Which of the following animals is warm-blooded?
Frog
Lizard
Bird
Snake

Cold-blooded animals, like reptiles and fish, adjust their body temperature according to the environment, making them sensitive to extreme temperatures. They rely on external heat sources and their metabolism varies with environmental conditions. Warm-blooded animals, such as birds and mammals, maintain a constant internal temperature regardless of the outside climate, allowing them to survive across diverse environments. They derive energy from food, which keeps their metabolic rate steady.
Cold-blooded animals, also known as ectotherms, regulate their body temperature through external sources such as sunlight or a heated rock surface. They do not generate their own heat internally in significant amounts, which means their body temperature varies with the ambient environment. This characteristic is typical of reptiles, amphibians, and fish.
Warm-blooded animals, known as endotherms, maintain a constant body temperature irrespective of the environment. They generate heat through internal processes, primarily metabolism, which keeps their body at a steady temperature. This group includes mammals and birds, which have adapted various mechanisms to preserve body heat.
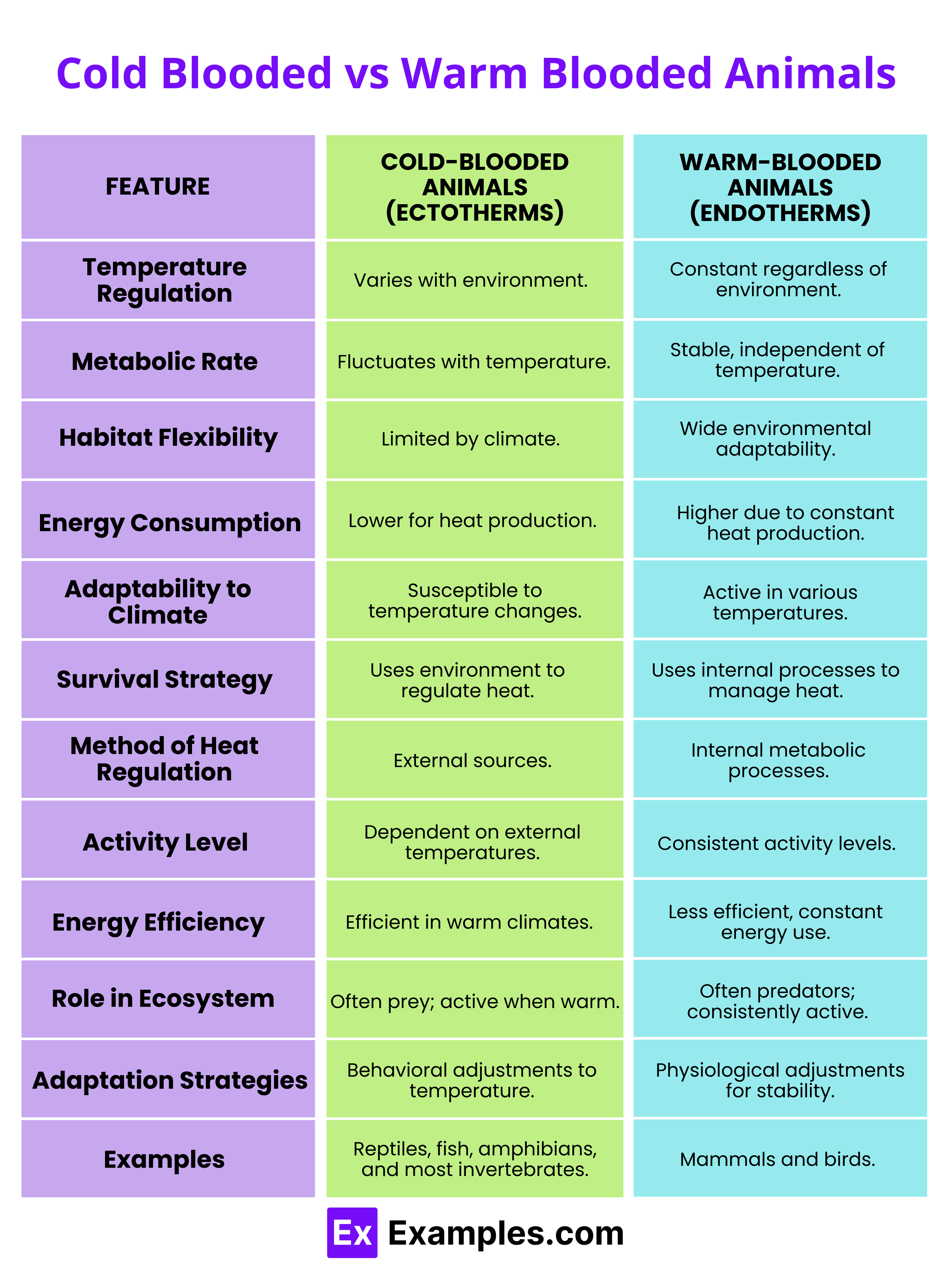
| Aspect | Cold-Blooded Animals (Ectotherms) | Warm-Blooded Animals (Endotherms) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Regulation | Body temperature varies with environmental conditions. | Maintain a constant body temperature regardless of environment. |
| Metabolic Rate | Lower metabolic rate; fluctuates with temperature. | Higher, stable metabolic rate independent of external temperatures. |
| Habitat Flexibility | Often restricted by climatic conditions. | Can inhabit a wider range of environments. |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy consumption for heat production. | Higher energy consumption due to constant heat production. |
| Adaptability to Climate | More susceptible to temperature changes, limiting active periods. | Can remain active across a wide range of temperatures. |
| Survival Strategy | Often use behavioral adaptations like basking or burrowing to regulate temperature. | Physiological adaptations like sweating or shivering to control body heat. |
| Method of Heat Regulation | Rely on environmental heat sources for body temperature regulation. | Generate and regulate their own heat through metabolic processes. |
| Activity Level | Activity levels are heavily influenced by external temperatures. | Generally maintain consistent activity levels regardless of external temperatures. |
