What is the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of 8 and 12?
2
4
6
8


To find the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of 8 and 12, use one of three methods: prime factorization, long division, or listing common factors. By prime factorization, 8 is 2³ and 12 is 2²× 3 , with the common factor being 2², which is 4. Using the long division method, dividing 12 by 8 gives a remainder of 4, and dividing 8 by 4 leaves a remainder of 0, making 4 the GCF. Listing factors, 8’s factors are 1, 2, 4, 8, and 12’s factors are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12; the greatest common factor is 4. Thus, the GCF of 8 and 12 is 4.
The GCF of 8 and 12 is 4, found by prime factorization (common factor 2²), long division (remainder zero at 4), or listing common factors (1, 2, 4).
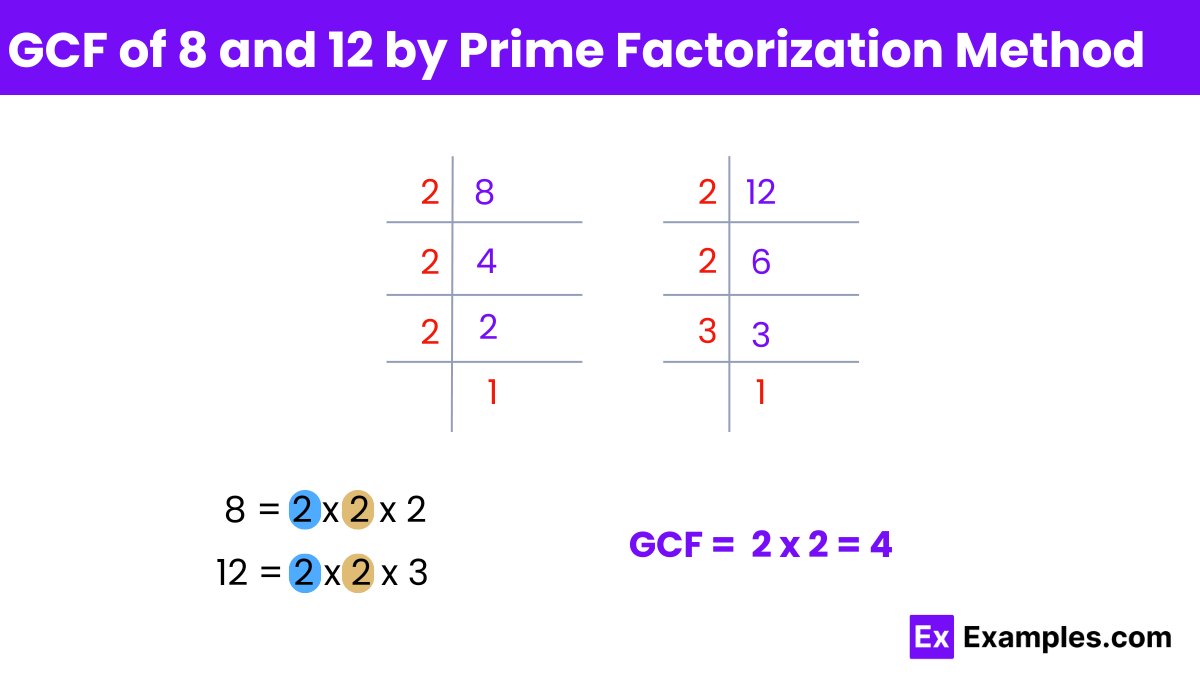
Prime factorize each number:
Identify the common prime factors:
Multiply the common prime factors with the smallest exponents:
GCF = 2² = 4
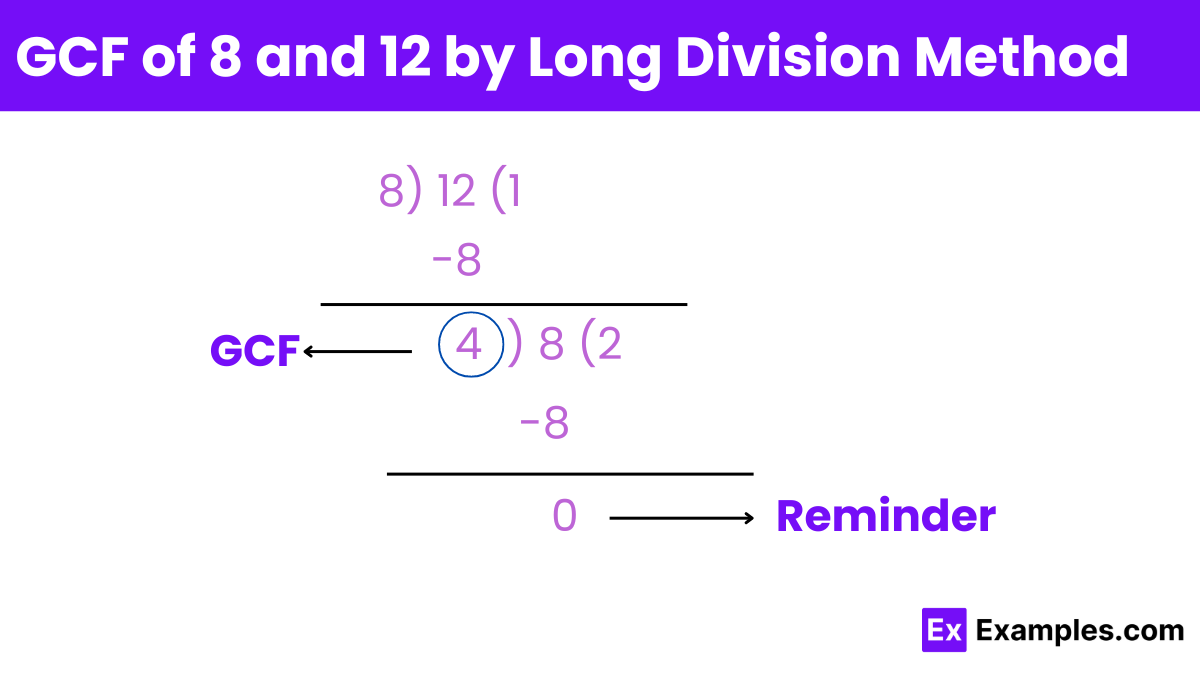
Divide the larger number by the smaller number:
12 ÷ 8 = 1 (quotient), remainder = 12 − (8×1) = 4
Replace the larger number with the smaller number and the smaller number with the remainder:
Divide the new larger number by the new smaller number:
8 ÷ 4 = 2 (quotient), remainder = 8 − (4×2) = 0
Repeat the process until the remainder is 0:
The divisor at this step is the GCF:
The divisors at the last step before the remainder became 0 is 4.
