What is the primary purpose of genetic engineering?
To create new species
To modify organisms for desired traits
To study evolutionary biology
To preserve biodiversity

Genetic engineering, a vital field in biotechnology, involves modifying an organism’s DNA to achieve desired traits. This technology enables scientists to insert, delete, or alter genetic material, revolutionizing medicine, agriculture, and industry. Applications include creating genetically modified organisms (GMOs), developing gene therapy for diseases, and producing bioengineered pharmaceuticals. Genetic engineering holds immense potential for innovation, improving crop yields, and advancing medical treatments, making it a cornerstone of modern biotechnology.
Genetic engineering is the deliberate modification of an organism’s genetic material using biotechnology. It involves manipulating DNA to alter genes, enabling the creation of organisms with desired traits, such as disease resistance in crops or the production of insulin by bacteria.
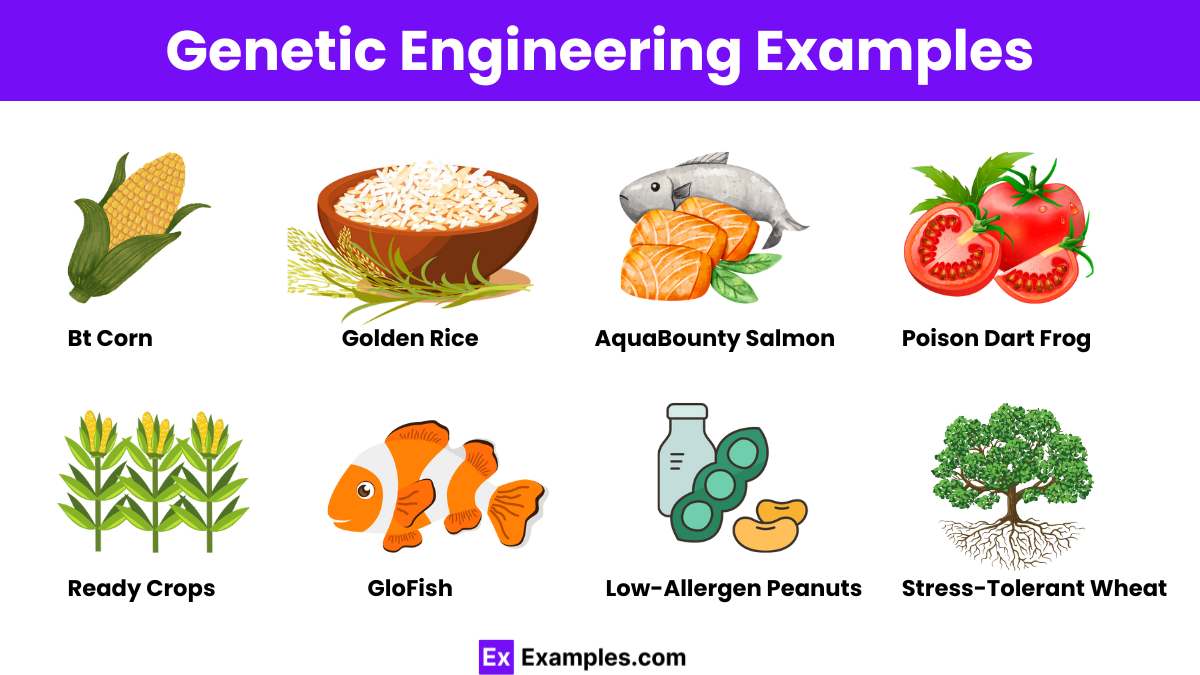
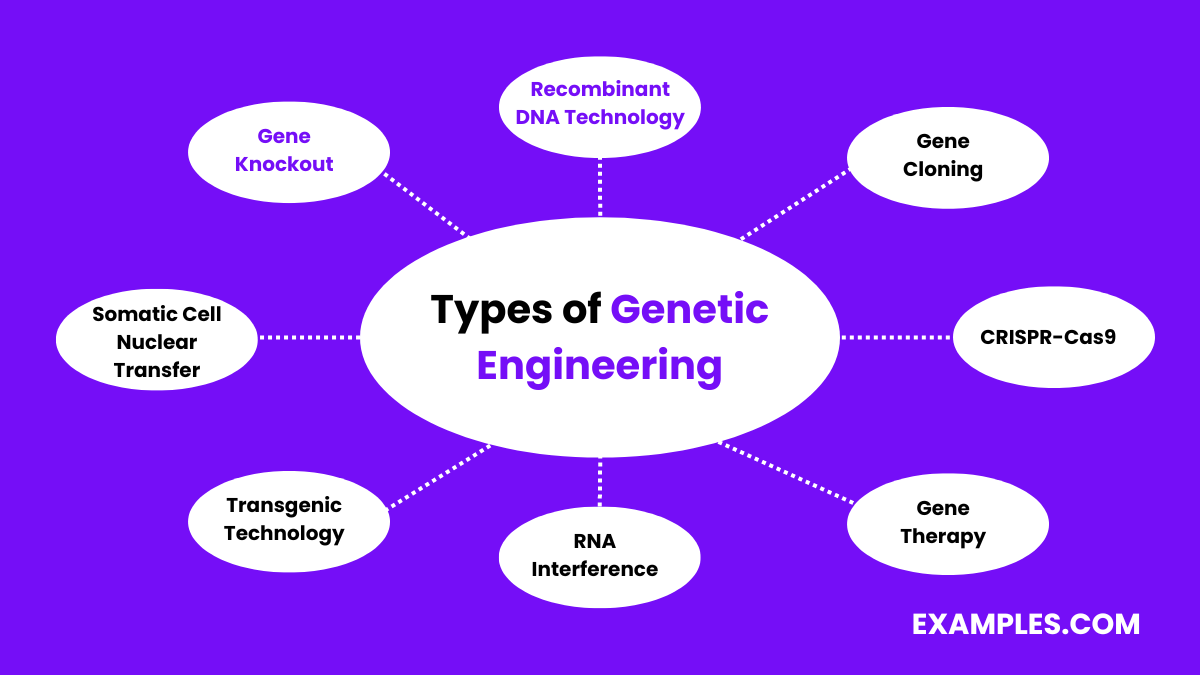
Recombinant DNA technology involves combining DNA from two different sources to create a new genetic combination. This technique utilizes competent cells to uptake and express foreign DNA and is widely used in biotechnology for producing insulin, growth hormones, and other therapeutic proteins..
