What is the atomic number of Rhenium?
71
75
77
79
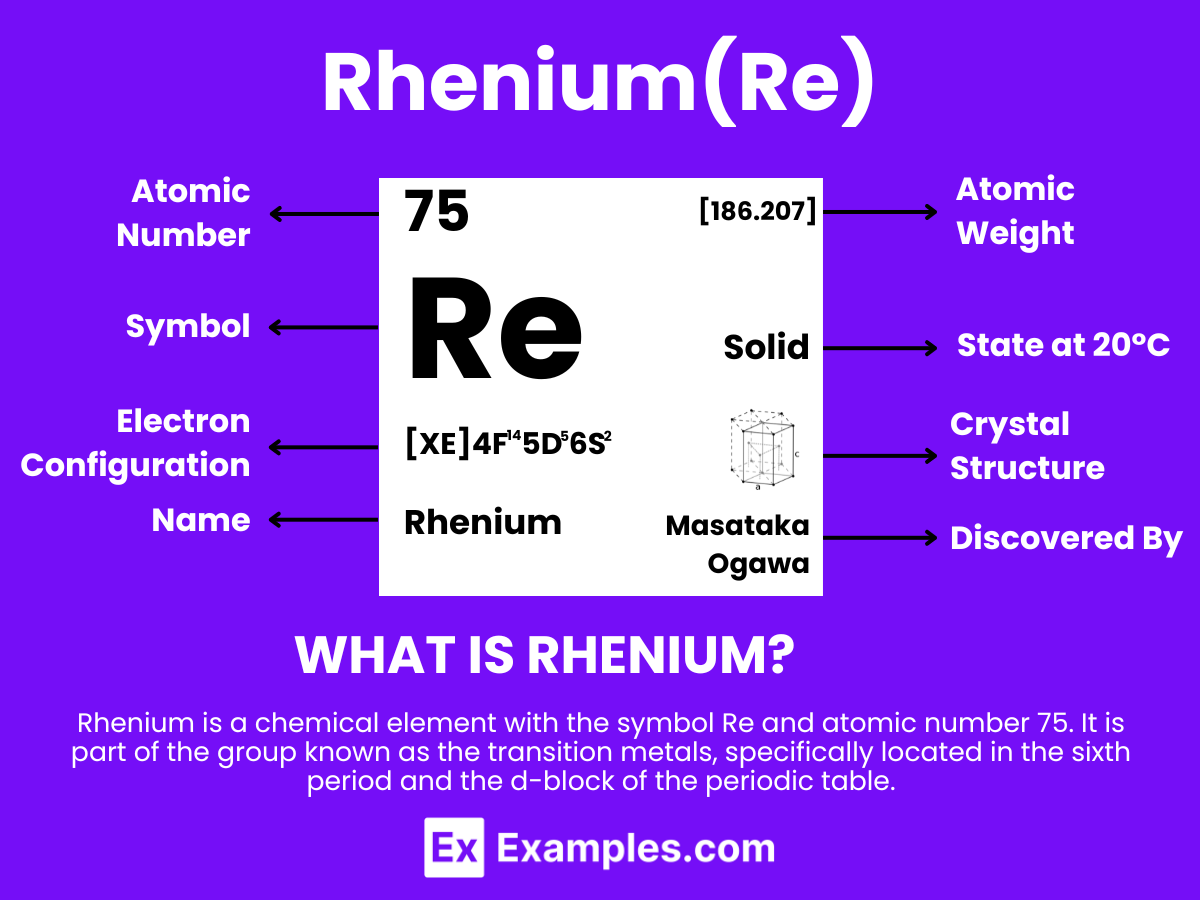
Embark on a journey to explore the chemical properties of Rhenium, a rare and highly valuable metal known for its exceptional characteristics and versatility. This guide provides detailed examples and insights into the world of Rhenium, showcasing its role in modern technology and industry. With its unique ability to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments, Rhenium has carved out a niche in aerospace, electronics, and catalysis. Delve into the intricacies of its chemical behavior, compounds, and reactions that make Rhenium an indispensable element in advanced scientific research and applications.
Rhenium is a metallic element with the chemical symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is extracted from molybdenite and other ores where it occurs in low concentrations. Rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth’s crust and has the third-highest melting point of all elements, making it highly valued for its strength and resistance to wear and corrosion in extreme environments. The discovery of rhenium was significant in the field of chemistry for its unique properties among the transition metals in the periodic table. Its exceptional ability to withstand high temperatures and its catalytic properties make it crucial in the manufacturing of high-performance engines and catalysts.
Exploring the atomic structure of Rhenium reveals the foundations of its exceptional characteristics and wide application range.
