What is biomimicry?
The process of creating synthetic materials
The use of biological systems to solve human problems
The study of genetic modifications
The study of ecosystems for environmental preservation

Biomimicry is the practice of emulating nature’s designs and processes to solve human problems. It involves studying biological structures, functions, and systems, and applying these insights to develop innovative solutions in technology, engineering, medicine, and sustainable practices. Examples include designing more efficient wind turbines inspired by whale fins or creating adhesive materials modeled after gecko feet. By mimicking nature, biomimicry aims to create products and systems that are efficient, sustainable, and harmonious with the environment.
Biomimicry is the practice of emulating nature’s designs and processes to develop sustainable and efficient solutions for human challenges. It involves studying biological systems and applying these insights to innovate in technology, engineering, and medicine, promoting harmony with the environment.
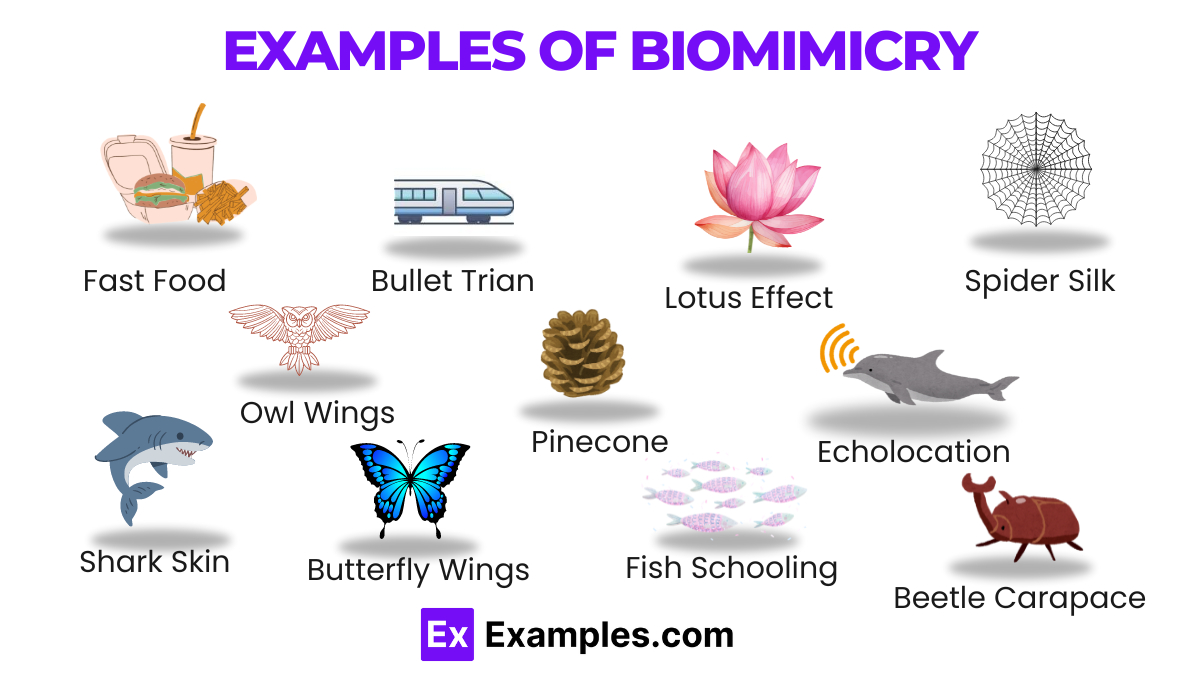
Nature offers countless models of efficient and sustainable design. By observing the structures, processes, and ecosystems in the natural world, we can develop technologies and methods that mimic these effective designs. For instance:
Nature provides a benchmark for sustainable solutions. By understanding and applying nature’s principles, we can create designs that are both effective and environmentally friendly. This principle involves evaluating human innovations against the standards of the natural world to ensure they contribute positively to the ecosystem.
Nature teaches us valuable lessons in resilience, adaptation, and interconnectedness. Biomimicry encourages us to shift our perspective from exploiting nature to learning from it. This principle promotes a respectful and symbiotic relationship with the natural world, fostering innovation that supports both human and ecological health.
Natural processes are inherently sustainable, operating on the principles of energy efficiency and resource conservation. Biomimicry aims to replicate these principles to create solutions that minimize waste and reduce environmental impact. Examples include:
Nature continuously adapts and evolves to meet environmental challenges. Biomimicry leverages this adaptive ability to develop technologies that can respond to changing conditions. This principle is evident in the development of materials and structures that can self-repair, self-clean, or adapt to varying environments.
In nature, every organism and system is interconnected, contributing to the overall health and balance of the ecosystem. Biomimicry emphasizes the importance of designing systems and technologies that work harmoniously within larger networks. This approach encourages collaboration and the sharing of resources to create holistic and sustainable solutions.
Biomimicry Architecture involves designing buildings inspired by nature’s forms, processes, and ecosystems. Architects use natural principles to create sustainable, efficient, and innovative structures. Examples include self-cooling buildings modeled after termite mounds and water-efficient designs inspired by desert plants. This approach promotes harmony between human habitats and the natural environment.
It promotes sustainable and efficient solutions by learning from nature’s time-tested patterns.
Examples include Velcro inspired by burrs, and wind turbines designed after whale fins.
Biomimicry in architecture involves designing buildings with natural cooling, heating, and lighting systems.
Industries such as medicine, agriculture, engineering, and product design benefit from biomimicry.
Biomimicry improves sustainability by reducing waste and enhancing resource efficiency through natural models.
An example is adhesives inspired by the feet of geckos.
It leads to innovative designs like energy-efficient wind turbines mimicking whale fins.
Biomimicry promotes sustainable farming practices like natural pest control.
Vehicles are designed with aerodynamics inspired by the shapes of fish and birds.
Designing cities using principles from natural ecosystems for better sustainability and livability.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is biomimicry?
The process of creating synthetic materials
The use of biological systems to solve human problems
The study of genetic modifications
The study of ecosystems for environmental preservation
Which of the following is an example of biomimicry?
The design of an airplane wing based on bird wings
Cloning organisms for medical research
Genetically modifying crops for better yield
Creating synthetic fibers for clothing
Which organism inspired the development of Velcro through biomimicry?
Geckos
Burdock plants
Spiders
Bees
How does the study of shark skin influence biomimicry in modern technology?
It inspired anti-bacterial surfaces
It led to the creation of waterproof clothing
It led to the development of efficient wind turbines
It inspired adhesive technologies
What is a key principle of biomimicry?
Utilizing chemical engineering for material production
Learning from and emulating nature's strategies to solve human challenges
Relying on artificial intelligence to create sustainable solutions
Cloning organisms to replicate natural processes
Which organism has inspired the design of more efficient solar cells through biomimicry?
Butterflies
Dolphins
Ants
Birds
Which of the following technologies was inspired by the way geckos stick to surfaces?
Anti-fog lenses
Reusable adhesive tapes
Self-cleaning windows
Waterproof fabrics
How has the structure of termite mounds inspired modern architectural design?
For improved wind resistance
For energy-efficient ventilation systems
For earthquake-resistant foundations
For soundproof building materials
Which animal has inspired the development of new underwater adhesive technologies in biomimicry?
Starfish
Octopus
Barnacles
Jellyfish
Which plant structure has influenced the design of self-cleaning surfaces?
Rose petals
Lotus leaves
Pine needles
Oak tree bark
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

