What is the primary function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)?
Lipid synthesis
Energy production
DNA replication
Protein synthesis


Dive into the fascinating world of cell biology with our complete guide to the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), the cellular powerhouse pivotal in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and calcium storage. This comprehensive exploration sheds light on the ER’s critical roles, from supporting the immune system to its involvement in various diseases. Illustrated with vivid examples, understand how this intricate network functions within cells. Perfect for students, researchers, and curious minds alike, our guide is your key to unlocking the secrets of one of life’s essential components.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a complex network of membranous tubes and sacs called cisternae, found within the cells of all eukaryotic organisms. It plays a crucial role in several cellular processes, including the synthesis of proteins and lipids, which are vital for the cell’s structure and function. The ER is divided into two main types: the rough ER, studded with ribosomes, where protein synthesis occurs, and the smooth ER, which is involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium storage. Acting as a cellular highway, it transports substances throughout the cell and is essential for the maintenance of cellular health and the production of key molecules.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a vital cellular organelle found in all eukaryotic cells, characterized by its extensive network of membranous tubules and sacs known as cisternae. It extends from the nuclear envelope to various parts of the cell, serving multiple functions, including protein and lipid synthesis.
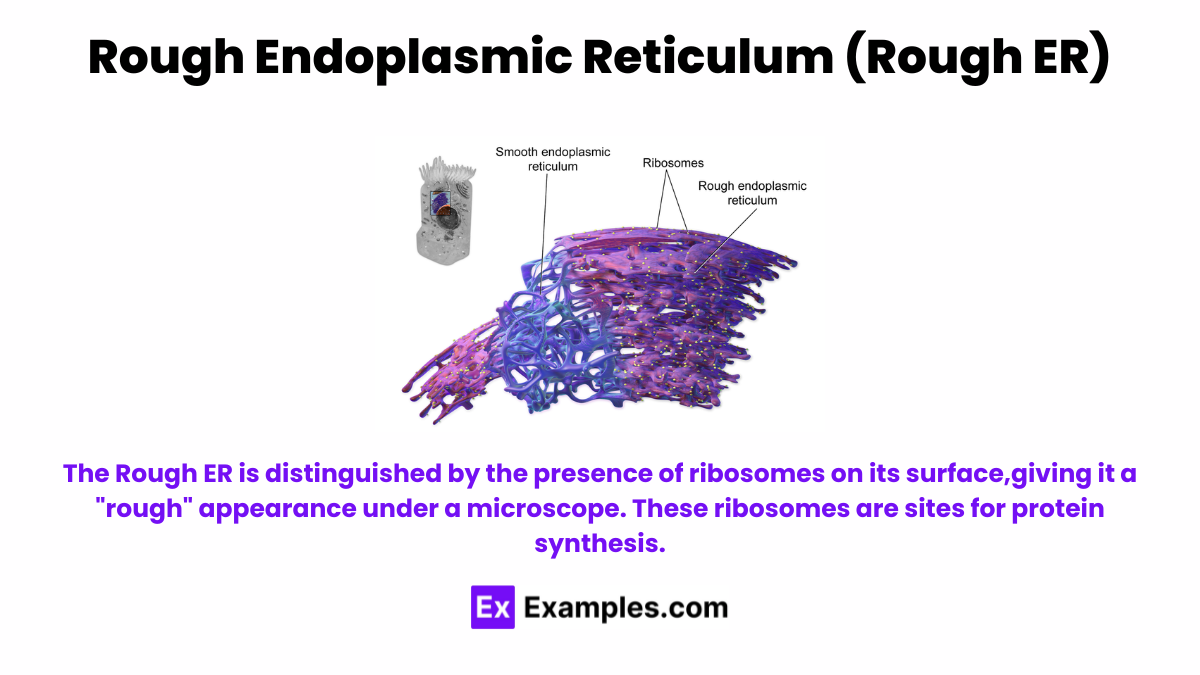
The Rough ER is distinguished by the presence of ribosomes on its surface, giving it a “rough” appearance under a microscope. These ribosomes are sites for protein synthesis. Newly synthesized proteins enter the Rough ER lumen, where they undergo folding and modifications. The Rough ER is pivotal in producing proteins destined for secretion, incorporation into the cell membrane, or delivery to other organelles.
