Which of the following pairs is a coprime pair?
(14, 21)
(15, 28)
(16, 24)
(18, 27)

Coprime numbers, also known as relatively prime numbers, are pairs of numbers that share no common factors other than 1. This concept is a cornerstone of number theory and plays a vital role in various mathematical applications, from cryptography to algorithm design. Through engaging examples and clear explanations, our guide aims to illuminate the significance of coprime numbers, making this fundamental mathematical concept both accessible and intriguing.
Coprime numbers are two or more integers that have no common divisors except for 1. In other words, their greatest common divisor (GCD) is 1. This definition underscores the importance of understanding divisibility and factors in mathematics. Coprime numbers are essential in areas such as fraction simplification and the Chinese Remainder Theorem, showcasing their broad applicability. Through the study of coprime numbers, students can gain deeper insights into the fabric of mathematics, developing a stronger foundation for advanced mathematical exploration and problem-solving.
A prime example of coprime numbers is the pair 8 and 15. To understand why these two numbers are coprime, we examine their factors. The factors of 8 are 1, 2, 4, and 8, while the factors of 15 are 1, 3, 5, and 15. The only common factor between 8 and 15 is 1, which means they share no other divisors. This characteristic defines them as coprime numbers.
The significance of using 8 and 15 as an example lies in their clear demonstration of the concept. Neither number is prime themselves, yet they do not share any prime factors, illustrating that coprime numbers do not have to be prime. This pair exemplifies the essence of coprimality— a mutual lack of divisibility by any number other than 1, highlighting the beauty of number theory in describing unique relationships between different integers. This example not only aids in grasping the concept of coprime numbers but also underscores the diversity and depth found within mathematical relationships.
To identify co-prime numbers, follow these simple steps:
Example: Consider the numbers 9 and 28. The factors of 9 are 1, 3, and 9, while the factors of 28 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, and 28. The only common factor is 1, so 9 and 28 are co-prime.
| Coprime Numbers | Factors of First Number | Factors of Second Number |
|---|---|---|
| 5 and 8 | 1, 5 | 1, 2, 4, 8 |
| 7 and 10 | 1, 7 | 1, 2, 5, 10 |
| 9 and 28 | 1, 3, 9 | 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 28 |
| 14 and 25 | 1, 2, 7, 14 | 1, 5, 25 |
| 21 and 22 | 1, 3, 7, 21 | 1, 2, 11, 22 |
Here’s a list showcasing pairs of co-prime numbers, illustrating the diversity of these number pairs:
Each pair in this list shares no common factors other than 1, exemplifying their co-primality. This diversity underscores that co-prime numbers can be found across the number spectrum, offering infinite possibilities for exploration within mathematics.
