Types of Communication Skills
Understanding the diverse types of communication skills is crucial in our interconnected world. This guide delves into various communication methods, from oral communication to non-verbal cues, providing practical communication examples. Whether in the workplace, family dynamics, or personal relationships, these skills are foundational for successful interactions. By exploring different styles and techniques, you’ll gain insights into how effective communication can enhance every aspect of life. Stay tuned for a journey through the art of communicating effectively
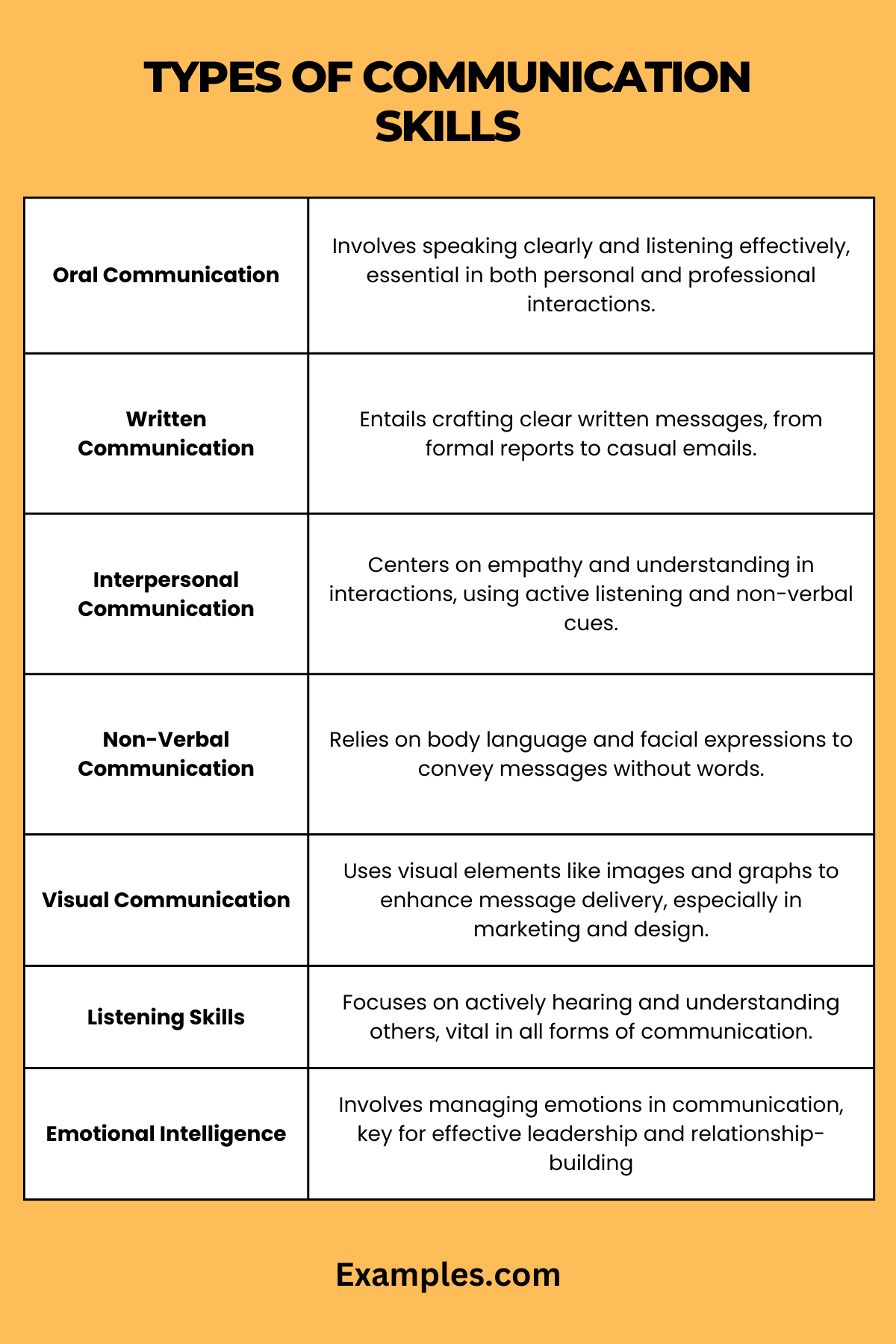
What are Types of Communication Skills?
