What is the Curie-Weiss Law formula?
χ = C/(T + θ)
χ = C/(T - θ)
χ = Cθ/T
χ = CT/θ


The Curie-Weiss Law is a fundamental principle in the field of physics that extends the Curie Law for magnetic susceptibility to paramagnetic materials at temperature above the Curie point. This law plays a crucial role in the study of magnetic phenomena and the laws of physics governing them.
The formula for the Curie-Weiss Law is expressed as:
where:
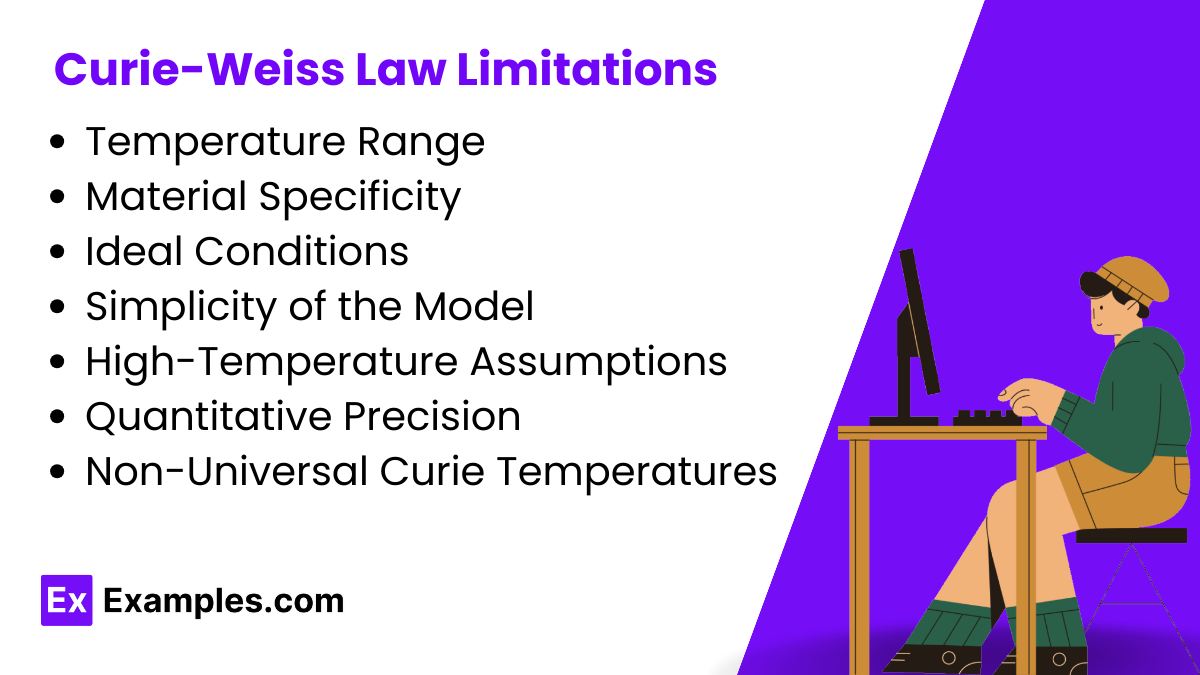
The Curie-Weiss Law, essential for studying magnetic behaviors, has several limitations:
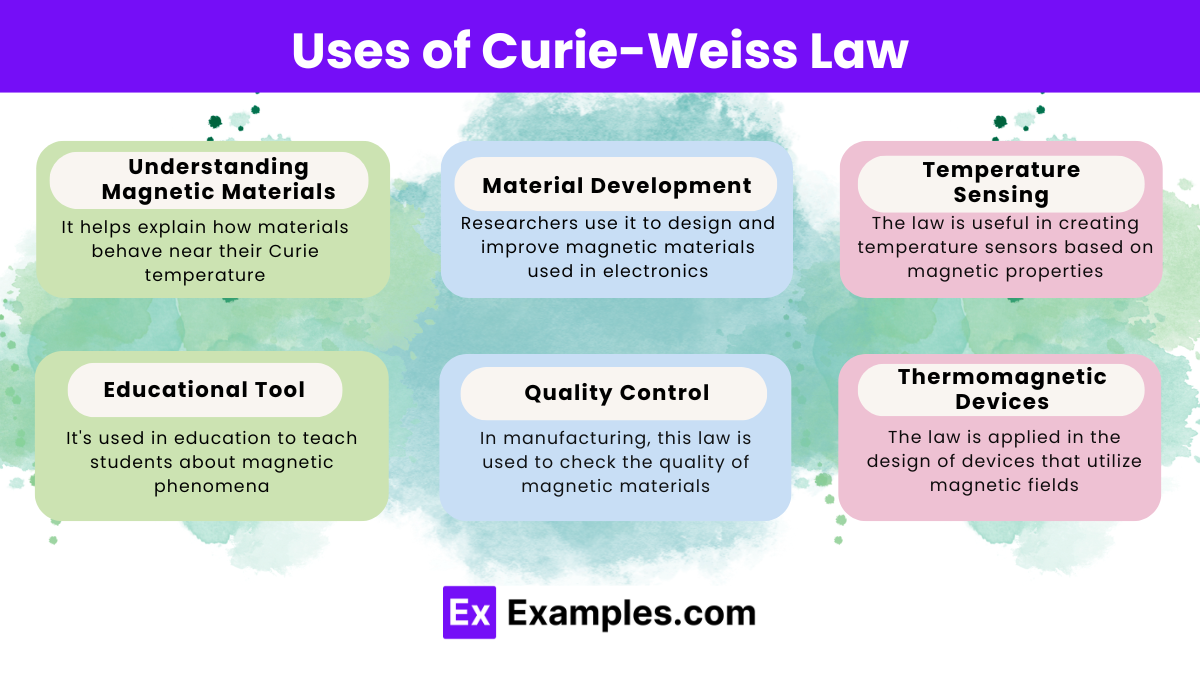
The Curie-Weiss Law is important in physics and materials science, especially for studying magnetic materials. Here are some simple and practical uses of this law:
The law is named after Pierre Curie and Pierre-Ernest Weiss, who developed the theory based on Curie’s earlier work.
Magnetic susceptibility measures how much a material becomes magnetized when placed in an external magnetic field.
The Curie temperature is the critical point where a material transitions from ferromagnetic to paramagnetic.
The law shows that susceptibility inversely relates to the difference between the absolute temperature and the Curie temperature.
The Curie constant provides insights into the magnetic properties of the material, like magnetic moment and atom density.
No, it mainly applies to temperatures above the Curie point for paramagnetic materials.
While focused on magnetic properties, the concepts can indirectly help understand other types of phase transitions.
Values vary widely depending on the material’s magnetic ions and their interactions.
It describes behavior approaching ferromagnetism, which occurs below the Curie temperature.
Variations account for different material properties and temperature ranges, refining its predictions.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the Curie-Weiss Law formula?
χ = C/(T + θ)
χ = C/(T - θ)
χ = Cθ/T
χ = CT/θ
In the Curie-Weiss Law, what does 'χ' represent?
