What is the primary function of mitochondria in a cell?
Protein synthesis
Energy production
DNA replication
Cell division

Mitochondria, often hailed as the powerhouse of the cell, play a pivotal role in energy production, supporting various cellular functions. This comprehensive guide delves into the essence of mitochondria, elucidating their unique features, including their double-membrane structure and DNA. Through practical examples, we explore their critical role in cellular respiration and energy conversion processes. Perfect for students and enthusiasts alike, our guide demystifies the complex world of mitochondria, enhancing understanding of cell biology and bioenergetics.
Mitochondria, often referred to as the “powerhouses” of the cell, are unique organelles present in the cells of virtually all eukaryotic organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi. These organelles are critical for energy production, playing a central role in converting nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main energy currency. This process, known as cellular respiration, involves a series of biochemical reactions that break down glucose and oxygen, releasing energy that the cell can use for various functions.
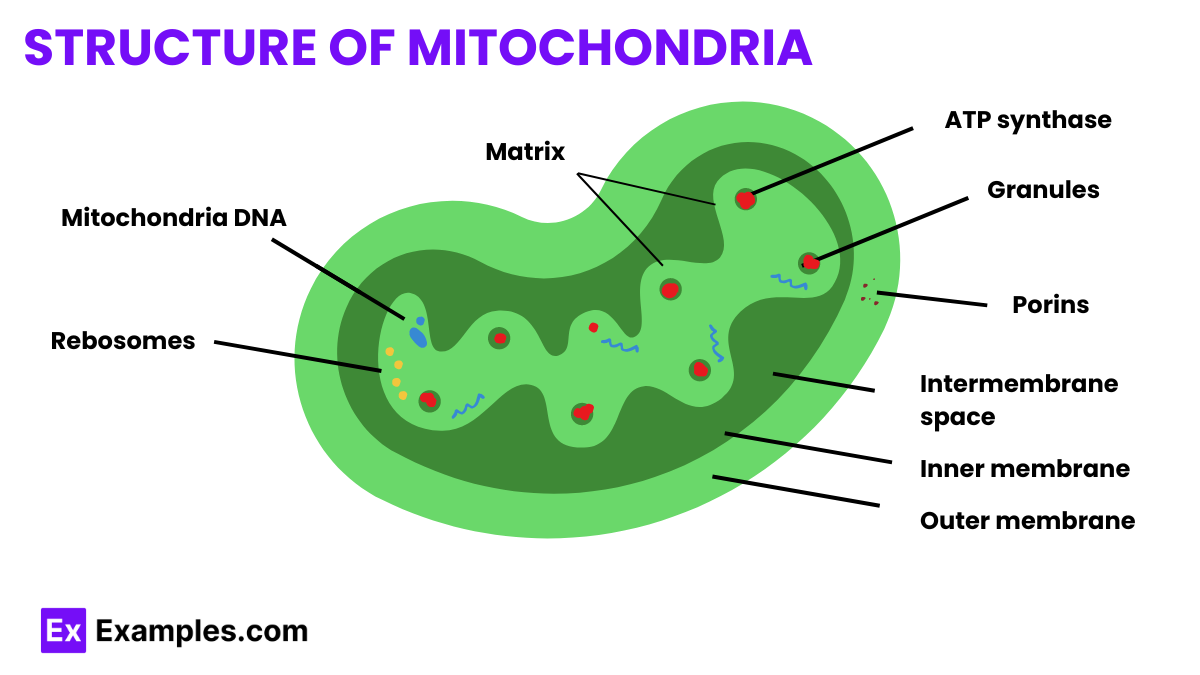
Mitochondria, often referred to as the “powerhouses of the cell,” are double-membraned organelles found in most eukaryotic cells. Their primary function is to generate most of the cell’s supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. The structure of mitochondria is key to their function and includes several distinct components:
Mitochondria play several critical roles in cellular metabolism and beyond, including:
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is a small circular strand of DNA found within mitochondria, the energy-producing organelles located in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Unlike the bulk of DNA which is contained within the cell nucleus and inherited from both parents, mtDNA is unique in that it is inherited almost exclusively from the mother. This maternal inheritance is due to the fact that mitochondrial DNA comes from the mitochondria present in the egg cell; sperm mitochondria are typically lost during fertilization.
Mitochondrial diseases are a group of disorders caused by dysfunctions in mitochondria. These diseases can result from mutations in mitochondrial DNA or in nuclear DNA that affects mitochondrial function. Because mitochondria play a crucial role in energy production within cells, mitochondrial diseases often affect organs and systems with high energy demands such as the brain, heart, liver, skeletal muscles, and the endocrine and respiratory systems.
The symptoms and severity of mitochondrial diseases can vary widely, often making them difficult to diagnose. They can present at any age and can include:
The role of mitochondria in aging is a growing area of research, with evidence suggesting that mitochondrial dysfunction is a significant contributor to the aging process and the onset of age-related diseases. As the primary site of energy production in cells, mitochondria are critical for maintaining cellular health. However, over time, mitochondria can accumulate damage to their DNA (mtDNA), proteins, and lipids due to reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced during ATP generation and external factors.
Mitochondrial disorders encompass a broad spectrum of conditions resulting from dysfunctional mitochondria, where the mitochondria fail to produce enough energy for the cell or organ to function correctly. Mitochondrial disorders are highly variable in presentation and can affect almost any part of the body, including the muscles, brain, heart, liver, sensory organs, and the endocrine and respiratory systems.
Mitochondria are called the “powerhouse of the cell” because they produce ATP, the cell’s main energy currency, fueling cellular activities.
In daily life, mitochondria support energy-demanding activities, from physical exercise to cognitive processes, by powering cells.
Mitochondria play a crucial role in cellular energy production, aging, and various diseases. Understanding these organelles’ functions and dysfunctions is essential for unraveling the complexities of cellular health and aging. As research advances, it offers hope for innovative treatments targeting mitochondrial disorders, highlighting the importance of these “powerhouses” in maintaining overall health and combating age-related decline.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary function of mitochondria in a cell?
Protein synthesis
Energy production
DNA replication
Cell division
Which structure within the mitochondria is the site of ATP synthesis?
Outer membrane
Inner membrane
Matrix
Ribosome
How many membranes surround a mitochondrion?
One
Two
Three
Four
What is the fluid-filled space inside the inner mitochondrial membrane called?
Cytosol
Matrix
Perimitochondrial space
Nucleus
Mitochondria are thought to have originated from which type of symbiotic relationship?
Endosymbiosis
Parasitism
Commensalism
Mutualism
What is the primary role of mitochondria in apoptosis?
Energy production
DNA replication
Triggering cell death
Protein synthesis
Which of the following is NOT a component of the mitochondrion?
Cristae
Matrix
Golgi apparatus
Outer membrane
What is the primary molecule produced by mitochondria during cellular respiration?
Glucose
ATP
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
What type of DNA is found in mitochondria?
Nuclear DNA
Circular DNA
Linear DNA
RNA
In which part of the mitochondrion does the Krebs cycle occur?
Outer membrane
Intermembrane space
Matrix
Cristae
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

