What process in the carbon cycle involves plants taking in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere?
Respiration
Photosynthesis
Decomposition
Combustion
On a journey through the Carbon Cycle, the cornerstone of Earth’s biosphere, intricately woven into the fabric of life. This comprehensive guide unravels the cycle’s pivotal role in regulating the planet’s climate, supporting ecosystems, and sustaining life. From the depths of the oceans to the heights of the atmosphere, learn how carbon travels through the Earth’s compartments in a mesmerizing dance of exchange. With vivid examples, we illuminate the cycle’s complexities and its significance in balancing ecological harmony. Dive into the world of carbon and discover its myriad pathways, influencing everything from global warming to the air we breathe. Join us to explore the carbon cycle’s wonders, understanding its vital importance in our world’s ecological and climatic equilibrium.
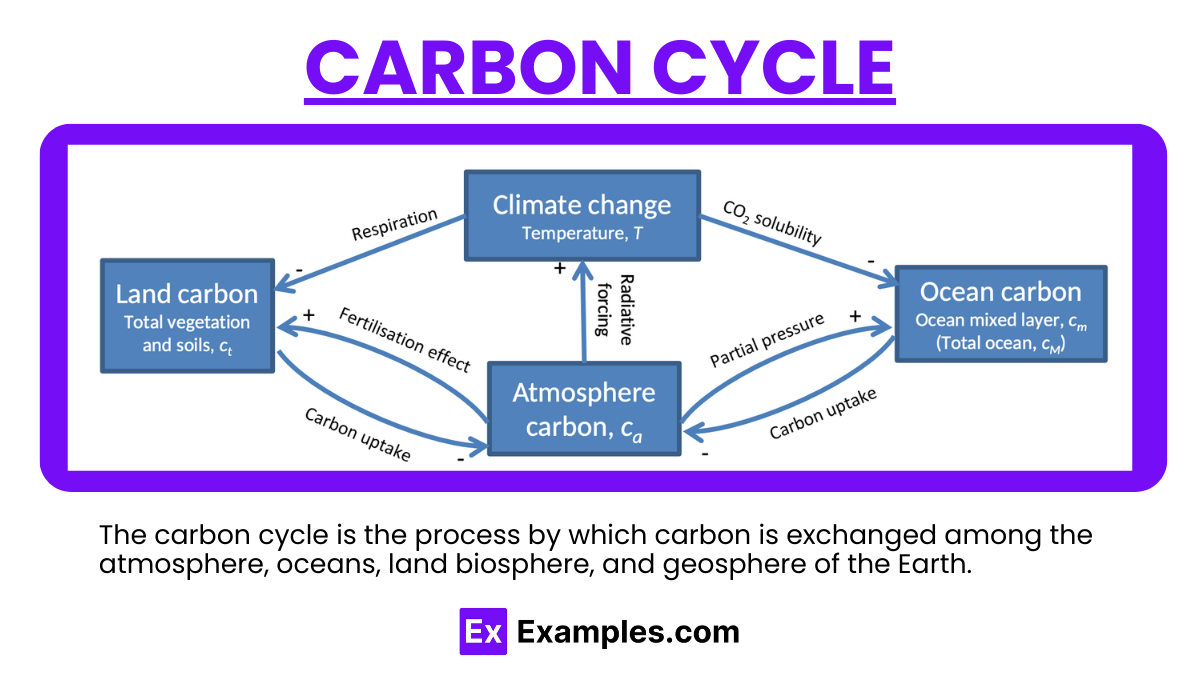
The carbon cycle is a natural process through which carbon is exchanged among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals of the Earth. It involves various chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes that transfer carbon compounds and use them in different ways across the planet’s various ecosystems. This cycle plays a key role in regulating the Earth’s climate by controlling the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
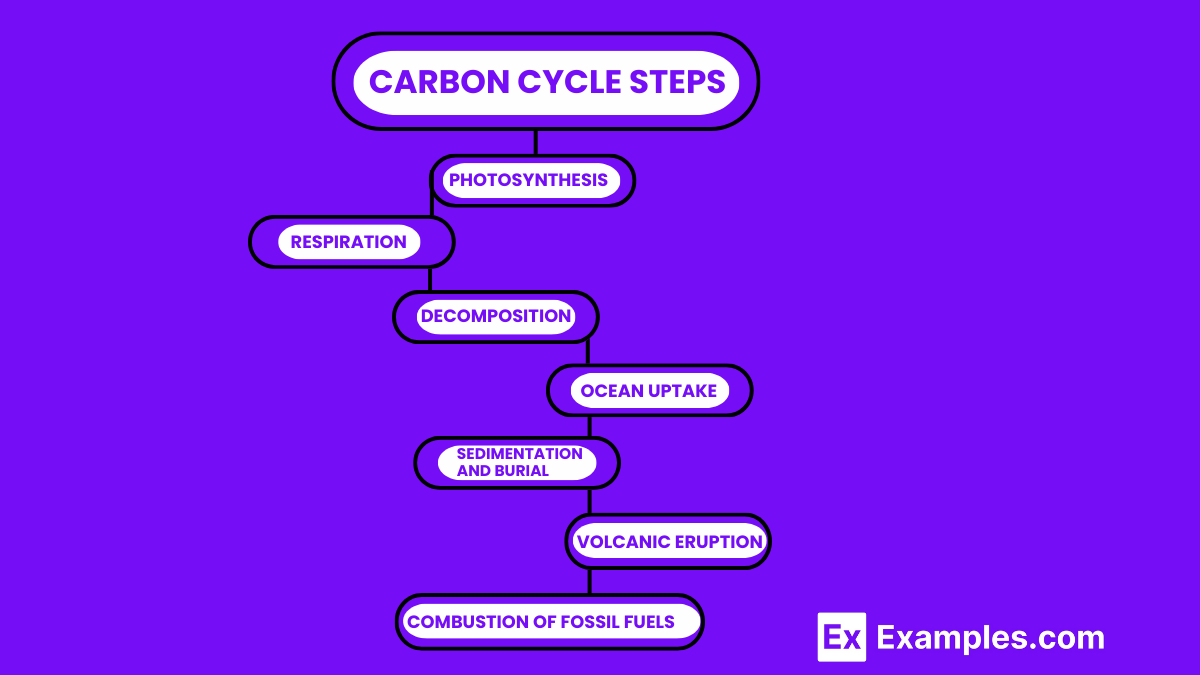
The Carbon Cycle is a fundamental process in Earth’s system, involving the movement of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, rocks, and living organisms. This cycle plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate, supporting plant life through photosynthesis, and maintaining the balance of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Here are the key steps explained:
In this crucial step, plants and other photosynthetic organisms (like some bacteria and algae) absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Using sunlight as energy, they convert CO2 and water into glucose and oxygen. This process not only supports the growth of these organisms but also provides oxygen for other living beings.
Respiration is the reverse of photosynthesis and occurs in plants, animals, and fungi. These organisms consume oxygen and glucose, which produces energy, carbon dioxide, and water. This process returns CO2 to the atmosphere or ocean, completing a part of the cycle.
When plants, animals, and other organisms die, decomposers like bacteria and fungi break down their bodies. This decomposition process releases carbon stored in the dead organisms as CO2 back into the atmosphere or converts it into compounds in the soil, contributing to the soil’s carbon storage.
The oceans play a significant role in the carbon cycle by absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Through physical and biological processes, dissolved CO2 is either used by marine organisms in the form of carbonate for shells and skeletons or stored in deep ocean waters for hundreds to thousands of years.
Over long time periods, carbon gets trapped in the Earth’s crust. Dead plant material and marine organisms can get buried under layers of sediment. Over millions of years, this organic material can turn into fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) through heat and pressure.
Volcanic eruptions release carbon stored deep within the Earth back into the atmosphere in the form of CO2. This process, although less frequent, contributes to the atmospheric carbon levels and is part of the long-term carbon cycle.
Human activities, especially the burning of fossil fuels for energy, release significant amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. This process has accelerated the movement of carbon into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change by enhancing the greenhouse effect.