Gene cloning is the process of making multiple copies of a specific gene. This technique allows researchers to study the function of genes and produce large quantities of a gene product.
CRISPR-Cas9 is a revolutionary gene-editing tool that allows for precise modifications to DNA. It is used for correcting genetic defects, studying gene function, and developing genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Gene therapy involves inserting, altering, or removing genes within an individual’s cells to treat or prevent disease. This approach holds promise for treating genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis and hemophilia.
RNA interference is a technique that silences specific genes by degrading their mRNA. It is used in research to study gene function and has potential therapeutic applications for conditions such as cancer and viral infections.
Transgenic technology involves introducing foreign genes into an organism to give it new traits. This method is commonly used in agriculture to create crops with improved resistance to pests, diseases, and environmental conditions.
SCNT is a cloning method where the nucleus of a somatic cell is transferred into an egg cell whose nucleus has been removed. This technique is used in cloning animals and for therapeutic cloning to produce stem cells.
Gene knockout involves inactivating a specific gene to study its function by observing the effects of its absence. This technique is essential for understanding gene roles in development, physiology, and disease.
Genetic engineering continues to evolve, offering new possibilities and ethical considerations. Its diverse techniques are transforming medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Disease Treatment | Ethical Concerns |
| Agricultural Benefits | Environmental Risks |
| Environmental Protection | Technical Limitations |
| Pharmaceutical Production | High Costs |
| Scientific Advancements | Public Perception |
| Food Security | Regulatory Hurdles |
It involves the addition, removal, or alteration of genetic material within an organism’s genome.
Benefits include improved crop yields, disease resistance, and medical advancements like gene therapy.
Risks include ethical concerns, potential environmental impact, and unintended genetic consequences.
It can be safe when conducted under strict regulations and scientific guidelines.
CRISPR is a precise genetic editing tool that allows for targeted modifications in DNA.
GMOs, or genetically modified organisms, are organisms whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques.
It holds potential for curing genetic diseases through gene therapy and other interventions.
Gene therapy is a technique that uses genetic engineering to treat or prevent diseases by correcting defective genes.
Genetically engineered foods are generally considered safe to eat when properly regulated.
A transgenic organism contains genes from another species inserted into its genome.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary purpose of genetic engineering?
To create new species
To modify organisms for desired traits
To study evolutionary biology
To preserve biodiversity
Which technique is commonly used to insert new genes into an organism's DNA?
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
Cloning
CRISPR-Cas9
Gel electrophoresis
What is a transgenic organism?
An organism that has undergone natural selection
An organism with DNA from another species
An organism that has not been genetically modified
An organism that can reproduce asexually
What is one potential benefit of genetic engineering in agriculture?
Reduced nutritional value of crops
Increased vulnerability to pests
Enhanced resistance to environmental stress
Longer growth periods
Which of the following is a concern associated with genetic engineering?
Increased food production
Unintended effects on non-target species
Decreased shelf life of produce
Improved nutritional content
What role do plasmids play in genetic engineering?
They are used for DNA sequencing
They serve as vectors to transfer genes
They are involved in protein synthesis
They help in cell division
What is gene therapy?
A method to enhance physical appearance
The use of genetic engineering to treat or prevent disease
The cloning of organisms for agricultural purposes
A technique for genetic modification of crops
Which organism was the first to be genetically modified for agricultural use?
Corn
Soybean
Tomato
Flavr Savr tomato
What is a common method for identifying successful genetic modifications in plants?
Visual inspection
Antibiotic resistance markers
Color change
Increased size
What ethical concern is often raised regarding genetic engineering?
Decreased agricultural yield
Accessibility of genetically modified foods
Potential for designer babies
Environmental sustainability
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