Communication skills encompass a wide range of abilities that are essential for effectively conveying information and understanding messages from others. These skills are not only crucial in professional settings but also play a significant role in personal and social interactions. Understanding and mastering different types of communication skills can lead to more effective and fulfilling interactions in all areas of life.
1. Conciseness
Conciseness in communication means being clear and brief, ensuring messages are understood without unnecessary details. It’s essential for effective communication, especially in business and academic settings.
Examples of Conciseness:
- Emails: Crafting short, to-the-point emails that convey essential information without fluff.
- Presentations: Delivering precise and concise presentations, focusing on key points.
- Meetings: Making statements briefly and clearly in meetings to respect others’ time.
- Instructions: Giving clear, brief instructions to avoid confusion.
- Reports: Writing reports that are succinct yet comprehensive.
How to Improve:
Practice summarizing complex ideas into a few sentences, avoid jargon, and always plan your communication beforehand to stay on topic.
2. Empathy
Empathy in communication is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others, vital for building strong relationships.
Examples of Empathy:
- Conflict Resolution: Showing understanding in conflicts helps in reaching amicable solutions.
- Customer Service: Demonstrating empathy when addressing customer complaints or concerns.
- Counseling: Counselors use empathy to connect with and help their clients.
- Negotiations: Understanding the other party’s perspective to find common ground.
- Parenting: Parents use empathy to understand their children’s feelings and perspectives.
How to Improve:
Practice active listening, put yourself in others’ shoes, and respond with understanding and compassion.
3. Active Listening
Active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, responding, and remembering what is being said.
Examples of Active Listening:
- Therapy Sessions: Therapists actively listen to understand their clients’ issues.
- Classrooms: Students practicing active listening to grasp lessons effectively.
- Meetings: Participating in meetings by listening, asking questions, and giving feedback.
- Customer Feedback: Companies use active listening to understand customer feedback.
- Friendships: Listening attentively to friends’ concerns and joys.
How to Improve:
Maintain eye contact, avoid interrupting, and summarize what you’ve heard to confirm understanding.
4. Mass Communication
Mass communication involves disseminating information to large audiences via media like TV, newspapers, and the internet.
Examples of Mass Communication:
- News Broadcasting: TV and radio news broadcasts reaching wide audiences.
- Social Media Campaigns: Using social media platforms to reach a global audience.
- Public Service Announcements: Spreading important messages to the public.
- Advertising Campaigns: Brands communicating to large audiences through advertisements.
- Documentaries: Documentaries on various platforms educating and informing masses.
How to Improve:
Focus on clear messaging, understand your audience, and utilize multiple media platforms for wider reach.
5. Writing
Writing is a fundamental communication skill involving expressing ideas and information through written words.
Examples of Writing:
- Blogs: Blogging to share insights, stories, or educate readers.
- Academic Papers: Writing research papers or essays in academic settings.
- Business Proposals: Crafting proposals to articulate business ideas or plans.
- Novels: Writing fiction or non-fiction books to tell stories or convey messages.
- Email Correspondence: Professional email writing for clear, effective workplace communication.
How to Improve:
Practice regularly, read diverse materials, and focus on clarity and structure in your writing.
6. Listening Skills
Listening skills involve effectively receiving and interpreting messages in the communication process.
Examples of Listening Skills:
- Customer Feedback: Businesses listening to customer opinions for improvement.
- Classroom Learning: Students absorbing and understanding lectures.
- Counseling Sessions: Counselors listening to clients to provide effective guidance.
- Team Meetings: Team members listening to each other for collaborative problem-solving.
- Peer Discussions: Engaging in discussions by attentively listening to peers.
How to Improve:
Avoid distractions, be present in the moment, and show interest in the speaker’s message.
7. Oral Communication Skills
Oral communication skills involve expressing ideas and information verbally in an effective and clear manner.
Examples of Oral Communication Skills:
- Public Speaking: Delivering speeches or presentations to an audience.
- Customer Service: Interacting with customers over the phone or in person.
- Teaching: Teachers explaining concepts to students in a clear, engaging way.
