Which of the following is an example of active immunity?
Receiving an antibody injection
Breastfeeding
Recovering from chickenpox
Receiving a tetanus antitoxin injection

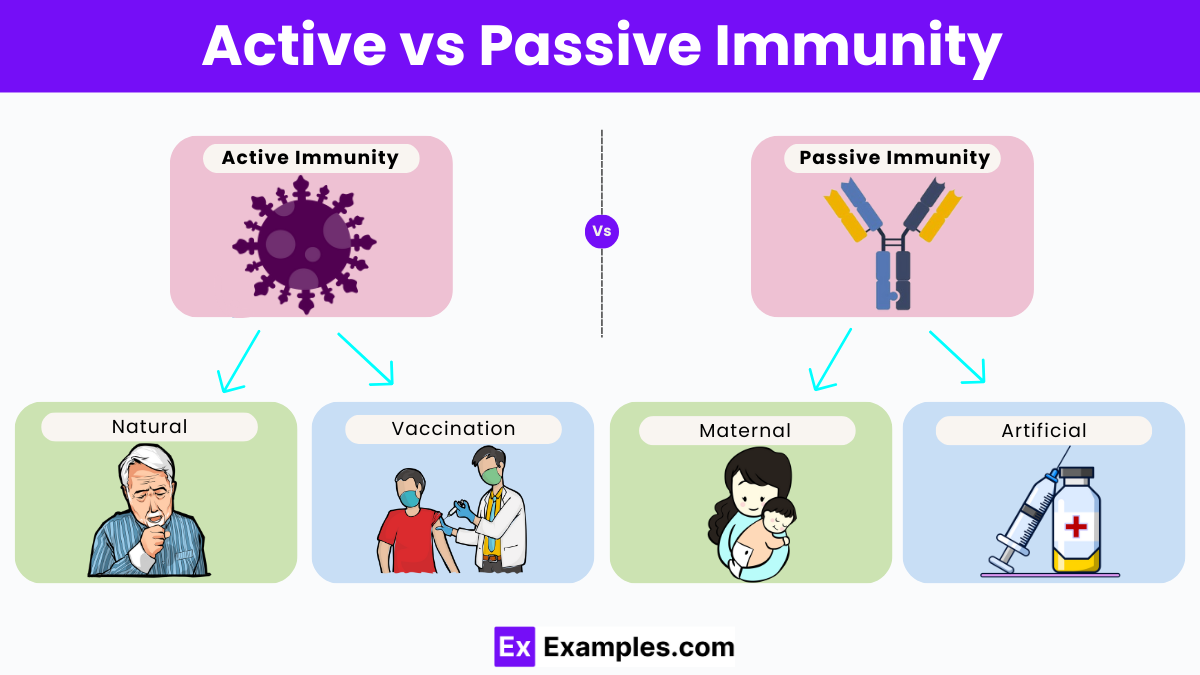
Active immunity is achieved by exposing the body to an antigen to trigger a long-lasting adaptive immune response. In contrast, passive immunity involves the transfer of antibodies from one individual to another, providing immediate but temporary protection. This can happen naturally, such as through maternal antibodies, or artificially via antibody injections. Passive immunity is crucial for combating new, resistant pathogens and protecting individuals with weakened immune systems. This overview highlights the key roles and differences between these two forms of immunity.
Active immunity occurs when an individual’s immune system generates a defense against a pathogen. This form of immunity can develop in two primary ways: through natural infection or through vaccination.
Active immunity is generally long-lasting and can often provide lifelong protection against a pathogen. Upon subsequent exposures to the disease, the immune system swiftly recognizes and combats the invader, thanks to the memory cells produced during initial exposure.
Passive immunity, unlike active immunity, involves the direct transfer of antibodies from one individual to another. This type of immunity can be acquired naturally or artificially:
Passive immunity offers rapid protection; however, it is temporary, lasting only a few weeks to months. The body does not develop memory cells in this type of immunity, so there is no long-term protection against future infections.
