Which of the following best describes an endothermic reaction?
Releases heat
Absorbs heat
No heat exchange
Produces light

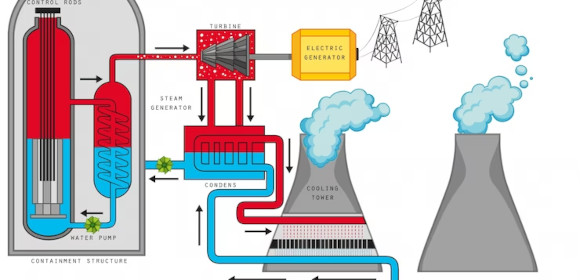
Heat is a pivotal part of a chemical reaction, as high temperatures excite the molecular structure of an object allowing it to create a chemical reaction. Endothermic reactions are one of the most pivotal interactions with heat in the natural world.




An endothermic reaction is the chemical property of an object or organism to absorb heat from its surroundings or environment. These reactions do not exert a lot of energy in the form of heat unlike their counterparts the exothermic reaction.
There are many ways to identify how the reaction will interact with heat due to the elements or factors that will surround said reaction. It is important to know whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic as this will indicate how much heat is required in the solution.
One of the easiest ways to identify and check if the reaction is endothermic is to monitor and calculate how the temperature in the environment and the object changes during the reaction. Begin by obtaining a thermometer to use as the main measuring tool in this reaction, you may use a normal thermometer or a digital thermometer for this effort.
Another way to identify whether or not heat is absorbed or emitted is through the formula of enthalpy of reaction. This formula is ?H = energy used in reactant bond breaking + energy released in product bond making, where ?H is the change or alteration of heat or the enthalpy change.
Using the thermometer you must check whether the temperature increases or decreases in the environment or the solution. If the overall temperature decreases then the reaction is endothermic, but if the temperature increases then it is exothermic.
Using the formula, you will calculate the ?H. If the result is a positive integer then the reaction is endothermic because there is the act of breaking apart the bond does not require more energy.
There are two ways the reaction will interact with heat, which are endothermic and exothermic. In an exothermic reaction outcome or the output will release heat as chemical energy or thermal energy. An endothermic reaction is the complete juxtaposition of the exothermic reaction, as the output will instead absorb heat from its surroundings.
There are many real-life phenomena we can set for the observation that will help our understanding of the concept of an endothermic reaction. A real-life example of an endothermic reaction is the melting of ice and the evaporation of water. Another example of an endothermic reaction is nuclear fission, which also uses endothermic reactions to create nuclear energy and convert it to electrical energy.
When a person does aerobic exercises or simple physical activities, the body converts complex carbohydrates and fats into energy. This creates heat and raises the internal body temperature of the person. To cool down, the body creates moisture and produces sweat through specific glands in the body. The sweat will try and absorb the heat from the body, which makes it an endothermic process.
A lot of processes and chemical reactions either produce or absorb heat as their primary consumption. The process of endothermic reactions is very pivotal in the survival of the human race because a lot of basic phenomena use endothermic reactions. For example, plants rely on endothermic processes to absorb the heat from the sunlight to create glucose and sugars, which allows these organisms to act as producers in the food web or food chain. Therefore, it is important to understand the role and phenomenon of endothermic reactions.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following best describes an endothermic reaction?
Releases heat
Absorbs heat
No heat exchange
Produces light
Which of the following is an example of an endothermic reaction?
Combustion of gasoline
Photosynthesis
Neutralization of an acid and a base
Condensation of steam
What happens to the temperature of the surroundings during an endothermic reaction?
Decreases
Increases
Fluctuates
Remains the same
Which of the following reactions is endothermic?
Burning of wood
Mixing water and acid
Melting of ice
Freezing of water
In an endothermic reaction, the enthalpy change (ΔH) is:
Positive
Negative
Zero
Variable
What is the role of energy in an endothermic reaction?
It is released into the surroundings
It is stored in the reactants
It is absorbed from the surroundings
It is not involved
Which of the following is NOT an endothermic reaction?
Decomposition of calcium carbonate
Dissolving ammonium nitrate in water
Photosynthesis
Burning of a candle
In an endothermic reaction, how does the potential energy of the products compare to that of the reactants?
It is lower
It is higher
It is the same
It fluctuates
When ammonium chloride is dissolved in water, the solution becomes colder. This process is an example of:
Exothermic reaction
Isothermal reaction
Endothermic reaction
Adiabatic reaction
Which of the following energy diagrams best represents an endothermic reaction?
Reactants lower than products
Reactants higher than products
Reactants equal to products
Energy remains constant
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

