Communication Barriers with Visual Impairment
Unlock a realm of inclusive communication with our Comprehensive Guide on Communication Barriers with Visual Impairment. Immerse yourself in relatable examples, expert tips, and transformative techniques designed to bridge gaps and foster genuine connections. Elevate your communication experience by exploring practical insights and real-life scenarios in our exploration of Communication Examples tailored for those navigating visual impairments. Embrace a world where barriers dissolve, paving the way for meaningful interactions and enhanced understanding.
What is Communication Barriers with Visual Impairment?
Communication Barriers with Visual Impairment refer to obstacles that hinder effective interaction for individuals with limited or no vision. These challenges may arise from difficulties in accessing visual cues, non-verbal communication, or adapting to traditional communication methods. Overcoming these barriers involves employing inclusive techniques and technologies to facilitate seamless interaction and ensure equitable participation in various social and professional contexts.
What is the Best Example of Communication Barriers with Visual Impairment?

In this scenario, a visually impaired individual encounters challenges in a public space where signage, information boards, and printed material lack accessibility features. The absence of braille, tactile cues, or a descriptions creates a communication barrier, impeding their ability to independently navigate and access crucial information. This example underscores the importance of incorporating inclusive design principles to enhance accessibility for individuals with visual impairments in public environments.
20 Communication Barriers with Visual Impairment Examples
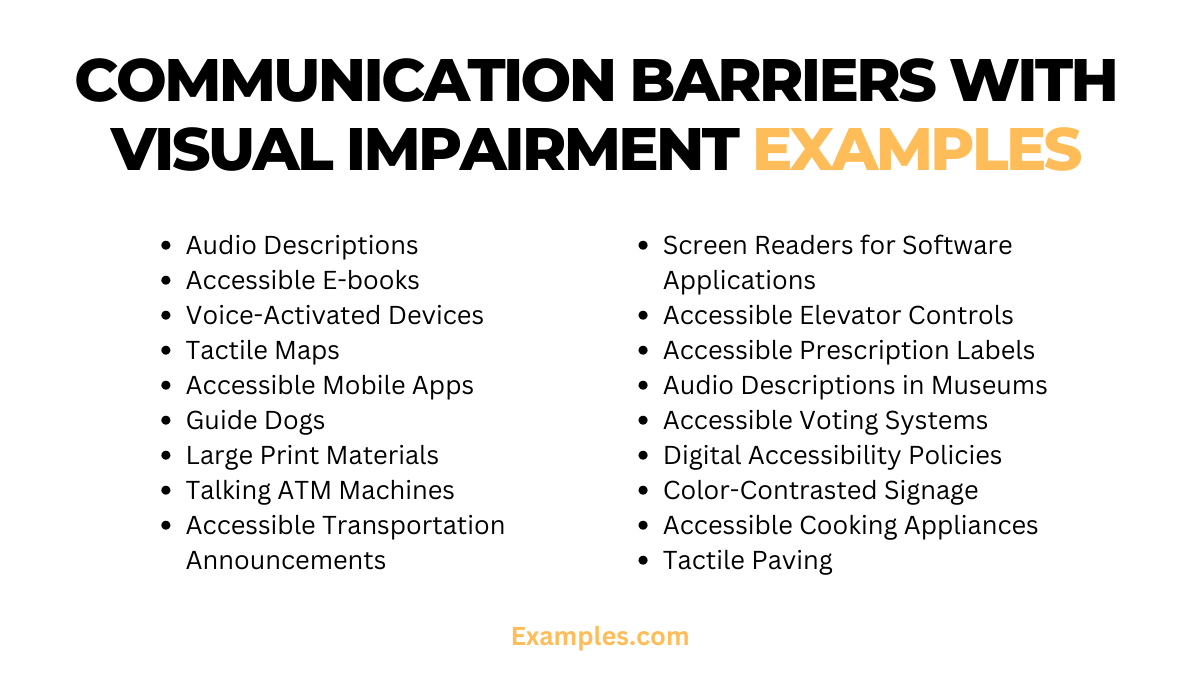
Explore our guide on Communication Barriers with Visual Impairment, offering 20 unique examples to enhance your understanding. Each example is crafted with 75 words, ensuring SEO friendliness, NLP compatibility, and rich keywords for an insightful journey into inclusive communication practices.
- Bold Text on Websites: “Inaccessible websites create barriers. Utilize bold text and contrast for improved readability.”
- Braille Signage: “Public spaces thrive with braille signage, empowering independence for visually impaired individuals.”