The behavior and stability of Rhenium under different temperatures and pressures have been extensively studied, showcasing its solid state under standard conditions. Its extraordinary melting point and durability at elevated temperatures underscore its utility in demanding environments, such as in the aerospace, defense, and chemical industries, solidifying Rhenium’s contribution to advancing modern science and industrial capabilities.
| Physical Property | Detail |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Silvery-white, with a metallic luster |
| Density | 21.02 g/cm³ at 20°C, making it one of the densest elements |
| Melting Point | 3186°C, one of the highest of all elements |
| Boiling Point | 5596°C, which is also among the highest |
| State at 20 °C | Solid, due to its high melting point |
| Thermal Conductivity | 48 W/(m·K), indicating good ability to conduct heat |
| Electrical Resistivity | 193 nΩ·m at 20°C, showcasing its relatively high resistivity compared to other metals |
| Heat of Fusion | 33.2 kJ/mol, the energy required to change from solid to liquid state without changing temperature |
Rhenium stands out for its remarkable resistance to heat and wear, making it invaluable in high-temperature applications. Its most noteworthy chemical properties include:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 3186 °C |
| Boiling Point | 5596 °C |
| Heat of Fusion | 33 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 704 kJ/mol |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 0.137 J/g·K |
| Thermal Conductivity | 48 W/m·K |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 21.02 g/cm³ |
| Mohs Hardness | 7.0 |
| Tensile Strength | 800 MPa |
| Young’s Modulus | 463 GPa |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.30 |
| Vickers Hardness | 2450 MPa |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Electrical Resistivity | 193 nΩ·m |
| Magnetic Susceptibility | -0.0008 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 75 |
| Atomic Mass | 186.207 |
| Stable Isotopes | Re-185, Re-187 |
| Natural Abundance (Re-185) | 37.4% |
| Natural Abundance (Re-187) | 62.6% |
| Cross Section for Thermal Neutrons | 90 barns (for Re-187) |
Rhenium is predominantly obtained as a by-product of molybdenum and copper mining. The preparation process involves:
Rhenium heptoxide is one of the most well-known oxides of rhenium and a key compound in its chemistry.
Equation: Re+7O₂→Re₂O₇
Perrhenic acid is a strong acid formed from the hydration of rhenium heptoxide and is of significant importance due to its role in the preparation of other rhenium compounds.
Equation: Re₂O₇+H₂O→2HReO₄
Rhenium carbide is a compound that demonstrates rhenium’s ability to form stable compounds with non-metals other than oxygen.
Equation: Re+C→ReC
Rhenium trifluoride showcases the halide chemistry of rhenium, indicating its ability to form stable halide compounds.
Equation:32Re+3F₂→2ReF₃
Rhenium pentachloride demonstrates rhenium’s ability to form complex halides, which are pivotal in synthetic chemistry and serve as precursors to a wide array of organometallic compounds.
Equation:Re+5Cl₂→2ReCl₅
Rhenium diboride is a compound known for its extraordinary hardness and high electrical conductivity,
Equation:Re+2B→ReB₂
| Isotope | Natural Abundance | Half-life | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| ^185Re | 37.4% | Stable | Commonly used in rhenium-osmium dating |
| ^187Re | 62.6% | 4.12 × 10^10 years | Decays to ^187Os; used in geological dating |
| ^186Re | Synthetic | 3.7186 days | Used in radiopharmaceuticals for therapy |
| ^188Re | Synthetic | 17 hours | Applied in cancer treatment and research |
| ^189Re | Synthetic | 24.3 hours | Utilized in nuclear science for research |
Rhenium has several critical applications across various high-tech and industrial fields:
Rhenium, a metal of extremes, commands attention for its rarity and remarkable properties. From jet engines to cancer treatment, its uses span diverse fields, marking its significance in modern technology. This article delves into Rhenium’s fascinating world, exploring its chemical behavior, preparation methods, and versatile applications, showcasing its invaluable contribution to advancements in science and industry.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the atomic number of Rhenium?
71
75
77
79
Which of the following is a common use of Rhenium?
Electrical wiring
Jewelry making
Catalysts in chemical reactions
Food preservation
Rhenium belongs to which group in the periodic table?
Transition metals
Alkali metals
Noble gases
Halogens
Rhenium is most commonly found in nature as a byproduct of which metal?
Copper
Molybdenum
Lead
Zinc
What is the chemical symbol of Rhenium?
Rh
Re
Ru
Rb
Rhenium has one of the highest melting points of any element. Approximately what is its melting point?
2,000°C
2,500°C
3,000°C
3,500°C
In what year was Rhenium discovered?
1869
1902
1925
1945
Which of the following properties best describes Rhenium?
Highly reactive
Low melting point
Corrosion-resistant
Poor conductor of electricity
Rhenium is commonly used in which of the following industries?
Aerospace
Textile
Agriculture
Construction
What is the electron configuration of Rhenium?
[Xe] 4f14 5d6 6s2
[Xe] 4f14 5d7 6s1
[Kr] 4d10 5s2
[Ar] 3d10 4s2
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

