What is the primary use of potassium permanganate in water treatment?
Disinfection
Softening
Sedimentation
pH adjustment


Potassium permanganate is a common chemical compound used in various applications, from water treatment to medical antiseptics. It is known for its distinct purple color, making it easily recognizable. This inorganic compound, with the chemical formula KMnO₄, serves as a strong oxidizing agent in chemistry labs across schools. It plays a crucial role in experiments due to its ability to react with different substances, teaching students about chemical reactions and their outcomes.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | KMnO₄ |
| Name | Potassium permanganate |
| Alternate Names | Cairox, Chameleon mineral, Condy’s crystals, Permanganate of potash, Potassium manganate(VII), Potassium permanganate(VII) |
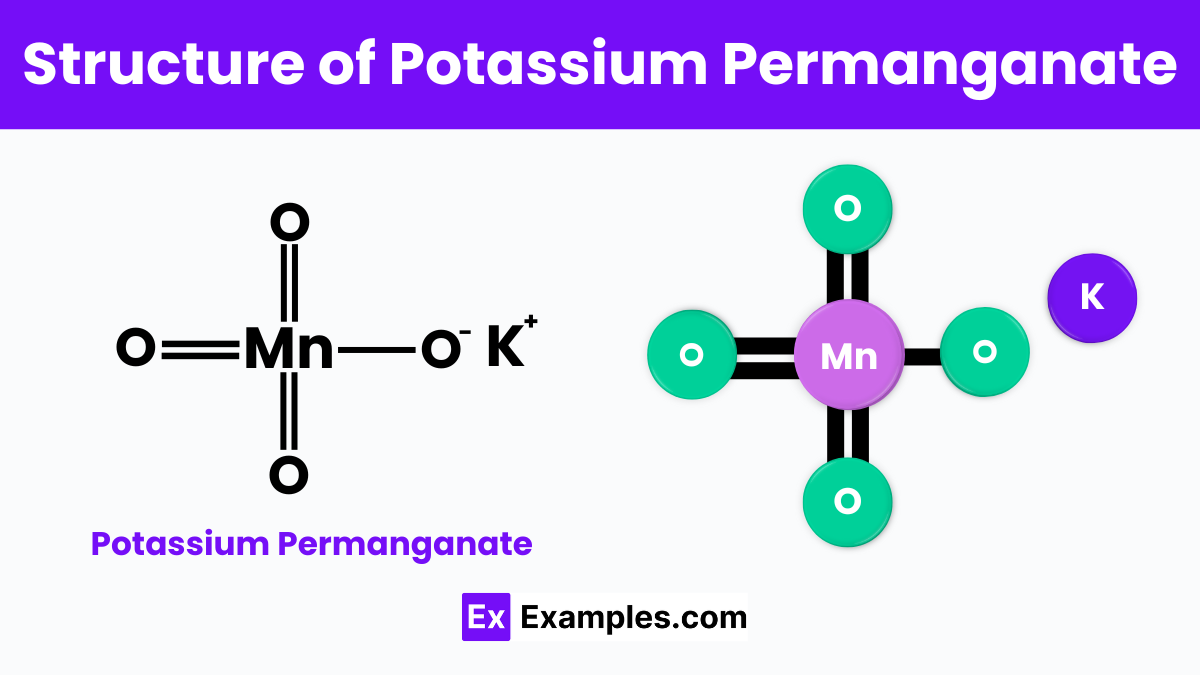
Potassium permanganate, with its chemical formula KMnO₄, consists of a potassium ion bonded to a permanganate ion. The structure is noteworthy because the permanganate ion forms a tetrahedral shape, which means it has a central manganese atom surrounded symmetrically by four oxygen atoms. This configuration is crucial for the compound’s strong oxidizing properties. The manganese atom in this structure has a high oxidation state of +7, which is key to its ability to accept electrons from other substances, leading to its use in oxidation reactions and various applications in chemical processes.
Potassium permanganate is prepared through a chemical process involving the reaction of Manganese dioxide (MnO₂) with Potassium hydroxide (KOH). This mixture is heated, and then potassium chlorate (KClO₃) is added to supply oxygen, enhancing the manganese’s oxidation state. The reaction produces potassium manganate (K₂MnO₄), which is green in color. This intermediate compound undergoes an electrolytic oxidation, where it is further oxidized and converted into potassium permanganate. The final step involves a purification process, ensuring the product’s quality and stability.