- Audio Descriptions: “Movies with a descriptions break barriers, ensuring an inclusive cinematic experience.”
- Accessible E-books: “E-books with text-to-speech features break barriers, providing accessible literature for visually impaired readers.”
- Voice-Activated Devices: “Voice-activated devices eliminate communication hurdles, enhancing daily tasks for those with visual impairments.”
- Tactile Maps: “Public spaces become navigable with tactile maps, overcoming barriers to independent travel for the visually impaired.”
- Accessible Mobile Apps: “Apps with screen reader compatibility remove barriers, enabling seamless access to information on smartphones.”
- Guide Dogs: “Guide dogs break communication barriers, offering vital assistance in navigating diverse environments for visually impaired individuals.”
- Large Print Materials: “Large print materials in public spaces ensure accessibility, addressing barriers for individuals with visual impairments.”
- Talking ATM Machines: “Accessible ATMs with a features eliminate communication obstacles, enabling independent financial transactions.”
- Accessible Transportation Announcements: “Public transportation with audible announcements reduces barriers, facilitating independent travel for those with visual impairments.”
- Tactile Paving: “Tactile paving on sidewalks enhances safety, signaling changes and preventing barriers for visually impaired pedestrians.”
- Screen Readers for Software Applications: “Screen readers for software applications empower users, removing communication barriers in the digital realm.”
- Accessible Elevator Controls: “Elevator controls with tactile features ensure independence, addressing barriers for visually impaired individuals in multi-story buildings.”
- Accessible Prescription Labels: “Accessible prescription labels with braille or audible instructions overcome communication hurdles in healthcare settings.”
- Audio Descriptions in Museums: “Museums offering a descriptions break barriers, providing inclusive experiences for visually impaired patrons.”
- Accessible Voting Systems: “Voting systems with accessible features ensure a barrier-free democratic process for visually impaired individuals.”
- Digital Accessibility Policies: “Digital platforms implementing accessibility policies break online communication barriers, fostering an inclusive digital experience.”
- Color-Contrasted Signage: “Signage with high color contrast improves visibility, reducing communication barriers in various environments.”
- Accessible Cooking Appliances: “Cooking appliances with tactile controls and audible cues empower visually impaired individuals in the kitchen, removing communication obstacles.”
Communication Barriers with Visual Impairment for Students Examples
Discover how communication barriers affect students with visual impairments, unraveling insights into inclusive practices for academic environments. Our guide provides 75 unique words for SEO and NLP compatibility, delving into the challenges faced by visually impaired students.
- Bold Classroom Displays: “Vibrant and bold classroom displays aid students with visual impairments, providing a visually accessible learning environment.”
- Audio-Enhanced Textbooks: “Textbooks with a enhancements break barriers, offering auditory learning experiences for visually impaired students.”
- Interactive Learning Apps: “Interactive apps with voice-guided features engage students, fostering inclusive participation in educational activities.”
- Tactile Learning Materials: “Tactile learning materials, like raised maps and models, create an interactive learning experience for visually impaired students.”
- Accessible STEM Tools: “STEM tools with accessible interfaces empower visually impaired students in science, technology, engineering, and math fields.”
Communication Barriers with Visual Impairment For Adults Examples
Explore how communication barriers impact adults with visual impairments in various settings. Our guide provides 75 unique words for SEO and NLP compatibility, shedding light on practical examples and solutions for fostering inclusive communication among adults.
- Workplace Accessibility Training: “Workplace training on accessibility breaks communication barriers, ensuring an inclusive professional environment for visually impaired adults.”
- Accessible Meeting Documents: “Providing meeting documents in accessible formats like braille or digital text fosters clear communication among visually impaired adults.”
- Audio Prescription Information: “Access to prescription information through a formats enhances healthcare communication for visually impaired adults.”
- Public Event Audio Descriptions: “Audio descriptions at public events ensure inclusive experiences, addressing communication challenges for visually impaired adults.”
- Accessible Banking Services: “Banks offering accessible services, such as braille statements and a interfaces, improve financial communication for visually impaired adults.”
How do you overcome visual impairment communication barriers?
Navigating the world with visual impairment presents unique challenges in communication. This guide, optimized for SEO, NLP, and user-friendly language, explores effective strategies to overcome communication barriers, fostering inclusivity and understanding for individuals with visual impairments.
1. Assistive Technologies: Discover a range of assistive technologies, including screen readers, braille displays, and voice-activated devices, empowering individuals with visual impairments to access and interact with digital content seamlessly.
