Which of the following is a primary characteristic of algae?
They are always unicellular.
They can perform photosynthesis.
They lack a cell wall.
They are decomposers.


Algae and fungi, though often mistaken for one another, represent two distinct and fascinating groups of organisms with unique characteristics and vital roles in ecosystems. Algae, primarily aquatic, perform photosynthesis and contribute significantly to global oxygen production. In contrast, fungi, found in various environments, play crucial roles in decomposition and nutrient cycling. This article explores the fundamental differences between algae and fungi, delving into their classifications, structures, and ecological functions, to provide a clear understanding of their distinct yet interconnected roles in the natural world.
Algae are a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms found in various aquatic environments, including oceans, freshwater bodies, and even moist terrestrial locations. They range from microscopic phytoplankton to large seaweeds like kelp.
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms, including yeasts, molds, and mushrooms, that absorb nutrients from organic matter. They play key roles as decomposers in ecosystems, recycling nutrients, and form symbiotic relationships with plants. Fungi reproduce through spores and are vital in various industrial processes like fermentation and antibiotic production.
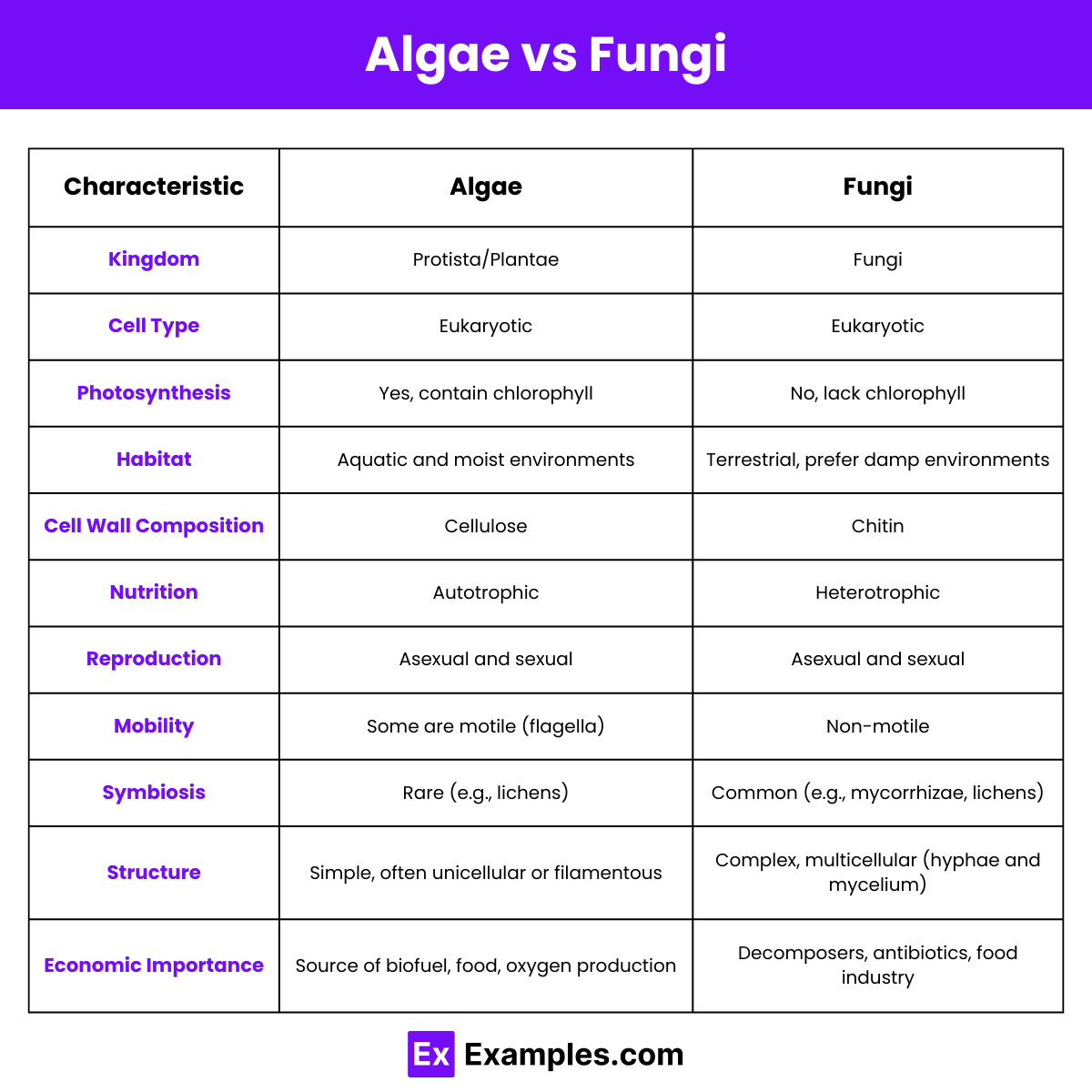
| Feature | Algae | Fungi |
|---|---|---|
| Kingdom | Protista (primarily) | Fungi |
| Cell Type | Eukaryotic | Eukaryotic |
| Nutrition | Photosynthetic (autotrophic) | Absorptive (heterotrophic) |
| Chlorophyll | Present in most algae | Absent |
| Habitat | Aquatic (freshwater and marine) | Terrestrial and some aquatic environments |
| Cell Wall Composition | Cellulose and sometimes silica | Chitin |
| Reproduction | Sexual and asexual (spores, fragmentation) | Sexual and asexual (spores) |
| Role in Ecosystem | Primary producers, oxygen production | Decomposers, nutrient cycling |
| Symbiosis | Forms symbiotic relationships like lichens (with fungi) | Forms symbiotic relationships like mycorrhizae (with plants) |
| Examples | Green algae, red algae, brown algae | Yeasts, molds, mushrooms |
| Motility | Some have flagella for movement | Generally non-motile |
| Structure | Simple structures, often single-celled or simple colonies | Complex structures, multicellular (hyphae and mycelium) |
| Economic Importance | Used in food industry, biofuels, and as bioindicators | Used in food industry (e.g., mushrooms, yeast), medicine (antibiotics), and biotechnology |
| Pigments | Contain various pigments like chlorophyll, carotenoids, and phycobilins | Lack pigments for photosynthesis |