Here’s a simplified version of the chemical equation for this process:
Conversion to potassium permanganate: 3K₂MnO₄ + 2H₂O → 2KMnO₄ + 4KOH + MnO₂
This sequence of reactions demonstrates the industrial synthesis of potassium permanganate, establishing it as a key component in various chemical applications.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Dark purple or almost black granular solid or crystals. |
| Solubility in Water | Highly soluble, forming a bright purple solution. |
| Odor | Odorless, making it easy to handle without any strong smell. |
| Melting Point | Decomposes at about 240°C (464°F), does not melt at a stable point. |
| Density | Approximately 2.7 g/cm³, making it denser than water. |
| Molecular Weight | 158.034 g/mol, indicative of its relatively heavy atomic composition. |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 7722-64-7 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 516875 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 24859164 |
| SMILES Identifier | [O-]Mn(=O)=O.[K+] |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/K.Mn.4O/q+1;;;;;-1 |
| RTECS Number | SD6475000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00011364 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA Health Rating | 3 |
| NFPA Fire Rating | 3 |
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 0 |
| NFPA Hazards | Oxidizing agent |
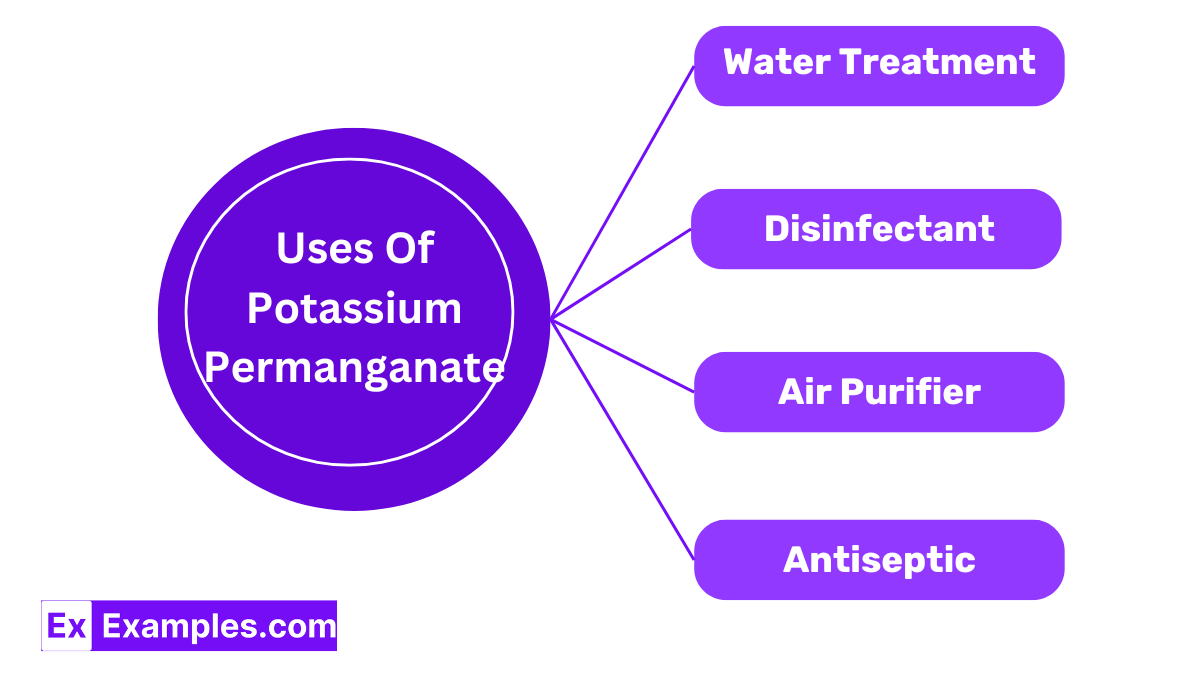
Potassium permanganate removes iron and hydrogen sulfide from water, making it clearer by oxidizing these elements.
Its strong oxidizing abilities allow potassium permanganate to kill bacteria and fungi, useful from wound care to aquarium cleaning.
Used in air purifiers, potassium permanganate cleans indoor air by breaking down organic pollutants.
Potassium permanganate acts as a reagent in labs, aiding in the creation of various chemical compounds due to its reactive nature.
As an antiseptic, potassium permanganate treats skin conditions like dermatitis and fungal infections, typically used in diluted forms for soaking.
Potassium permanganate is safe when used correctly and in prescribed concentrations. Mishandling can lead to burns or respiratory issues.
Although potassium permanganate is not illegal, authorities regulate it because of its strong oxidizing properties and its potential for misuse in illegal activities.
Potassium Permanganate can be harmful if ingested, inhaled, or improperly handled, causing respiratory, skin, and eye irritation.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary use of potassium permanganate in water treatment?
Disinfection
Softening
Sedimentation
pH adjustment
What is the oxidation state of manganese in potassium permanganate?
+2
+3
+4
+7
Which color does potassium permanganate impart to a solution?
Green
Blue
Purple
Red
Potassium permanganate can act as a strong:
Reducing agent
Oxidizing agent
Buffer
Catalyst
Which industry extensively uses potassium permanganate for oxidation processes?
Textile
Food
Electronics
Automotive
In which type of reaction is potassium permanganate used to determine the presence of unsaturation in organic compounds?
Hydrogenation
Bromination
Permanganate test
Sulfonation
Potassium permanganate is used in which medical application?
Antiseptic
Anesthetic
Analgesic
Antipyretic
What is the byproduct when potassium permanganate is used to oxidize primary alcohols to carboxylic acids?
Water
Hydrogen peroxide
Carbon dioxide
Oxygen
Which laboratory technique uses potassium permanganate to titrate reducing agents?
Gravimetric analysis
Volumetric analysis
Chromatography
Spectroscopy
What happens to the color of potassium permanganate solution when it is reduced?
Turns green
Turns yellow
Turns colorless
Turns blue
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

