1,000 mH |
| Millihenry (mH) | Microhenry (µH) | 1 mH = 1,000 µH |
| Microhenry (µH) | Nanohenry (nH) | 1 µH = 1,000 nH |
| Nanohenry (nH) | Picohenry (pH) | 1 nH = 1,000 pH |
| Picohenry (pH) | Nanohenry (nH) | 1 pH = 0.001 nH |
One Henry is equivalent to one thousand Millihenries. This conversion is crucial for understanding and working with inductance in various applications, particularly in electronic circuits where smaller units are commonly used.
One Millihenry is approximately equal to one thousand Microhenries. This allows for precise measurements and specifications in more finely-tuned electronic components.
One Microhenry converts to one thousand Nanohenries, facilitating detailed work in high-frequency electronic applications like signal processing and RF engineering.
One Nanohenry is equivalent to one billionth of a Henry, used for precise calculations in advanced technological applications and theoretical physics.
Converting from Picohenries to Nanohenries involves multiplying by 0.001, enabling precise calculations in advanced technological applications and theoretical physics.
The purpose of inductance is to resist changes in current flow in an electrical circuit, storing energy in a magnetic field. It’s essential for filtering, energy storage, and electromagnetic compatibility.
Inductance is a property of a circuit component, measuring its ability to store energy in a magnetic field, while an inductor is the physical component itself, such as a coil or solenoid, exhibiting inductance.
Inductance is a property related to a component’s ability to resist changes in current flow, whereas frequency refers to the rate of oscillation or repetition of a periodic event in a circuit. They are fundamentally different concepts in electronics.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the SI unit of inductance?
Ohm
Henry
Farad
Tesla
Which symbol is used to represent inductance?
L
C
R
G
How is 1 Henry defined in terms of voltage, current, and time?
1 Volt per Ampere per second
1 Volt per Coulomb
1 Ampere per second
1 Joule per second
If an inductor has an inductance of 2 H, what is the inductance in milliHenries (mH)?
20 mH
200 mH
2 mH
2000 mH
What is the unit of inductance in the cgs (centimeter-gram-second) system?
Gauss
Statvolt
Maxwell
Abhenry
Convert 500 milliHenries (mH) to Henrys (H).
0.5 H
5 H
50 H
0.05 H
Which physical quantity does the Henry measure?
Capacitance
Inductance
Resistance
Conductance
How is inductance related to the magnetic flux and current in a coil?
Inductance is the product of magnetic flux and current
Inductance is the ratio of magnetic flux to current
Inductance is the sum of magnetic flux and current
Inductance is the difference between magnetic flux and current
If an inductor has an inductance of 0.75 H, what is the inductance in microHenries (μH)?
7500 μH
75 μH
75000 μH
750000 μH
What happens to the inductance of a coil if the number of turns in the coil is doubled?
It remains the same
It is halved
It doubles
It quadruples
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

