Which division of the autonomic nervous system is primarily responsible for the "fight or flight" response?
Parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Central nervous system
Enteric nervous system
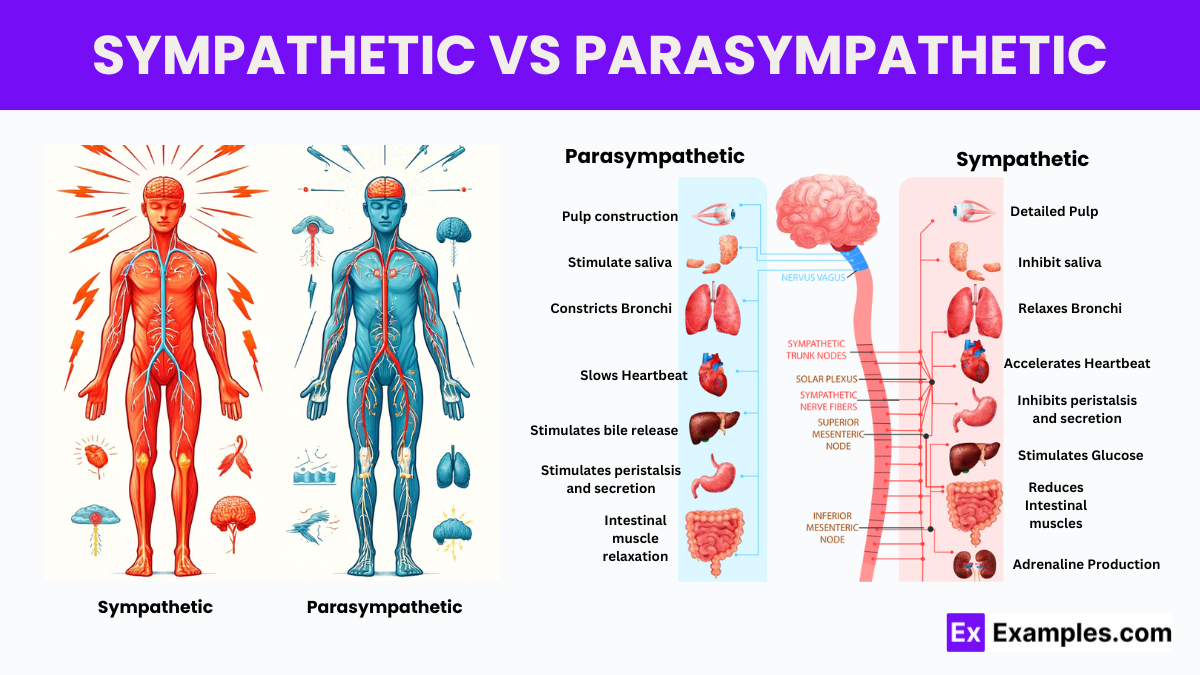
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a critical component of the human body that regulates a variety of involuntary physiological processes, including blood circulation, digestion, and breathing. Operating independently from our conscious awareness, the ANS ensures the maintenance of internal stability and balance, known as homeostasis. By controlling essential functions such as heartbeat, breathing rate, body temperature, and more, this system plays a pivotal role in our daily survival.
Within the autonomic nervous system, there are two main subdivisions that work in tandem to maintain bodily functions: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system is often characterized as the body’s “fight or flight” response, activating during times of stress to prepare the body for rapid action. In contrast, the parasympathetic nervous system is associated with “rest and digest” activities, promoting relaxation and conservation of energy.
Sympathetic Autonomic Nervous System: Located along the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord, the sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for rapid, emergency responses, known as the “fight-or-flight” reaction. It increases heart rate, speeds up respiration, and dilates pupils to enhance survival-critical bodily functions.
Parasympathetic Autonomic Nervous System: In contrast, the parasympathetic nervous system, situated between the brainstem and the sacral spinal cord, manages the “rest and digest” activities that conserve and restore energy. It slows the heart rate, reduces respiration, and stimulates digestive processes, supporting functions that aid in relaxation and recovery.