| Energy Efficiency | More energy-efficient in warm climates due to lower need for internal heat production. | Less energy-efficient due to continuous energy use for heat regulation. |
| Role in Ecosystem | Often prey due to fluctuating activity levels; predators during optimal temperatures. | Predators or dominant species due to ability to sustain prolonged activity. |
| Adaptation Strategies | Develop behavioral strategies to cope with environmental temperatures. | Physiological adaptations allow for greater resistance to temperature extremes. |
Warm-blooded animals regulate body temperature internally, while cold-blooded animals depend on environmental heat sources.
Cold-blooded animals, or ectotherms, include reptiles, amphibians, and most fish, relying on the environment for body temperature.
Humans are warm-blooded, maintaining a constant body temperature through internal metabolic processes.
Cold-blooded animals lack the physiological mechanisms to generate and maintain body heat independently from the environment.
Recent studies suggest dinosaurs were not entirely cold-blooded; they might have had mixed metabolic adaptations.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following animals is warm-blooded?
Frog
Lizard
Bird
Snake
What is another term for warm-blooded animals?
Ectotherms
Poikilotherms
Endotherms
Mesotherms
Which of the following is a characteristic of cold-blooded animals?
They maintain a constant body temperature.
They rely on external sources of heat.
They have a high metabolic rate.
They can live in extremely cold environments without hibernating.
Which class of animals includes warm-blooded species?
Reptiles
Amphibians
Mammals
Fish
Why do cold-blooded animals often bask in the sun?
To cool down
To increase their metabolic rate
To avoid predators
To decrease their body temperature
Which of the following is an advantage of being warm-blooded?
Reduced need for food
Ability to remain active in cold environments
Dependence on external temperatures
Lower energy expenditure
What is a common behavior of cold-blooded animals during cold weather?
Increased activity
Hibernation or reduced activity
Migration
Increased feeding
Which group of animals is primarily cold-blooded?
Fish
Birds
Mammals
Insects
How do warm-blooded animals generate heat?
Through external heat sources
By absorbing heat from the environment
Through metabolic processes
By hibernating
Which of the following is true about the energy needs of warm-blooded animals compared to cold-blooded animals?
Warm-blooded animals require less energy.
Cold-blooded animals require more energy.
Warm-blooded animals require more energy.
Both have similar energy needs.
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