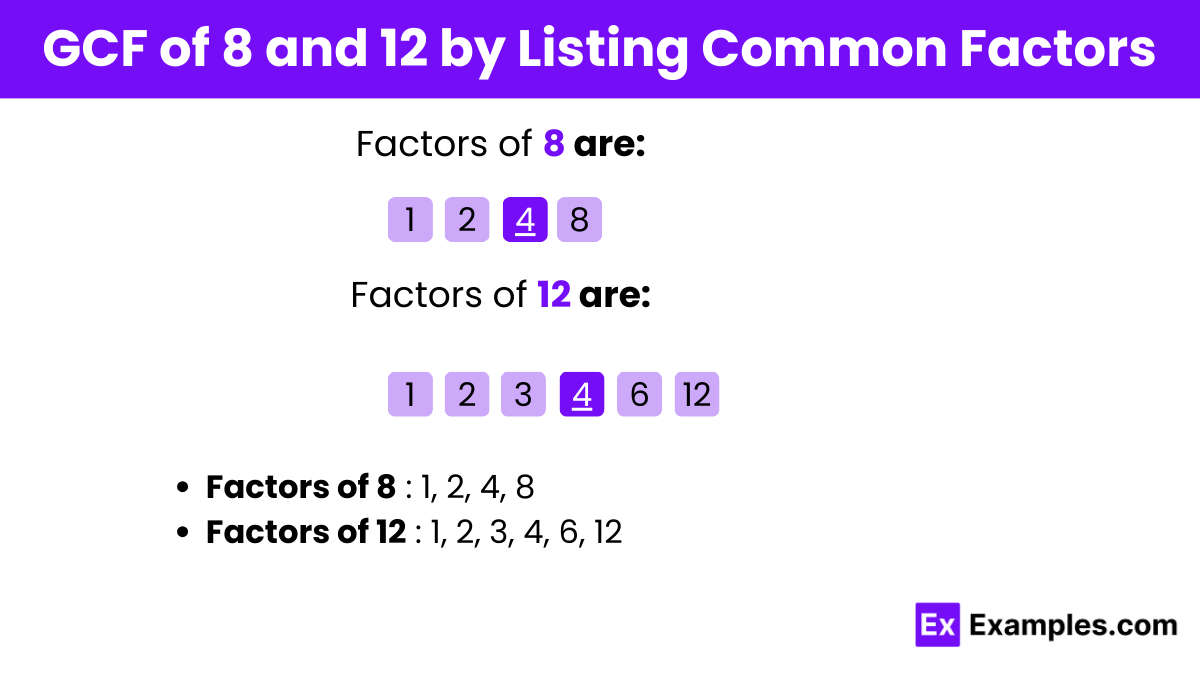
List the factors of each number:
Factors of 8: 1, 2, 4, 8
Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
Identify the common factors:
The common factors of 8 and 12 are: 1, 2, 4
Determine the greatest common factor:
Among the common factors, the largest one is 4.
The Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of 8 and 12 is 4.
No, the GCF cannot be larger than the smallest of the given numbers.
The product of the GCF and the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of two numbers equals the product of the numbers themselves.
Understanding GCF helps students simplify fractions, solve problems involving divisors, and enhance their number theory skills.
The GCF can be used for reducing fractions, dividing items into equal groups, and solving problems in finance, engineering, and computer science.
Yes, if one number is a multiple of the other, the GCF is the smaller number. For example, the GCF of 4 and 8 is 4.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of 8 and 12?
2
4
6
8
Which of the following is a common factor of both 8 and 12?
2
5
6
9
How many common factors do 8 and 12 have?
1
2
3
4
What is the smallest common factor of 8 and 12?
1
2
3
4
Which of the following numbers is not a common factor of both 8 and 12?
1
2
3
4
The GCF of 8 and 12 is a factor of which of the following numbers?
4
8
12
All of the above
If you multiply the GCF of 8 and 12 by 2, what do you get?
6
8
10
12
Which of the following pairs of numbers has the same GCF as 8 and 12?
4 and 6
10 and 12
16 and 20
8 and 16
What is the GCF of 8, 12, and 16?
2
4
6
8
The sum of the GCF of 8 and 12 and the smallest prime number is:
5
6
7
8
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

