Which of the following describes the brain?
A physical organ that controls bodily functions
An abstract concept representing thoughts
A state of consciousness
A philosophical entity

The brain and the mind are two concepts often used interchangeably, yet they represent distinct aspects of human existence. The brain, a physical organ located within the skull, comprises billions of neurons and glial cells that work together to regulate bodily functions and enable cognitive abilities. In contrast, the mind refers to the abstract set of cognitive processes that include thoughts, consciousness, emotions, and perceptions. Understanding the difference between the brain and the mind is crucial for comprehending how humans think, feel, and behave. This article explores the unique characteristics of both the brain and the mind, highlighting their interconnections and individual roles in shaping our experiences and identity.
The brain is a complex, physical organ located within the skull. It serves as the control center for the entire body. The brain comprises billions of neurons and glial cells, which communicate through electrical and chemical signals. Here are key aspects of the brain:
Reaction to a Hot Surface: When you touch a hot surface, sensory neurons in your skin send a signal to your brain. The brain processes this information and immediately triggers a reflex to pull your hand away, preventing injury.
The mind refers to the intangible aspects of our consciousness and cognitive processes. It encompasses our thoughts, emotions, perceptions, memories, and imagination. Unlike the brain, which is a physical structure, the mind is abstract and involves the following key aspects:
Daydreaming: While sitting in a meeting, you might start daydreaming about your upcoming vacation. This involves your mind creating vivid images and scenarios, drawing from your thoughts, memories, and imagination, even though you are physically present in the meeting.
The mind’s role extends beyond mere cognitive functions, deeply influencing how we interact with ourselves and others. It shapes our personality, drives our motivations, and underpins our understanding of the world. By studying the mind, we gain insights into human behavior, mental health, and the essence of consciousness.
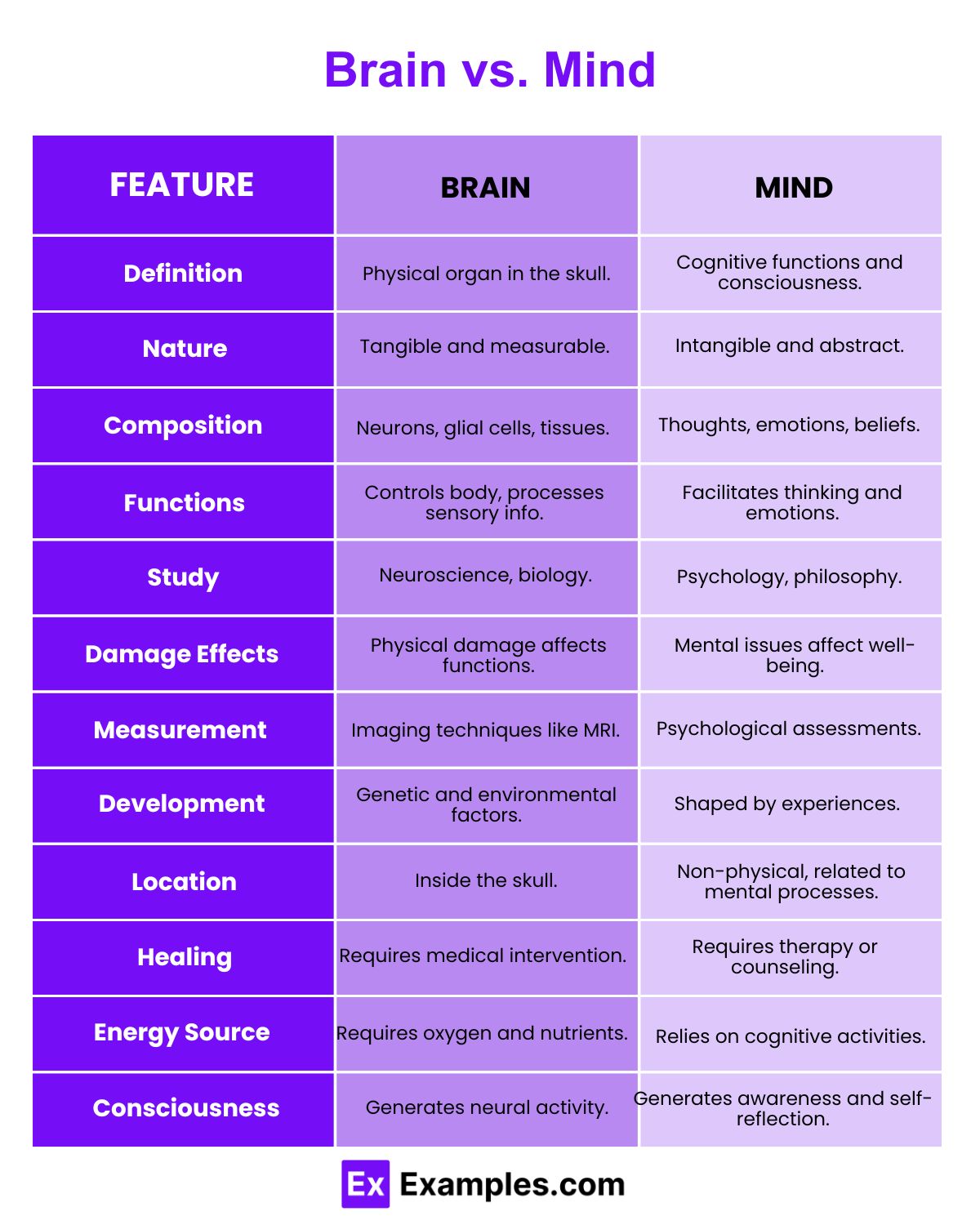
| Aspect | Brain | Mind |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Physical organ | Abstract concept |
| Location | Inside the skull | Non-physical, linked to consciousness |
| Components | Neurons, glial cells, brain regions | Thoughts, emotions, perceptions, memories |
| Functions | Regulates bodily functions, processes sensory input | Enables thinking, feeling, imagining, decision-making |
| Structure | Cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem | No physical structure, composed of mental processes |
| Role in Cognition | Provides the biological basis for cognition | Represents cognitive processes and consciousness |
| Regulation | Controls motor functions, homeostasis | Influences behavior, emotions, and self-awareness |
| Communication | Uses electrical and chemical signals | Uses mental processes and subjective experiences |
| Neuroplasticity | Physical reorganization of neural connections | Changes in thought patterns, beliefs, and attitudes |
| Studies In | Neuroscience, neurobiology | Psychology, philosophy, cognitive science |