Co-prime numbers, also known as relatively prime numbers, share distinct characteristics that make identifying them straightforward. Here are some key properties:
Identifying co-prime pairs among the first 100 numbers involves applying the properties mentioned above. While listing every co-prime pair within this range is extensive, understanding the outlined properties allows for quick identification. For instance:
These examples illustrate the application of co-prime properties, emphasizing patterns like the relationship between prime pairs, consecutive integers, and specific divisibility rules to identify co-prime numbers effectively.
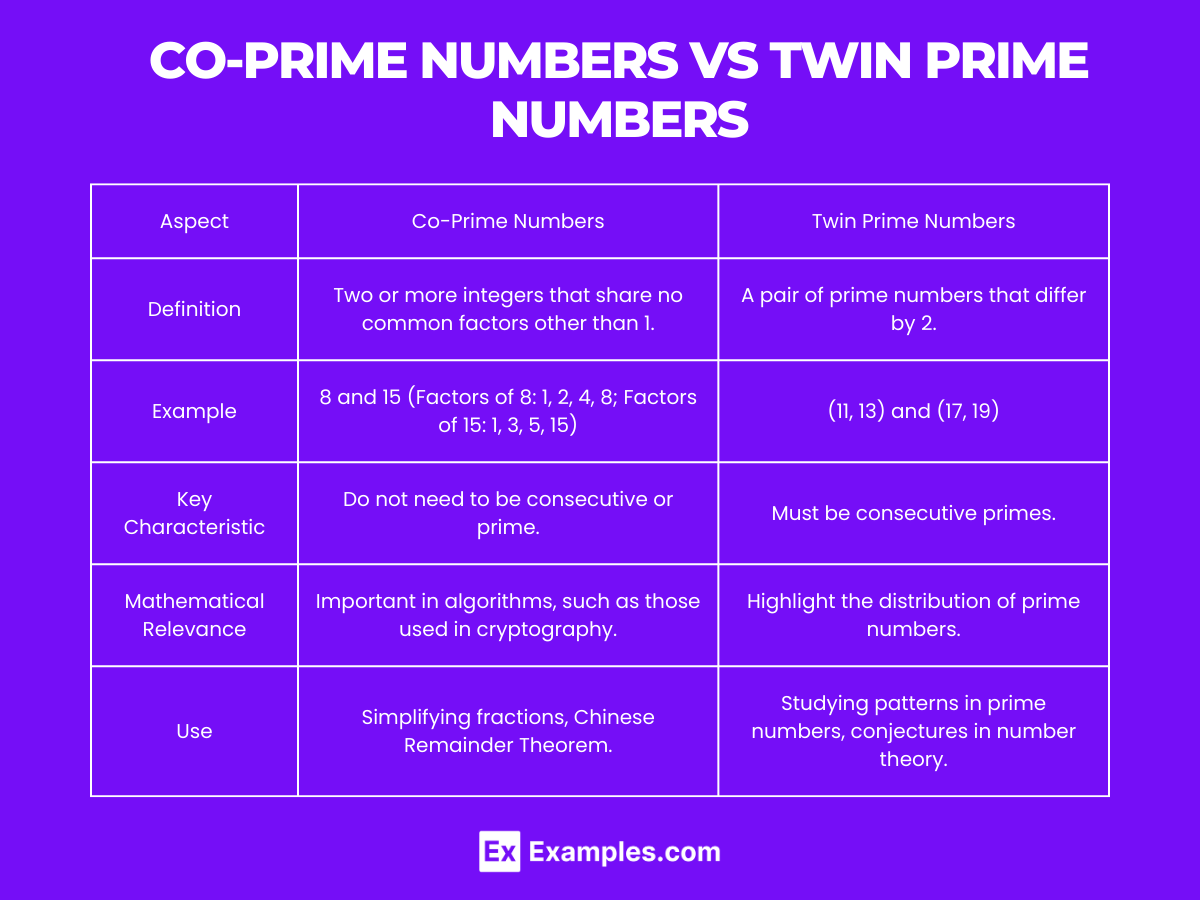
Co-prime numbers and twin prime numbers represent intriguing concepts in number theory, each with unique characteristics and applications. Below is a table comparing these two types of numbers:
| Aspect | Co-Prime Numbers | Twin Prime Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two or more integers that share no common factors other than 1. | A pair of prime numbers that differ by 2. |
| Example | 8 and 15 (Factors of 8: 1, 2, 4, 8; Factors of 15: 1, 3, 5, 15) | (11, 13) and (17, 19) |
| Key Characteristic | Do not need to be consecutive or prime. | Must be consecutive primes. |
| Mathematical Relevance | Important in algorithms, such as those used in cryptography. | Highlight the distribution of prime numbers. |
| Use | Simplifying fractions, Chinese Remainder Theorem. | Studying patterns in prime numbers, conjectures in number theory. |
Coprime numbers hold several fascinating properties that make them a subject of study in mathematics. Here are some key facts:
Coprime numbers are a fundamental concept in mathematics, providing deep insight into the structure and properties of integers. Their study not only enriches our understanding of number theory but also finds practical applications in areas ranging from cryptography to algorithm design, showcasing the vast applicability of mathematical principles in solving real-world problems.
Text prompt
Add Tone
How to Find Co-prime Numbers?
Co-prime Numbers List
Which of the following pairs is a coprime pair?
(14, 21)
(15, 28)
(16, 24)
(18, 27)
What is the GCD of the coprime pair (9, 28)?
2
3
1
4
Which of the following pairs is a coprime pair?
(2, 3)
(4, 8)
(10, 15)
(12, 18)
What is the smallest pair of coprime numbers?
(2, 3)
(1, 2)
(3, 4)
(4, 5)
Which of these pairs is a coprime pair?
(21, 22)
(24, 28)
(30, 35)
(32, 36)
What is the GCD of the coprime pair (11, 13)?
1
2
3
4
Which of these pairs is a coprime pair?
(17, 19)
(18, 20)
(21, 25)
(22, 28)
Which of these pairs is not a coprime pair?
(10, 21)
(11, 22)
(12, 23)
(13, 24)
Which of the following pairs is a coprime pair?
(8, 15)
(12, 18)
(21, 28)
(24, 32)
Which of the following pairs of numbers are co-prime?
14 and 21
18 and 35
24 and 36
27 and 45
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

