What is the chemical formula for calcium chloride?
CaCl
CaCl₂
CaCl₃
Ca₂Cl


Calcium chloride is a widely used inorganic compound in chemistry, recognized by its chemical formula CaCl₂. It appears as a white, crystalline substance at room temperature and is highly soluble in water. This compound is essential in various applications, including road deicing, dust control on roads, and as a drying agent in many industrial processes. Its ability to absorb moisture makes it valuable in maintaining dry conditions where necessary. Calcium chloride is also used in food processing, swimming pool maintenance, and as an electrolyte in sports drinks, where it helps replenish minerals lost through sweat.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | CaCl₂ |
| Name | Calcium chloride |
| IUPAC Name | Calcium dichloride |
| Alternate Names | Calcium dichloride |
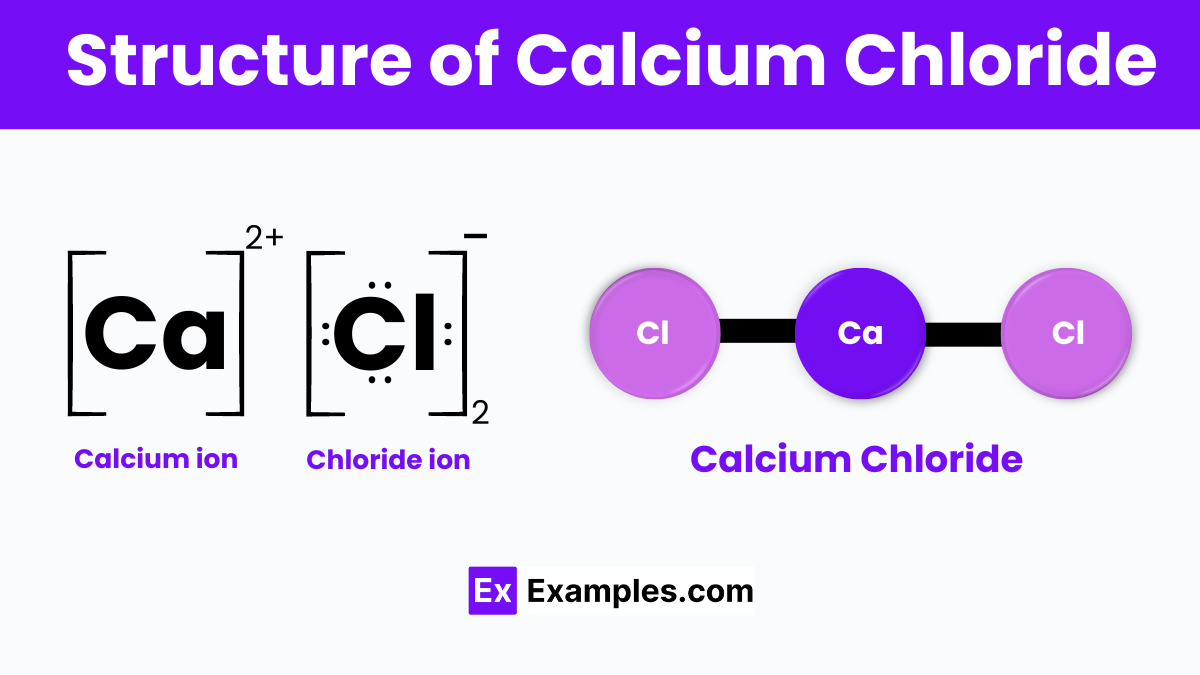
Calcium chloride is represented by the chemical formula CaCl₂, has a simple ionic structure. It consists of one calcium ion paired with two chloride ions. The calcium ion holds a positive charge (Ca²⁺), while each chloride ion carries a negative charge (Cl⁻). In its solid form, calcium chloride often exists as a crystalline lattice, meaning the ions are arranged in a highly ordered, repeating pattern. This structure allows the compound to dissolve easily in water, as the water molecules interact with the charged ions, separating them and incorporating them into the solution. This characteristic makes calcium chloride highly effective for uses like melting ice and absorbing moisture.