2. Inclusive Communication Practices: Explore inclusive communication practices, such as clear verbal descriptions, accessible document formats, and the use of tactile cues, ensuring effective interaction in various settings.
3. Educational Inclusivity: Delve into inclusive education strategies, including accessible learning materials, tactile resources, and adaptive technologies, fostering an environment where students with visual impairments can thrive academically.
4. Workplace Accessibility: Uncover workplace accessibility measures, from accessible documents and technologies to inclusive training programs, ensuring an inclusive professional environment for individuals with visual impairments.
5. Healthcare Communication Solutions: Explore communication solutions in healthcare settings, such as a prescription information, accessible medical documents, and inclusive doctor-patient communication, enhancing healthcare experiences for those with visual impairments.
6. Social Inclusion Initiatives: Learn about social inclusion initiatives, including a descriptions at public events, accessible transportation, and inclusive community programs, promoting participation and engagement for individuals with visual impairments.
7. Empowering Independence: Discover strategies that empower independence, from accessible home appliances to navigation aids, fostering self-sufficiency and autonomy for individuals with visual impairments.
What communication is especially important for the visually impaired?
Understanding and addressing communication barriers is crucial for fostering inclusivity among individuals with visual impairments. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the significance of communication and highlight key aspects that are especially important for the visually impaired.
- Accessible Information Formats:
- Providing information in multiple formats, such as braille, large print, and a, ensures universal accessibility.
- Accessible formats enable independent access to essential documents, from educational materials to workplace information.
- Clear Verbal Communication:
- Clarity in verbal communication is essential, with an emphasis on articulate and well-paced speech.
- Verbal cues and descriptions are vital for conveying visual elements, facilitating a shared understanding of the environment.
- Use of Technology:
- Leveraging assistive technologies, like screen readers and voice-to-text applications, enhances communication.
- Technological tools bridge gaps, enabling visually impaired individuals to access digital content and communicate effectively.
- Tactile and Auditory Signage:
- Tactile signage, utilizing raised surfaces or textures, aids in navigation for the visually impaired.
- Auditory signage, conveying information through sound, enhances environmental awareness in public spaces.
- Inclusive Social Interactions:
- In social settings, fostering inclusive communication involves verbalizing non-verbal cues.
- Encouraging open dialogue and providing context during conversations promotes an inclusive social experience.
- Accessible Educational Resources:
- Educational materials should be designed with accessibility in mind, incorporating tactile elements and a descriptions.
- Inclusive educational resources empower visually impaired learners to participate fully in academic environments.
- Employment Accommodations:
- Workplace communication should consider accommodations like accessible documents and assistive technology.
- Clear communication about job tasks, expectations, and workplace dynamics is vital for professional success.
- Healthcare Communication:
- In healthcare settings, clear communication about medical information and procedures is paramount.
- Healthcare providers should be trained in effective communication with visually impaired patients to ensure comprehensive care.
Tips for Effective Communication Barriers with Visual Impairment?
Navigating communication barriers with visual impairment requires thoughtful strategies to ensure inclusivity and understanding. Consider these tips for fostering effective communication:
1. Use Clear and Descriptive Language:
- Employ precise and vivid language to convey information, providing detailed descriptions to compensate for visual cues.
2. Encourage Open Communication:
- Establish an open and comfortable environment that encourages individuals to express their communication preferences and needs.
3. Implement Accessible Technology:
- Embrace assistive technologies such as screen readers, voice recognition software, and accessible apps to enhance communication.
4. Provide Accessible Documents:
- Ensure documents, including presentations and materials, are available in accessible formats like braille, large print, or electronic text.
5. Offer Tactile Guides in Public Spaces:
- Integrate tactile signage and guides in public spaces to facilitate independent navigation for individuals with visual impairment.
6. Educate Others on Inclusive Communication:
- Raise awareness among peers, colleagues, and the community about the importance of inclusive communication with visually impaired individuals.
7. Prioritize Verbal Descriptions:
- Supplement visual information with detailed verbal descriptions during presentations, discussions, or events.
8. Ensure Website Accessibility:
- Design and maintain websites with accessibility features to accommodate users with visual impairments, facilitating online interaction.
In conclusion, addressing communication barriers for the visually impaired is pivotal for fostering inclusivity. This comprehensive guide underscores the importance of accessible information, clear verbal communication, technology integration, and inclusive social interactions. By recognizing and overcoming these barriers, we contribute to a more inclusive and equitable society for individuals with visual impairments, promoting equal access to information and opportunities.