Curie constant
Magnetic susceptibility
Temperature
Weiss constant
What is the significance of the Curie constant (C) in the Curie-Weiss Law?
It indicates the strength of the magnetic field
It is a material-specific constant related to magnetic properties
It represents the temperature at which a material becomes paramagnetic
It is the inverse of magnetic susceptibility
What does the Weiss constant (θ) indicate in the Curie-Weiss Law?
The temperature at which magnetic susceptibility is zero
The strength of the magnetic field
The critical temperature for ferromagnetic materials
The inverse of the Curie constant
According to the Curie-Weiss Law, what happens to magnetic susceptibility (χ) as temperature (T) approaches the Weiss constant (θ)?
χ becomes infinite
χ becomes zero
χ becomes negative
χ remains constant
If the temperature (T) is much higher than the Weiss constant (θ), how does the Curie-Weiss Law simplify?
χ = C/T
χ = Cθ/T
χ = CT/θ
χ = C/(T + θ)
What type of materials does the Curie-Weiss Law primarily describe?
Diamagnetic materials
Paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials
Antiferromagnetic materials
Non-magnetic materials
Which of the following is true for ferromagnetic materials below the Curie temperature according to the Curie-Weiss Law?
They exhibit zero magnetic susceptibility
They exhibit paramagnetic behavior
They exhibit spontaneous magnetization
They exhibit diamagnetic behavior
In the context of the Curie-Weiss Law, what happens to a ferromagnetic material when it is heated above its Curie temperature?
It becomes diamagnetic
It becomes paramagnetic
It becomes non-magnetic
It retains its ferromagnetic properties
How does the magnetic susceptibility (χ) change with temperature (T) for a paramagnetic material according to the Curie-Weiss Law?
χ increases linearly with T
χ decreases linearly with T
χ increases exponentially with T
χ decreases exponentially with T
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