| Energy Storage | Store energy as starch | Store energy as glycogen |
| Environmental Tolerance | Some can tolerate extreme environments (e.g., thermophilic algae) | Many can tolerate extreme environments (e.g., extremophilic fungi) |
| Pathogenicity | Generally non-pathogenic to humans | Some species are pathogenic to plants, animals, and humans |
| Thallus Structure | Thallus can be filamentous, sheet-like, or unicellular | Thallus is composed of hyphae forming mycelium |
Algae are photosynthetic organisms found in aquatic environments, producing oxygen and serving as primary producers in ecosystems.
Fungi are decomposers that absorb nutrients from organic matter, playing crucial roles in nutrient cycling and ecosystem stability.
Algae obtain energy through photosynthesis, using sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Fungi absorb nutrients from organic matter through their hyphae, breaking down complex substances into simpler compounds.
No, algae primarily belong to the Protista kingdom, while fungi belong to the Fungi kingdom.
The main difference is that algae are autotrophic and perform photosynthesis, while fungi are heterotrophic and absorb nutrients from organic matter.
Yes, they can form symbiotic relationships; for example, lichens are a partnership between algae and fungi.
Examples of algae include green algae, red algae, and brown algae.
Examples of fungi include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms.
Fungi are important as decomposers, breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the environment.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following is a primary characteristic of algae?
They are always unicellular.
They can perform photosynthesis.
They lack a cell wall.
They are decomposers.
Fungi obtain their nutrients by:
Photosynthesis
Ingesting food particles
Absorbing nutrients from organic matter
Producing their own food through chemosynthesis
Which of the following best describes the cell wall composition in fungi?
Cellulose
Chitin
Lignin
Glycogen
Which group includes both multicellular and unicellular organisms?
Algae
Fungi
Both
Neither
Algae primarily live in:
Terrestrial environments
Aquatic environments
Underground environments
Host organisms
Which of the following is a reproductive structure found in fungi?
Spores
Seeds
Cones
Tubers
A common use of fungi in human industries is:
Producing antibiotics
Producing plastics
Generating biofuels
Extracting metals
Which of the following organisms is a type of algae?
Mushroom
Yeast
Kelp
Mold
Fungi that form symbiotic relationships with plant roots are known as:
Mycorrhizae
Lichens
Rhizomes
Hyphae
Lichens are a symbiotic association between:
Fungi and bacteria
Algae and bacteria
Algae and fungi
Fungi and mosses
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