Calcium chloride can be prepared through a simple reaction between limestone (calcium carbonate) and hydrochloric acid. First, the limestone is treated with hydrochloric acid, which results in the formation of calcium chloride, water, and carbon dioxide. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
This process is commonly used in laboratories and industries due to its efficiency and the availability of the starting materials. Once the reaction completes, the calcium chloride can be purified and dried for various uses, such as de-icing roads and controlling dust. This method is straightforward, allowing for the easy production of calcium chloride in bulk.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White, crystalline solid; can also be found in flake, pellet, or granular form. |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Salty and slightly bitter |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water, which means it dissolves easily when mixed with water. |
| Melting Point | About 772°C (1422°F) |
| Boiling Point | About 1935°C (3515°F) |
| Density | 2.15 g/cm³ (solid) |
| Hygroscopic | Yes, it readily absorbs moisture from the environment. |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 10043-52-4 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 24854 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 10330 |
| SMILES Identifier | [Cl-].[Cl-].[Ca+2] |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/Ca.2ClH/h;21H/q+2;;/p-2/fCa.2Cl/h;21h/qm;2*-1 |
| InChI Key | UXVMQQNJUSDDNG-HQDHFEKBCV |
| RTECS Number | EV9800000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00010903 |
Widely used in the food industry, calcium chloride improves texture, preserves freshness, and maintains nutritional content in various products. Manufacturers add this inorganic compound to canned vegetables to maintain firmness, to sports drinks to replenish electrolytes, and to baked goods as a stabilizer to prevent spoilage and improve consistency. Food safety authorities generally recognize its use in food processing as safe, although manufacturers always use it in moderate amounts to avoid altering the taste or properties of the final product.
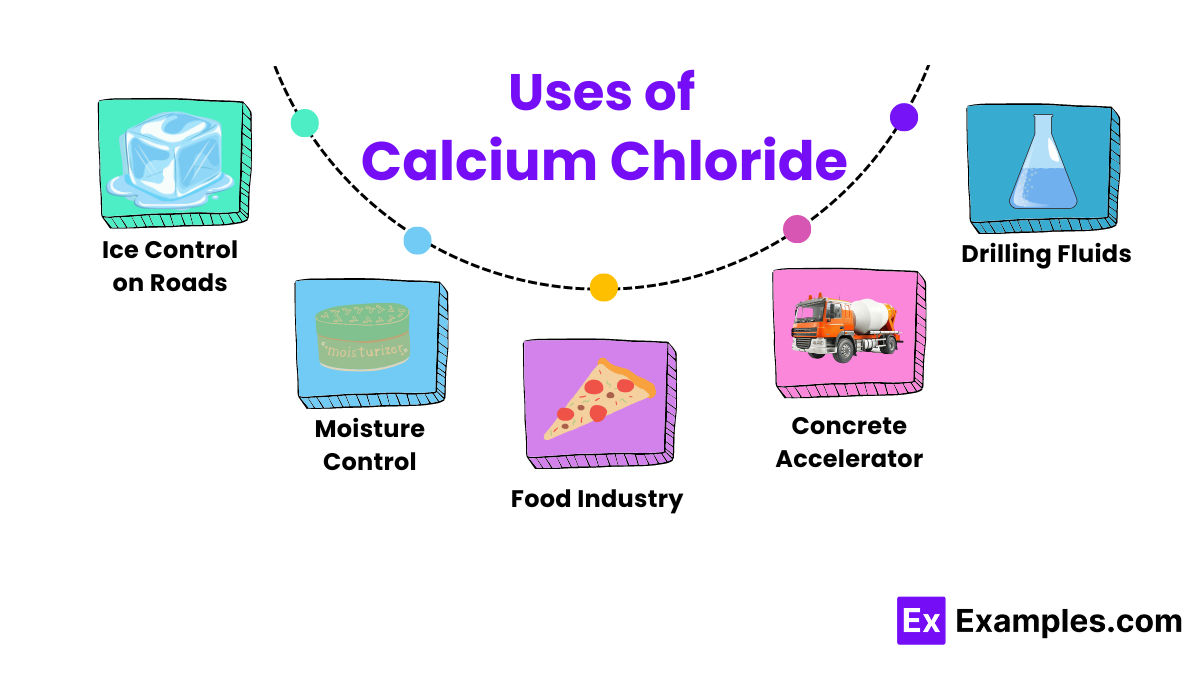
Calcium chloride is highly effective at melting ice on roads and sidewalks. It lowers the freezing point of water, which helps prevent ice formation and makes it safer to travel in winter conditions.
