What does the Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum state?
Momentum is created
Momentum is destroyed
Total momentum remains constant
Momentum depends on temperature

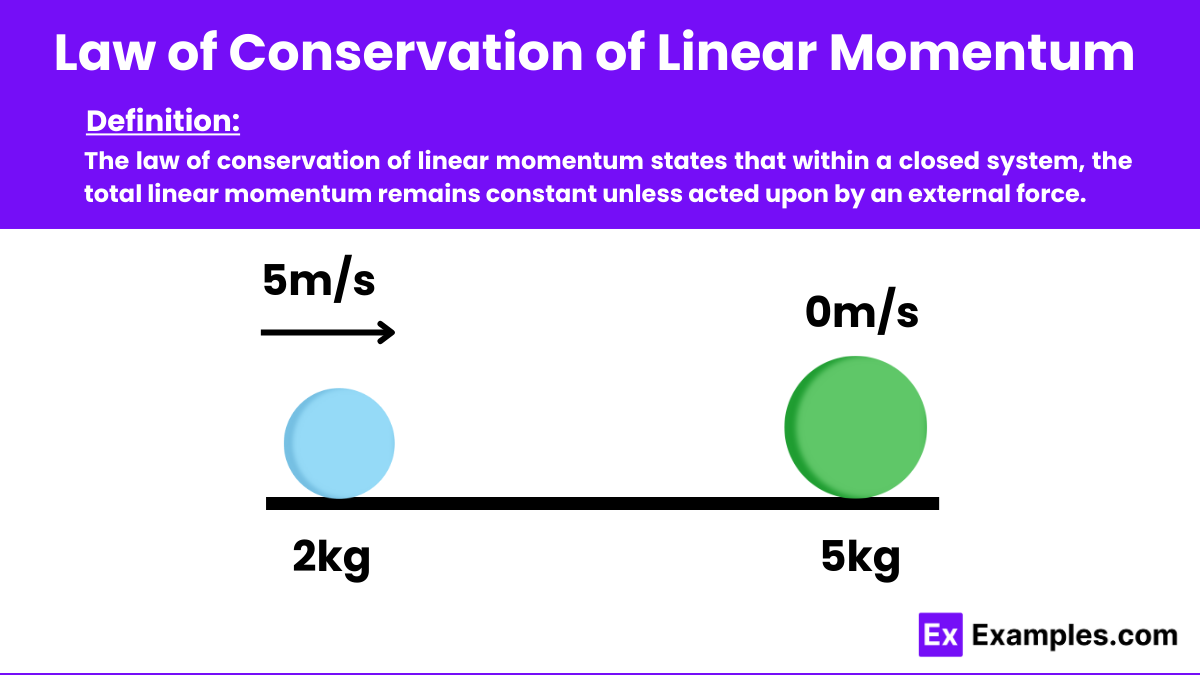
In physics, the law of conservation of linear momentum states that within a closed system, the total linear momentum remains constant unless acted upon by an external force. This fundamental principle of the laws of physics implies that the total momentum of all objects within an isolated system, where no external forces are at play, will not change over time.
The Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum can be expressed using the formula:
This formula shows that the total linear momentum before an interaction (left side of the equation) is equal to the total linear momentum after the interaction (right side of the equation). Provided no external forces act on the system.
Here’s a simplified derivation of the Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum:
Initial State: Consider two objects moving in an isolated system, which means there are no external forces acting on them. Each object has its own momentum based on its mass and velocity.
Interaction: When these objects interact (collide or push against each other), they exert equal and opposite forces on one another, as per Newton’s Third Law.
Change in Momentum: Due to the interaction, each object’s momentum will change. One object might speed up, slow down, or change direction, and the same will happen for the other object, but in an opposite way.
Final State: After the interaction, the total momentum of the system remains the same as it was before the interaction. The changes in momentum of the individual objects cancel each other out. Meaning that the sum of their momenta remains unchanged.
The Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum tells us that as long as no external forces are acting on a system, the total momentum of the system remains constant. Even though the individual momenta of the objects within the system may change due to their interactions.
An investigation tests this law by analyzing collisions or interactions, checking if the total momentum before and after remains constant when no external forces act.
This principle links impulse (force times time) to momentum change, implying that momentum changes based on external forces over time, but remains conserved in isolated systems.
In physics, the momentum of an object, a product of its mass and velocity, is measured in kilogram meters per second (kg·m/s).
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What does the Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum state?
Momentum is created
Momentum is destroyed
Total momentum remains constant
Momentum depends on temperature
In an isolated system, what happens to the total linear momentum when two objects collide?
It increases
It decreases
It remains constant
It becomes zero
Which of the following best describes an isolated system?
A system with no external forces
A system with constant external forces
A system with increasing mass
A system with varying energy
How is the total momentum of a system calculated?
Sum of individual masses
Sum of individual velocities
Sum of individual momenta
Sum of individual accelerations
What is the formula for linear momentum?
p = mv
p = ma
p = mgh
p = m/v
If two objects collide and stick together, what type of collision is this?
Elastic collision
Inelastic collision
Perfectly elastic collisio
Gravitational collision
In an elastic collision, how are kinetic energy and momentum conserved?
Only momentum is conserved
Only kinetic energy is conserved
Both kinetic energy and momentum are conserved
Neither kinetic energy nor momentum are conserved
Which principle explains the recoil of a gun when fired?
Law of Conservation of Energy
Law of Conservation of Mass
Law of Conservation of Linear Momentum
Newton's Second Law
How does the mass of an object affect its momentum if the velocity is constant?
Increases momentum
Decreases momentum
No effect on momentum
Depends on the shape of the object
When two ice skaters push off each other, what happens to their combined momentum?
It increases
It decreases
It remains the same
It becomes zero
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