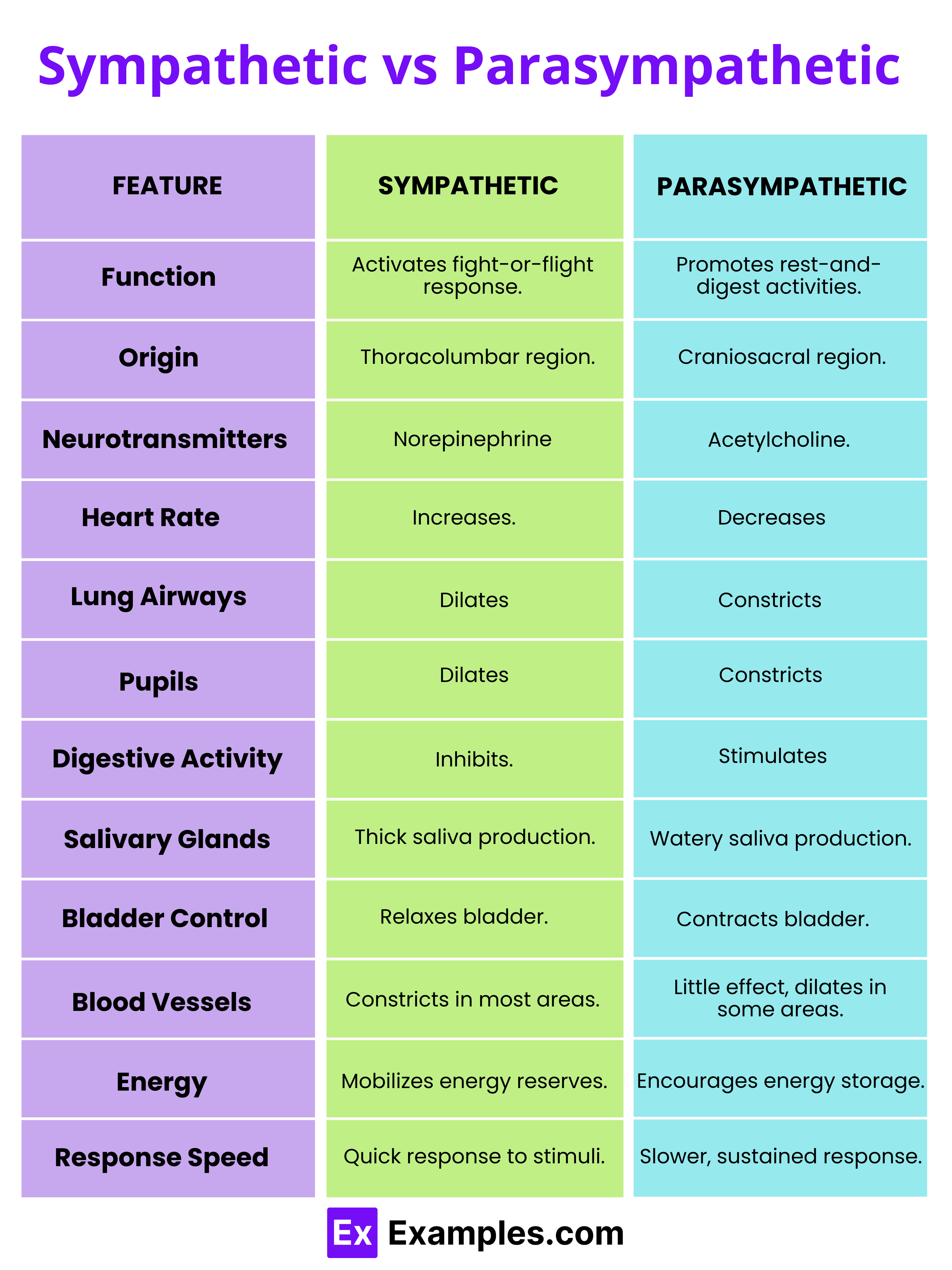
| Aspect | Sympathetic Nervous System | Parasympathetic Nervous System |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Prepares the body for stress or emergency situations (fight-or-flight response). | Promotes the maintenance of the body at rest (rest-and-digest response). |
| Origin of Nerve Fibers | Thoracolumbar region of the spinal cord. | Craniosacral region (brainstem and sacral spinal cord). |
| Neurotransmitters | Mainly uses norepinephrine (noradrenaline). | Primarily uses acetylcholine. |
| Effects on Heart | Increases heart rate and the force of heart contractions. | Decreases heart rate and the force of heart contractions. |
| Effects on Lungs | Dilates bronchi, which increases air flow to the lungs. | Constricts bronchi, which reduces air flow to the lungs. |
| Effects on Eyes | Dilates pupils to improve vision. | Constricts pupils and focuses the lens for near vision. |
| Effects on Digestion | Inhibits digestive activity. | Stimulates digestive activity. |
| Effects on Salivary Glands | Produces thick, viscous saliva. | Produces watery saliva to aid in digestion. |
| Effects on Bladder | Relaxes the bladder. | Contracts the bladder to promote urination. |
| Effect on Blood Vessels | Generally constricts blood vessels in the skin and abdominal organs, but dilates blood vessels in muscles. | Generally has little effect on blood vessels, but may cause dilation in the genital areas to enhance function. |
| Energy Mobilization | Stimulates the release of glucose from energy stores. | Promotes the storage of glucose. |
| Response Time | Rapid response to stress, preparing for quick action. | Slower, more sustained response, geared towards conservation and restoration of body resources. |
The sympathetic nervous system triggers the fight-or-flight response, while the parasympathetic system promotes rest and digestion.
Remember “Sympathetic = Stress” and “Parasympathetic = Peace” to differentiate their primary functions easily.
Stress activates the sympathetic nervous system, preparing the body for quick action and response.
Increased blood pressure is typically a result of sympathetic nervous system activation, which constricts blood vessels.
To calm the parasympathetic nervous system, engage in relaxing activities like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which division of the autonomic nervous system is primarily responsible for the "fight or flight" response?
Parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Central nervous system
Enteric nervous system
Which nervous system division promotes relaxation and digestion?
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
Somatic nervous system
What is the effect of the sympathetic nervous system on heart rate?
It decreases heart rate
It has no effect on heart rate
It increases heart rate
It maintains heart rate
Which neurotransmitter is most commonly associated with the parasympathetic nervous system?
Norepinephrine
Acetylcholine
Epinephrine
Dopamine
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect digestion?
It enhances digestion
It has no effect on digestion
It inhibits digestion
It starts digestion
Which system is activated during a calm, restful state, such as after a meal?
Parasympathetic nervous system
Central nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
What is the primary effect of the sympathetic nervous system on pupil size?
Constriction
No change
Dilation
Irregular changes
Which of the following actions is primarily controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system?
Increased sweating
Increased heart rate
Dilated pupils
Increased digestive activity
What effect does the sympathetic nervous system have on bronchioles in the lungs?
Constriction
No effect
Dilation
Irregular changes
Which system is responsible for the "rest and digest" functions?
Sympathetic nervous system
Central nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