Because it is hygroscopic, manufacturers use calcium chloride in products that control humidity. It absorbs moisture from the air, helping keep warehouses and storage areas dry.
In the food industry, calcium chloride acts as a firming agent in canned vegetables and in cheese making. It maintains the firmness of vegetables and aids the coagulation of milk proteins during cheese production.
On unpaved roads and construction sites, workers use calcium chloride to suppress dust. It keeps the surface moist and binds dust particles together, reducing air pollution
Operators use calcium chloride in pools and wastewater treatment plants to increase water hardness. This reduces the erosion of concrete in pools and enhances the effectiveness of certain water purification processes.
In the oil and gas industry, workers add Calcium Chloride to drilling fluids to stabilize shale formations and make drilling processes more efficient.
Workers use Calcium Chloride in concrete to speed up the initial setting time, which is especially useful in cold weather, allowing for faster curing and build up of concrete.
In controlled amounts, you can use Calcium Chloride as a calcium extra. It helps strengthen bones and maintain proper nerve and muscle functions.
Calcium Chloride can act as an irritant. Direct contact with the skin, eyes, or inhaling its dust can cause irritation, leading to skin redness and respiratory discomfort.
In medical treatments like saline solutions, it helps manage the body’s electrolyte balance, which is crucial for proper organ function.
Due to its highly Hygroscopic nature, excessive ingestion can lead to dehydration by pulling water from body tissues. Consequently, this process can result in various health problems, including but not limited to, electrolyte imbalances, organ dysfunction, and cardiovascular issues.
The properties and uses of Calcium Chloride (CaCl₂) are completely distinct from those of table salt (NaCl).
Calcium Chloride can affect the heart by increasing blood calcium levels, potentially stabilizing heart rhythms in specific medical scenarios.
The main issues with Calcium Chloride include its potential to cause skin, eye, and respiratory irritations upon exposure.
Manufacturers add Calcium Chloride to bottled water to enhance taste by making better mineral balance and mouthfeel.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the chemical formula for calcium chloride?
CaCl
CaCl₂
CaCl₃
Ca₂Cl
Calcium chloride is commonly used for which of the following purposes?
Fertilizer
Food additive
Road de-icer
Textile dye
What state of matter is calcium chloride at room temperature?
Solid
Liquid
Gas
Plasma
Which of the following is a common industrial use for calcium chloride?
Water treatment
Cosmetic production
Paper manufacturing
Paints
What happens when calcium chloride is dissolved in water?
It forms a basic solution
It forms a neutral solution
It forms an acidic solution
It forms a gas
Calcium chloride is classified as what type of compound?
Organic
Inorganic
Polymer
Radioactive
Which of the following best describes the solubility of calcium chloride in water?
Insoluble
Slightly soluble
Moderately soluble
Highly soluble
What is the pH range of a calcium chloride solution?
Acidic
Neutral
Slightly basic
Strongly basic
Calcium chloride can be used as a drying agent because:
It absorbs water from the air
It releases water vapor
It reacts with water to form a gas
It forms a solid in water
In which form is calcium chloride often used in food products?
Powder
Liquid
Tablet
Granules
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