Despite their differences, the brain and mind share several important similarities. These connections highlight their interdependent roles in shaping human experience.
These similarities illustrate the intricate relationship between the brain and mind, showing how they work together to create a cohesive human experience.
The brain is a physical organ in the skull, responsible for controlling bodily functions, processing sensory information, and enabling cognitive abilities.
The mind is the abstract set of cognitive processes, including thoughts, emotions, perceptions, and consciousness.
The brain provides the biological basis for the mind, enabling cognitive processes and mental functions through neural activity.
No, the mind relies on the brain’s neural structures to function, making them interdependent.
Yes, brain injuries can impact cognitive functions, emotions, and behavior, affecting the mind’s processes.
The brain stores and retrieves memories through neural connections, facilitating recall and learning.
The mind evaluates thoughts and emotions, guiding decision-making and actions based on cognitive and emotional processes.
Yes, neuroplasticity allows the brain to reorganize and form new connections throughout life, adapting to experiences.
Thoughts are mental processes, while brain activity involves the physical neural actions that enable these processes.
Understanding both helps in comprehending human behavior, improving mental health, and enhancing cognitive abilities.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following describes the brain?
A physical organ that controls bodily functions
An abstract concept representing thoughts
A state of consciousness
A philosophical entity
The mind is best defined as:
A biological organ
The seat of emotions, thoughts, and consciousness
A part of the central nervous system
A mechanical system in the body
Which of the following functions is primarily controlled by the brain?
Solving a philosophical question
Regulating heart rate and breathing
Understanding abstract concepts
Experiencing subjective emotions
What is the relationship between the brain and the mind?
The brain creates the mind
The mind creates the brain
The brain and the mind are the same
The brain and the mind are entirely unrelated
Which process is associated with the mind rather than the brain?
Electrical signaling between neurons
Cognitive decision-making
Digesting food
Reflex responses to stimuli
How can the mind influence the brain?
By changing the brain's physical structure
By creating neurons
By stimulating involuntary reflexes
By generating random thoughts
What aspect of human experience is primarily linked to the mind?
Perception of pain
Digestion of food
Muscle contraction
Sweating
Which of the following best distinguishes the mind from the brain?
The mind can be measured scientifically
The mind is an abstract entity
The brain controls voluntary actions only
The mind controls only involuntary functions
What is neuroplasticity?
The brain’s ability to heal itself
The brain's capacity to change and reorganize itself
The mind’s ability to generate thoughts
The brain's inability to function properly
Which of the following is considered a function of the mind?
Releasing hormones
Processing thoughts and emotions
Coordinating reflexes
Generating blood flow
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