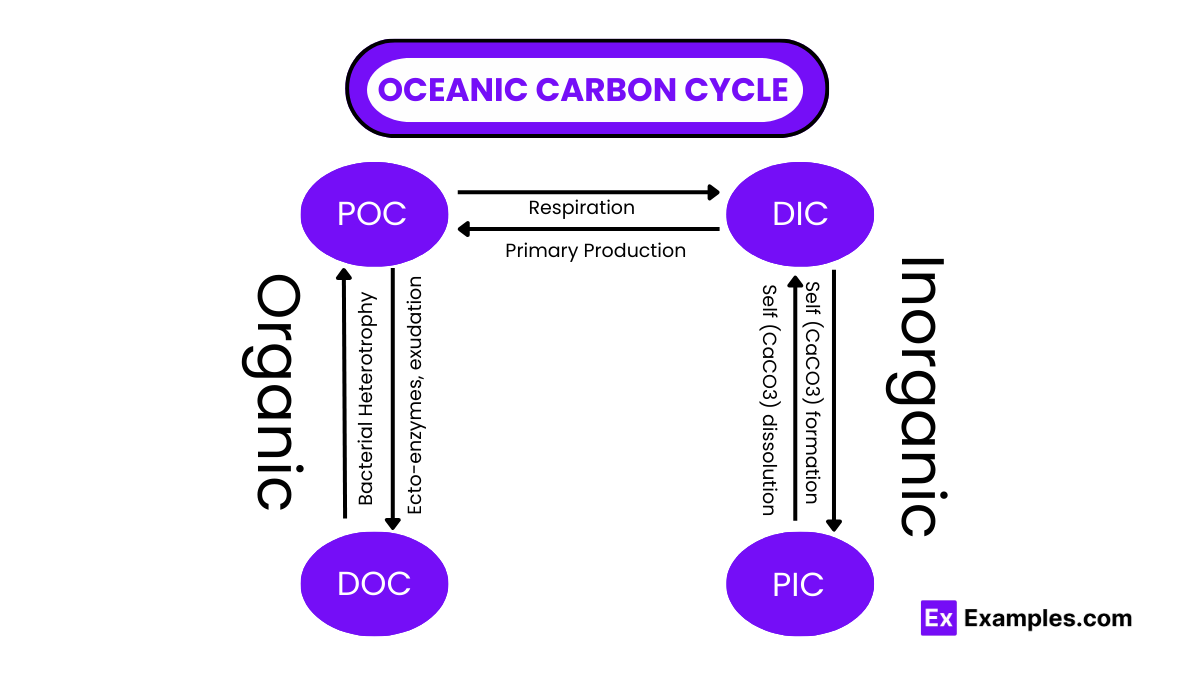
The oceanic carbon cycle is a critical component of the global carbon cycle, involving the exchange of carbon among the Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and marine organisms. Here’s a detailed explanation broken down into key points:
The carbon cycle is fundamental to Earth’s climate, ecosystems, and life forms. Its importance can be understood through several key points:
The Carbon Cycle is a natural process where carbon is exchanged among Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms, crucial for maintaining the planet’s climate and life.
Through photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, ocean uptake, volcanic activity, and human activities, the Carbon Cycle balances atmospheric CO2, supporting life and climate.
It regulates Earth’s climate, supports ecosystems, and controls CO2 levels, essential for life’s sustainability and climate stability.
Human activities, like burning fossil fuels and deforestation, increase atmospheric CO2, disrupting the natural balance and contributing to climate change.
Enhancing carbon sinks and reducing emissions can balance the Carbon Cycle, mitigating climate change impacts through sustainable practices and renewable energy.
Carbon dioxide can linger in the atmosphere for centuries, with its removal dependent on natural processes like photosynthesis and ocean absorption.
The carbon cycle is a crucial planetary system that regulates climate, supports life, and maintains ecological balance. Human activities have significantly impacted this cycle, emphasizing the urgent need for sustainable practices to restore equilibrium. Understanding and protecting the carbon cycle is essential for preserving environmental health, mitigating climate change, and ensuring the future prosperity of our planet.
Text prompt
Add Tone
Carbon Cycle Steps
Importance of Carbon Cycle
What process in the carbon cycle involves plants taking in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere?
Respiration
Photosynthesis
Decomposition
Combustion
Which of the following processes releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere?
Photosynthesis
Erosion
Respiration
Nitrogen fixation
What role do decomposers play in the carbon cycle?
They produce oxygen
They convert carbon dioxide into organic matter
They break down dead organisms and return carbon to the soil
They absorb carbon dioxide for photosynthesis
How does combustion affect the carbon cycle?
It decreases atmospheric carbon dioxide
It converts carbon dioxide into oxygen
It releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere
It increases the amount of carbon stored in soils
Which process in the carbon cycle helps remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in oceans?
Respiration
Photosynthesis
Ocean absorption
Erosion
What is the term for the process by which carbon is stored in the form of fossil fuels?
Carbon sequestration
Photosynthesis
Respiration
Combustion
How do human activities contribute to the carbon cycle imbalance?
By reducing carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere
By increasing the rate of photosynthesis
By releasing excess carbon dioxide through deforestation and fossil fuel use
By enhancing natural carbon sinks
Which of the following processes is part of the natural carbon cycle?
Industrial emissions
Ocean acidification
Soil formation
Carbon trading
What happens to carbon stored in plants when they die and decompose?
It is converted into fossil fuels
It is released into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide
It is used for new plant growth
It is absorbed by the oceans
In which part of the carbon cycle does carbon dioxide dissolve into water?
During photosynthesis
During respiration
In the oceanic absorption process
During combustion
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