- Networking Events: Engaging in conversations at professional gatherings.
- Family Conversations: Discussing and resolving issues in family meetings.
How to Improve:
Practice speaking clearly, modulate your voice as needed, and be mindful of your body language.
8. Written Communication Skills
Written communication skills involve the ability to express thoughts and information clearly and effectively in writing.
Examples of Written Communication Skills:
- Report Writing: Creating detailed and clear reports in a professional setting.
- Email Etiquette: Writing professional and concise emails in the workplace.
- Social Media Posts: Crafting engaging and relevant content for social media platforms.
- Academic Essays: Structuring and articulating thoughts in academic essays.
- Letter Writing: Personal or formal letter writing to convey messages effectively.
How to Improve:
Focus on grammar and punctuation, be concise, and tailor your writing to your audience.
9. Interpersonal Communication Skills
Interpersonal communication skills involve effective verbal and non-verbal interactions between individuals.
Examples of Interpersonal Communication Skills:
- Team Collaboration: Collaborating with colleagues in a workplace setting.
- Friendship Building: Developing and maintaining friendships through effective communication.
- Family Dynamics: Navigating family relationships with clear and respectful communication.
- Networking: Building professional relationships through effective communication.
- Conflict Resolution: Resolving misunderstandings or disputes through dialogue.
How to Improve:
Be an active listener, express your thoughts clearly, and be open to feedback.
10. Non-Verbal Communication
Non-verbal communication involves conveying messages through body language, facial expressions, and gestures.
Examples of Non-Verbal Communication:
- Interviews: Using body language to convey confidence during job interviews.
- Presentations: Enhancing verbal communication with effective gestures and eye contact.
- Therapeutic Settings: Therapists understanding clients’ non-verbal cues.
- Cultural Interactions: Understanding and respecting cultural differences in non-verbal communication.
- Personal Relationships: Expressing emotions and feelings through non-verbal means.
How to Improve:
Be aware of your body language, observe others’ non-verbal cues, and ensure your non-verbal communication aligns with your verbal messages.
11. Visual Communication
Visual communication involves conveying ideas and information through visual elements like images, graphics, and videos.
Examples of Visual Communication:
- Infographics: Using infographics to present complex data in an understandable way.
- Branding: Creating visual brand elements like logos and color schemes.
- Instructional Design: Developing visual aids for educational purposes.
- Social Media Graphics: Enhancing social media posts with visuals.
- Advertising: Using visuals in advertising to attract and engage audiences.
How to Improve:
Learn basic design principles, use appropriate tools and software, and understand your audience’s visual preferences.
12. Clarity
Clarity in communication means conveying messages in a straightforward and unambiguous manner.
Examples of Clarity:
- Instruction Manuals: Writing clear and precise instruction manuals.
- Policy Documents: Creating unambiguous company policies.
- Client Proposals: Articulating business proposals clearly.
- Academic Explanations: Teachers explaining concepts without confusion.
- Legal Documents: Drafting legal documents with clear language.
How to Improve:
Use simple language, be specific, and avoid technical jargon unless necessary.
13. Assertiveness
Assertiveness in communication is about expressing one’s opinions and needs respectfully and confidently.
Examples of Assertiveness:
- Workplace Requests: Making requests or expressing needs assertively at work.
- Personal Boundaries: Communicating personal boundaries in relationships.
- Negotiations: Assertively stating one’s position in negotiations.
- Feedback Giving: Providing constructive feedback in a confident, respectful manner.
- Self-Advocacy: Advocating for oneself in personal and professional settings.
How to Improve:
Practice stating your needs clearly, respect others’ viewpoints, and maintain a calm and confident tone.
Each of these types of communication skills plays a vital role in different aspects of life. Developing a broad range of communication skills can lead to improved relationships, professional success, and personal fulfillment.
In conclusion, mastering various types of communication skills, including oral, written, interpersonal, non-verbal, visual, listening, and emotional intelligence, is crucial for personal and professional success. By actively practicing, seeking feedback, and adapting to different communication settings, individuals can enhance their ability to convey and interpret messages effectively, leading to improved relationships and greater achievement in diverse life aspects.