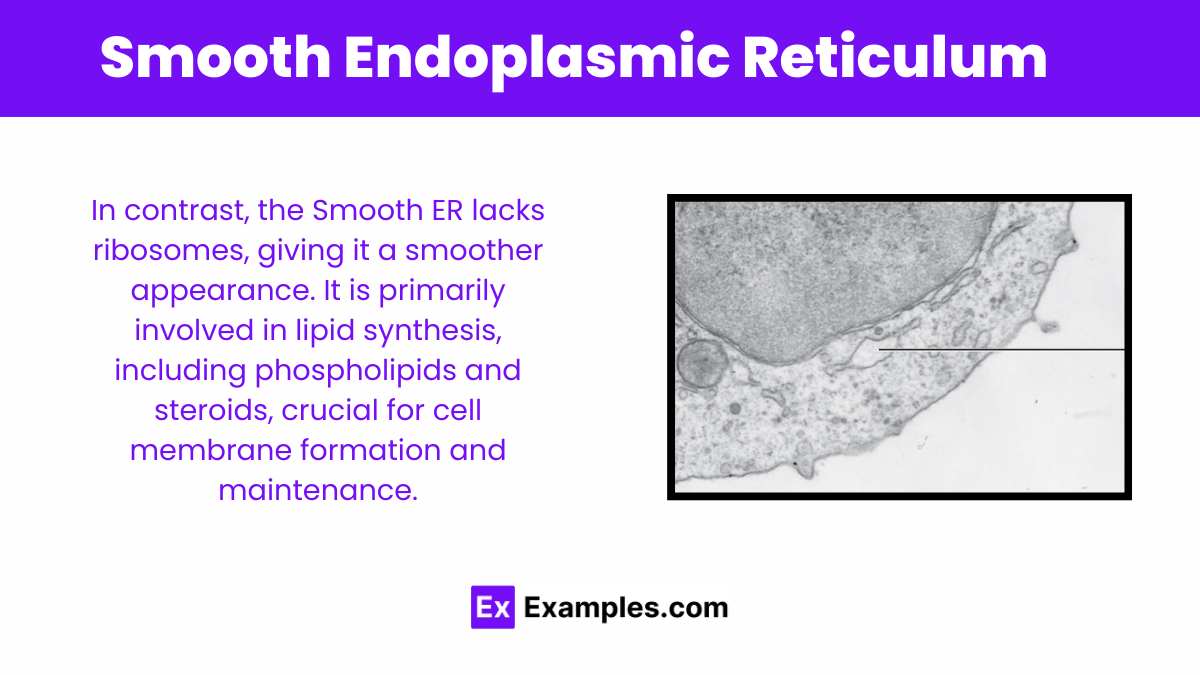
In contrast, the Smooth ER lacks ribosomes, giving it a smoother appearance. It is primarily involved in lipid synthesis, including phospholipids and steroids, crucial for cell membrane formation and maintenance. Additionally, it plays a role in detoxifying potentially harmful substances, carbohydrate metabolism, and the regulation of calcium ion concentration within the cell, essential for cellular signaling.
The ER is not an isolated entity but closely interacts with the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and plasma membrane, facilitating the transport and processing of proteins and lipids. This integration underscores the ER’s critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and executing specialized functions across different cell types.
The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) is essential for the synthesis of membrane-bound and secretory proteins. Ribosomes attached to the Rough ER’s surface translate mRNA into proteins, which are then folded and modified within the ER lumen. This process includes the addition of sugar molecules to form glycoproteins, proper folding with the help of chaperone proteins, and identification of misfolded proteins for degradation.
The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) plays a pivotal role in lipid and steroid hormone synthesis. It is responsible for the production of phospholipids and cholesterol, which are vital components of cellular membranes. The ER also synthesizes lipoproteins, which are essential for transporting fats through the body.
The ER serves as a major reservoir for calcium ions within the cell. Calcium ions are crucial for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release, and signal transduction. The ER regulates the release and uptake of calcium ions, maintaining intracellular calcium levels and ensuring proper cellular functioning.
The Smooth ER is involved in detoxifying potentially harmful biochemicals. It contains enzymes that modify these toxic substances, making them more soluble and easier to eliminate from the body. This function is particularly important in liver cells, where the ER detoxifies drugs and harmful substances.