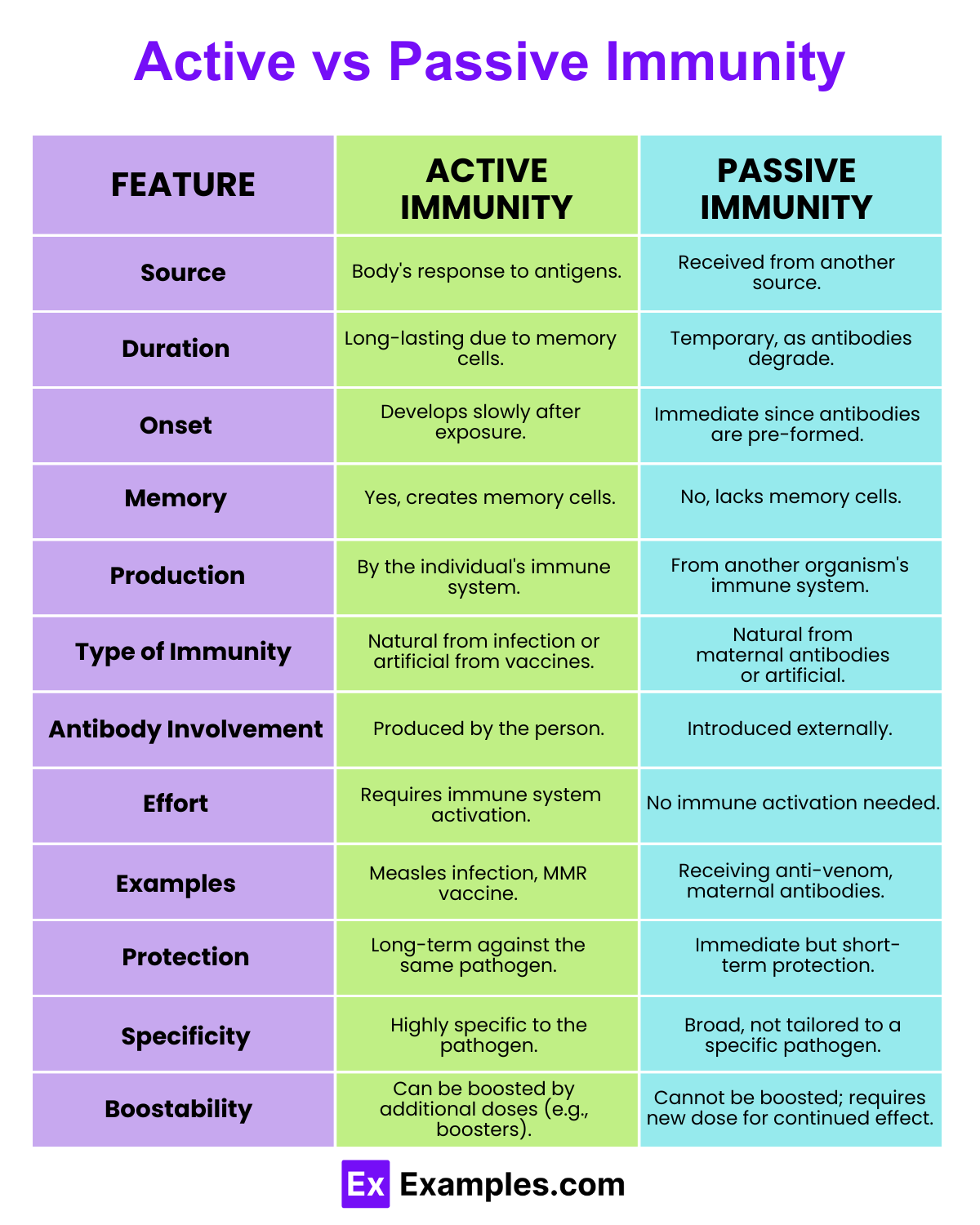
| Feature | Active Immunity | Passive Immunity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active immunity refers to the immunity that develops after exposure to a pathogen or through vaccination. It involves the production of antibodies by the immune system. | Passive immunity is the type of immunity acquired by the transfer of antibodies or activated T-cells from another individual, such as from mother to fetus or through antibody-containing products. |
| Source | Generated by the individual’s own immune system after exposure to an infectious agent or vaccine. | Acquired from another source, either naturally through maternal antibodies or artificially through injections of antibodies like immunoglobulins. |
| Duration | Long-lasting, often lifelong due to memory cell formation. | Short-term, lasting only a few weeks to months as the antibodies are eventually degraded. |
| Onset of Action | Slow, as it requires time for the immune system to recognize the pathogen, activate, and produce specific antibodies. | Immediate, as the antibodies or cells are already formed and active upon transfer. |
| Memory | Yes, involves the formation of memory cells which quicken the response upon future exposure to the same pathogen. | No, does not involve the formation of memory cells; no enhanced response upon future exposure. |
| Types of Agents Involved | Antigens that stimulate the immune response. These can be live-attenuated, killed, or parts of the pathogen such as proteins. | Antibodies or lymphocytes from an immune donor. |
| Example | Developing immunity after recovering from chickenpox or receiving a chickenpox vaccine. | Receiving anti-venom for a snake bite or antibodies passed from mother to baby during pregnancy. |
| Advantages | Provides durable protection; enhances the immune system’s ability to respond more rapidly and effectively on subsequent exposures. | Provides immediate protection; beneficial in cases where there is no time for the body to develop its own immune response. |
| Disadvantages | Takes time to develop; initial exposure or vaccination might lead to mild symptoms of the disease. | Temporary protection; can sometimes lead to allergic reactions or other side effects if the immune components are not fully compatible. |
Active and passive immunity share several crucial similarities, despite their differences in how they provide protection against diseases:
Active immunity involves your body producing antibodies, lasting years. Passive immunity provides immediate, short-term protection through external antibodies.
Receiving anti-venom for snake bites is an example of passive immunity, providing immediate, temporary protection.
Examples include immunity developed from measles recovery, flu vaccination, and exposure to chickenpox virus, all inducing long-term protection.
For IGCSE, active immunity results from direct exposure to pathogens, creating long-lasting memory cells. Passive immunity involves receiving pre-made antibodies for short-term defense.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following is an example of active immunity?
Receiving an antibody injection
Breastfeeding
Recovering from chickenpox
Receiving a tetanus antitoxin injection
Which type of immunity is provided by vaccines?
Passive immunity
Active immunity
Both active and passive immunity
Neither active nor passive immunity
Which type of immunity is usually short-term?
Active immunity
Passive immunity
Both active and passive immunity
Neither active nor passive immunity
Maternal antibodies passed to a baby through breast milk is an example of:
Active immunity
Passive immunity
Artificial active immunity
Artificial passive immunity
Which of the following provides long-lasting protection?
Passive immunity
Active immunity
Both active and passive immunity
Neither active nor passive immunity
Which type of immunity can be acquired through natural infection?
Active immunity
Passive immunity
Artificial immunity
None of the above
Receiving immunoglobulins for hepatitis exposure is an example of:
Active immunity
Passive immunity
Natural active immunity
Natural passive immunity
Which type of immunity involves the direct transfer of antibodies?
Active immunity
Passive immunity
Both active and passive immunity
Neither active nor passive immunity
How is passive immunity acquired?
By recovering from a disease
Through vaccination
Through the transfer of antibodies
Through exposure to pathogens
Which of the following best describes active immunity?
Immunity that lasts a few months
Immunity that involves the production of antibodies by the immune system
Immunity that is transferred from mother to child
Immunity that is acquired through antibody injections
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

