Which characteristic is unique to Porifera?
Bilateral symmetry
Presence of a notochord
Pores throughout their body
True tissues

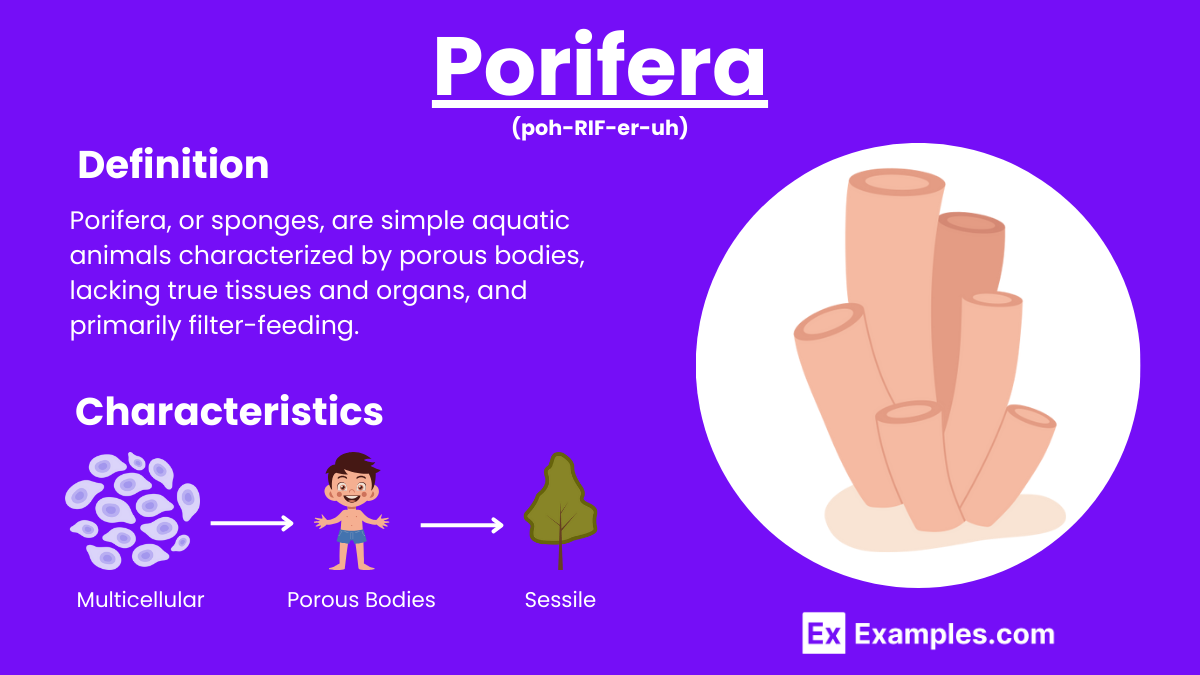
Porifera, commonly known as sponges, are simple, multicellular organisms found primarily in marine environments. Characterized by their porous bodies and lack of true tissues and organs, sponges filter water to obtain food and oxygen. They play a crucial role in aquatic ecosystem by maintaining water quality and providing habitat for other species. With their unique cellular structure and ability to regenerate, Porifera offer valuable insights into early animal evolution and developmental biology.
Porifera, or sponges, are simple, multicellular organisms lacking true tissues and organs. Found mainly in marine environments, they filter water through their porous bodies for nutrition and respiration, playing a vital role in aquatic ecosystems and offering insights into early animal evolution.

| Characteristic | Sponges (Porifera) | Cnidaria |
|---|---|---|
| Body Structure | Simple, porous bodies | Radially symmetrical bodies |
| Tissue Organization | Lack true tissues and organs | Have true tissues (epidermis, gastrodermis) |
| Feeding Mechanism | Filter feeders using choanocytes | Predators using tentacles with cnidocytes |
| Reproduction | Asexual (budding, fragmentation, gemmules) and sexual | Asexual (budding) and sexual |
| Movement | Sessile (immobile) | Sessile (polyps) and free-swimming (medusae) |
| Examples | Sponges like Demospongiae and Calcarea | Jellyfish, sea anemones, corals |
They filter food particles from water through specialized cells.
They are found in marine and freshwater environments worldwide.
Their bodies are multicellular but lack true tissues or organs.
They reproduce sexually and asexually through budding or fragmentation.
They filter water and recycle nutrients in aquatic ecosystems.
Yes, they are sensitive to pollution and habitat degradation.
No, they lack nervous systems and true muscles.
Some species can produce toxins as a defense mechanism.
Most are sessile as adults but some larval stages can move.
They regulate water flow for gas exchange and waste removal.
Yes, they are used in biotechnology and biomedical research.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which characteristic is unique to Porifera?
Bilateral symmetry
Presence of a notochord
Pores throughout their body
True tissues
What is the main function of the choanocytes in Porifera?
Protect the sponge
Help in digestion
Filter food particles from water
Provide structural support
How do Porifera reproduce asexually?
Budding
Fission
Fragmentation
All of the above
Which type of skeleton is commonly found in Porifera?
Hydrostatic skeleton
Endoskeleton
Exoskeleton
Siliceous or calcareous spicules
Which of the following best describes the body symmetry of most Porifera?
Radial symmetry
Asymmetrical
Bilateral symmetry
Spherical symmetry
What type of feeding mechanism do Porifera use?
Filter feeding
Carnivorous
Herbivorous
Parasitic
Which of the following is a common habitat for Porifera?
Freshwater only
Terrestrial environments
Marine environments
Both freshwater and marine environments
What type of cells are responsible for the structural support in Porifera?
Epithelial cells
Collencytes
Pinacocytes
Spicules
Which of the following processes allows sponges to obtain oxygen?
Diffusion
Active transpor
Photosynthesis
Respiration
What is the term for the jelly-like substance found in the body of sponges?
Mesoglea
Mesenchyme
Coelom
Cytoplasm
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