The ER interacts closely with the Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other organelles, facilitating the transport of proteins and lipids within the cell. This interaction is vital for the secretory pathway, where proteins synthesized in the ER are modified, packaged, and transported to their final destinations, including the cell surface or external environment.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is an extensive, interconnected network of membranous structures located within the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells, playing a crucial role in the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of proteins and lipids. Its structure and location are integral to its function, allowing it to interact with various cellular components and processes.
The ER is divided into two main sections: the Rough ER (RER) and the Smooth ER (sER), each with distinct functions and appearances. The RER is characterized by the presence of ribosomes on its surface, giving it a “rough” appearance under the microscope. These ribosomes are sites where proteins are synthesized. The RER is typically found surrounding the nucleus or extending from the nuclear envelope, forming a continuous network throughout the cell. This proximity to the nucleus is strategic, facilitating the direct transfer of mRNA from the nucleus to the RER for protein synthesis.
The sER, lacking ribosomes, appears smooth and is involved in various metabolic processes, including lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium ion storage. The sER is more dispersed throughout the cell than the RER, often found in regions specific to its functions. For example, in liver cells, the sER is abundant and plays a key role in detoxifying substances.
The ER’s location and structure are essential for its role as a central hub in cellular organization and function. It is connected to the nuclear envelope, allowing for the efficient transport of proteins and RNA molecules between the nucleus and the ER. Additionally, the ER’s extensive network facilitates the distribution of synthesized proteins and lipids to other parts of the cell, including the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and the cell membrane.
Moreover, the ER is not an isolated entity; it forms physical and functional contacts with other organelles, such as mitochondria and the plasma membrane. These contacts are crucial for the transfer of lipids and calcium ions, indicating the ER’s pivotal role in cellular signaling and metabolism.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum, with its Smooth and Rough regions, is a cornerstone of cellular function, orchestrating protein and lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium storage. Its complex roles underline the cell’s ability to maintain homeostasis and respond to environmental signals. Understanding the ER’s intricacies offers insights into cellular health and the basis for many diseases, highlighting its significance in biology.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is essential for various cellular processes, acting as a manufacturing and packaging system. It exists in two forms: Rough ER and Smooth ER. The Rough ER is coated with ribosomes and is central to protein synthesis and modification, ensuring proteins are correctly folded and processed. In contrast, the Smooth ER lacks ribosomes and specializes in lipid and steroid hormone synthesis, detoxification of harmful metabolic byproducts, and storage of calcium ions, crucial for numerous cellular activities. Together, these functions of the ER are vital for maintaining cellular health, managing biochemical pathways, and facilitating intercellular communication.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is divided into two main types: the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (sER) and the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER). The sER is characterized by its smooth appearance, lacking ribosomes, and is primarily involved in lipid and steroid hormone synthesis, detoxification of drugs and poisons, and calcium ion storage. In contrast, the RER has a rough appearance due to ribosomes on its surface, where it plays a crucial role in synthesizing and folding proteins destined for secretion or membrane insertion. Together, the sER and RER are fundamental in cellular processes, ensuring the cell’s proper function and survival.
The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is categorized into two main types based on its structure and function:
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)?
Lipid synthesis
Energy production
DNA replication
Protein synthesis
Which organelle is closely associated with the endoplasmic reticulum in terms of function and location?
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondria
Lysosome
Chloroplast
What distinguishes the rough ER from the smooth ER?
Presence of ribosomes
Location within the cell
Size of the organelle
Type of membrane
Which of the following is a function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)?
Protein synthesis
ATP production
Lipid metabolism
DNA transcription
Which cell type would likely have an abundant amount of smooth ER?
Muscle cells
Liver cells
Red blood cells
Neurons
The endoplasmic reticulum is part of which cellular system?
Endomembrane system
Cytoskeleton
Genetic material
Cellular respiration
What role does the rough ER play in the production of membrane-bound proteins?
It assembles protein subunits into complete proteins.
It transcribes DNA into RNA.
It provides a site for ribosome attachment and protein synthesis.
It packages proteins into vesicles for transport.
How are proteins synthesized in the rough ER typically transported to their next destination?
Via diffusion through the cytoplasm
Within transport vesicles
Directly through the plasma membrane
Through the nuclear pores
Which of the following is NOT a function of the smooth ER?
Detoxification of drugs and poisons
Synthesis of steroid hormones
Storage of calcium ions
Protein folding and quality control
Which structure within the cell is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum?
Mitochondria
Nuclear envelope
Plasma membrane
Lysosome
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

